Atom Bond
Atom Bond
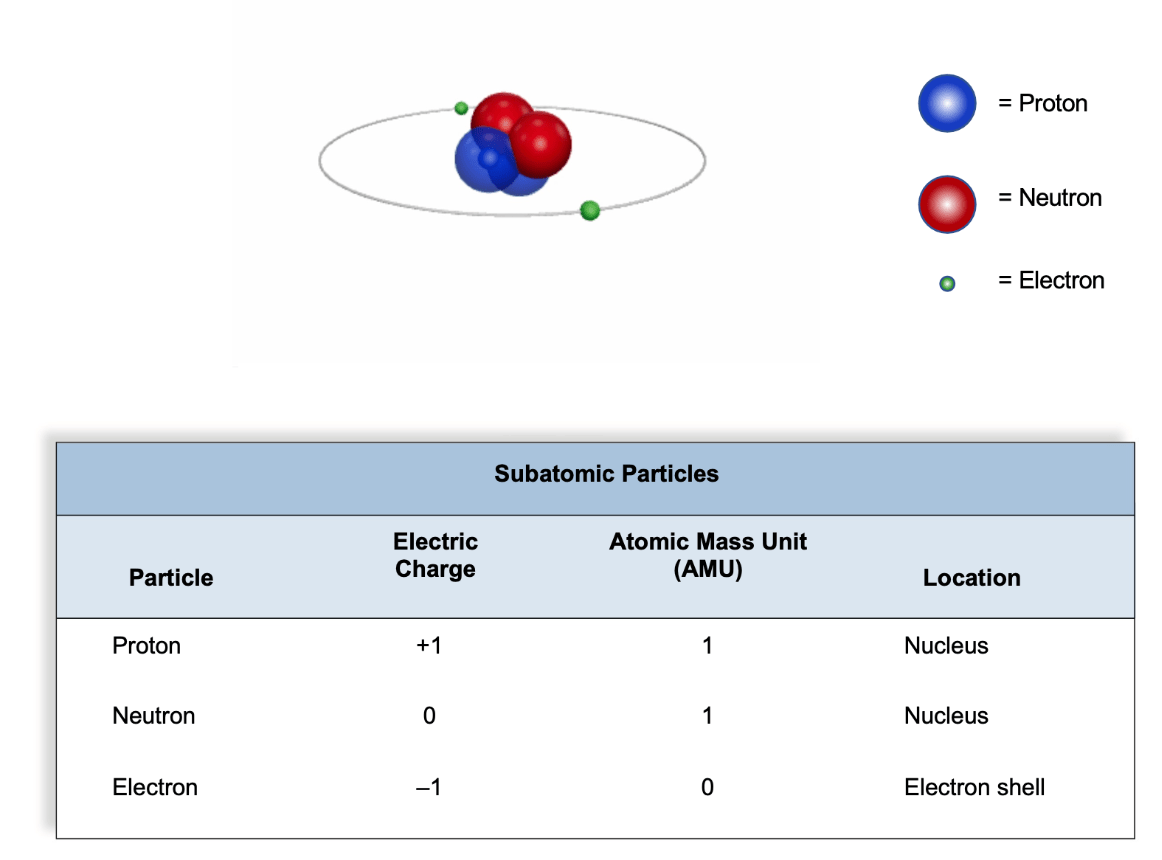
This subatomic particle is not located in the nucleus and has no mass.
What is an electron?
Hydrogen is attracted to these kinds of charges
What is negative?
e.g. nitrogen and oxygen in DNA
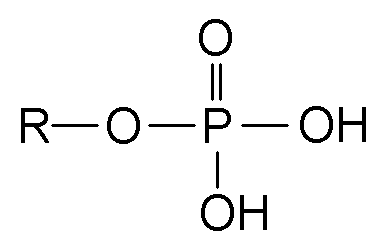
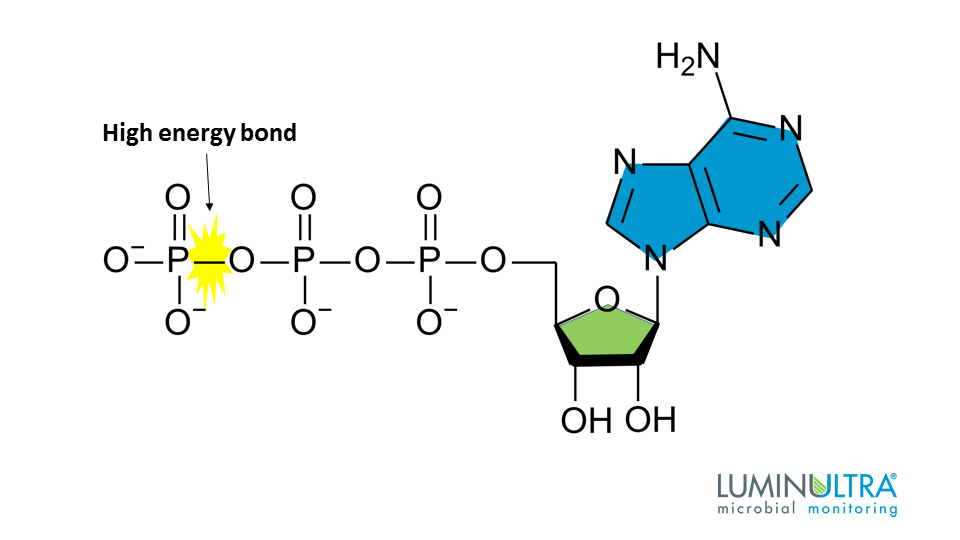
These functional groups are responsible for storing large amounts of chemical energy.
