What is in a straight line?
This is made of dust, gases, MANY stars, and the objects that orbit those stars.
What is a galaxy? By the way: Ours is the Milky Way.
Which would be warmer-an area near the equator (low latitude) or far from the equator (high latitude)?
The area near the equator with the low latitude would be warmer.
Forces are pushes and pulls. This force pulls objects DOWN.
What is gravity?
A. The dog is looking for food.
B. The dog sniffed the grass.
C. The dog likes to play in the grass.
B. is the observation. You can SEE the dog sniff the grass. The others are ideas/inferences.
What source of energy fuels the water cycle and sends light and heat to our planet?
What is the sun?
What happens to temperature when two objects rub against one another?
The temperature increases. They get warmer due to friction.
Uri plugs in a fan and turns it on. Tell what energy transformation has been made.
Electrical energy has been changed to mechanical energy (energy of motion).
Why do some stars (like the Sun) look larger and brighter to us?
They look larger and brighter because they are closer to us.
What happens to the temperature as elevation increases?
As elevation increases (like going up a mountain), the temperature decreases (gets colder).
This is the force that slows down or opposes motion.
What is friction?
Scientific investigations often begin with this.
What is a question?
Rudy is researching a planet. It has a relatively short year, warmer temperatures, a solid rocky surface, and no moons. Is this planet more likely to be inside the asteroid belt or outside the asteroid belt?
It would be inside the asteroid belt. These inner planets are solid surfaced, have fewer moons and rings, shorter years, and are closer to the sun giving them a warmer temperature.
Things that give off light often give off this form of energy also.
What is heat?
Julie plucks a stringed instrument, and it starts to vibrate more quickly. What will happen to the sound?
With a higher vibration, the pitch will get higher.
(If the vibration slows, the pitch will get lower.)
For each characteristic, decide if it describes "Inner Planets" or "Outer Planets."
1.) smaller in size
2.) no solid surface; thick gaseous atmosphere
3.) longer year (revolution time)
1.) inner
2.) outer
3.) outer
Which would be associated with stormy weather...
1.) high pressure or low pressure?
2.) which cloud type?
3.) which SOLID form of precipitation could fall?
1.) low pressure
2.) cumulonimbus clouds
3.) hail
1.) What would repel a positively charged item?
2.) What would repel the North pole of a magnet?
1.) Another positively charged item would repel it.
2.) Another North pole would repel it.
LIKES REPEL. OPPOSITES WOULD ATTRACT. (positive><negative; North pole><South pole)
What Earth movement causes the Sun to APPEAR to move across the sky each day and stars to APPEAR to move across the sky at night?
This is caused by the Earth's ROTATION. It rotates every 24 hours, causing day and night changes.
Would the circuit below work? Why or way not?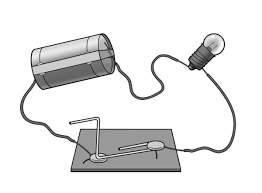 Describe how to make a circuit that will light a light bulb.
Describe how to make a circuit that will light a light bulb.
It would work. There is a complete loop. The wires and the paperclip are metal, so they are good conductors. The wires attach to each end of the battery and each end of the lightbulb.
Ivan breaks a stick into pieces. Would this be a physical change or a chemical change?
It would be a physical change.
Winnie places a stick in a container or water. She notices that the stick looks different under the water, making it appear broken. What causes this?
As light travels through the water, it is BENT or refracted. This makes the appearance of the stick different.
Name three characteristics common to ALL planets in our solar system.
They have mass, revolve around a star (Sun), and they rotate on an axis.
1.) Which would be the driest climate region?
2.) Which would be the coldest climate region?
3.) Which would be hot and humid year-round?
1.) desert
2.) tundra
3.) tropical rainforest
What two things have to be used to determine speed?
You need to know the distance traveled and the time it took to travel that distance.
True or False? Due to the movements of the Earth, stars appear to move across the sky each night and we can see different stars during different times of the year.
This is TRUE. It is caused by rotation (stars and objects move across the sky each day/night) and revolution (making different stars visible at different times of the year).
What is erosion?
What is weathering?
Erosion is when rock, soil, sand, etc. is moved from one place to another by wind, water, ice, or gravity.
Weathering is when rocks are broken down by wind, water, ice, temperature change, or plant roots.
The students in Mrs. Bahni's class heat up some water. It boils and changes from a liquid to a gas (evaporation). Is this a chemical or physical change?
It is a physical change. ANY change in the state of matter (melting, boiling, cooling/condensing, freezing) would be a physical change.
Which example does NOT show energy making a change?
A.) Kelly turns a light on.
B.) Jim throws a football.
C.) Tina holds a stone.
C. would NOT be an example of energy being used to make a change. Nothing is moving or changing.
Tia observes that the moon is full. Two weeks later, she goes outside to observe the moon again. What phase will she see?
Tia would see a NEW MOON. It takes the moon a month (four weeks) to get back to the same phase again. It would be halfway there, so it would be the new moon instead of the full moon.
Name the three global climate zones and describe each.
Tropical (near the equator)-always hot and humid
Temperate-has seasons with warmer summers and cooler winters
Polar-always cold
How can you tell if the forces acting on an object are balanced or unbalanced?
If the forces acting on an object are balanced, it will NOT MOVE.
If the forces acting on an object are unbalanced, the object will be moved by the greatest/strongest force(s).
This is the only state of matter that has a definite shape that does not change with the container.
What is a solid?
Where would more precipitation be likely-on the coast or inland?
More precipitation would be likely near the coast.
Tiana places a warm cup of coffee on the table. Which describes what will happen?
A. cold will move from the table to the cup of coffee
B. warmth will move from the cup of coffee to the table
B-Warmth always flows from the warmer object to the colder object.
What three things can happen when light strikes an object?
The light can be reflected (bounced back) like when it hits a mirror. It can also be bent or absorbed.
Which Earth movement causes our year?
This would be revolution, traveling around the sun for one complete orbit.
1.) a wet area with warm summers and cold winters; trees
2.) an area with more grass than trees; often has a rainy season and a dry season
1.) wetland/swamp
2.) grassland
Pete has been pushing a wagon. He loads it with cans to take to be recycled. If he wants to have the wagon move at the same speed with the additional mass of the cans, what will he need to do?
He will need to push with greater force because there is now more mass.
An object in motion will always change its ____________.
What is position? If an object moves, it will be in a different position.
Joey pushes a pencil and a brick with the same amount of force. What will most likely happen?
The pencil will move a lot, and the brick will not move as much because of its greater mass.
Harvey is testing a mineral to try to determine its identity. Which tests are being performed if he...
1.) looks at how the mineral reflects light (glass, dull, metallic, shiny, etc.)
2.) scratches the mineral with a steel file
3.) rubs the mineral against an unglazed tile and looks at the powder left behind
4.) examines the way the mineral breaks
1.) luster
2.) hardness
3.) streak
4.) cleavage