What are phosphate groups?
This molecule has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail.
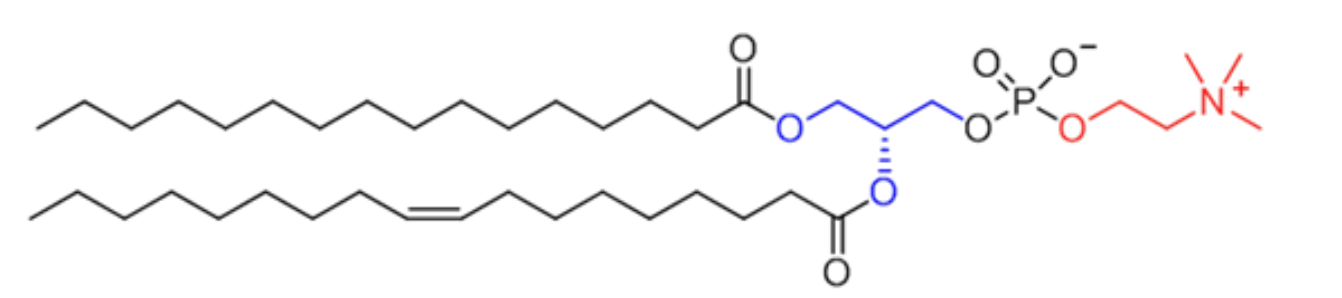
What are phospholipids?
These are the two main functions of carbohydrates.
What are fuel and structure?

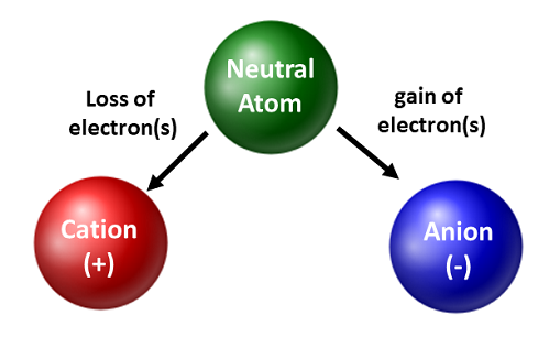
Atoms that have lost or gained an electron are known as this.
What are ions?
These occur when water surrounds ions or molecules and causes it to go into solution.
What are hydration shells?
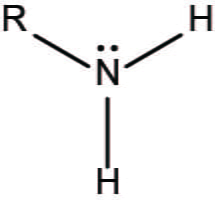
This functional group acts as a base and tends to attract protons.
What is an amino group?
This molecule has a carboxylic acid group and a long hydrocarbon chain.
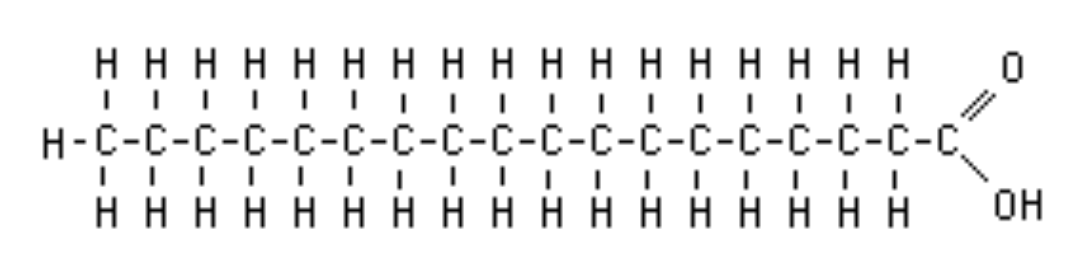
What is a fatty acid?

These "simple sugars" are the type of carbohydrate that cells use for energy.
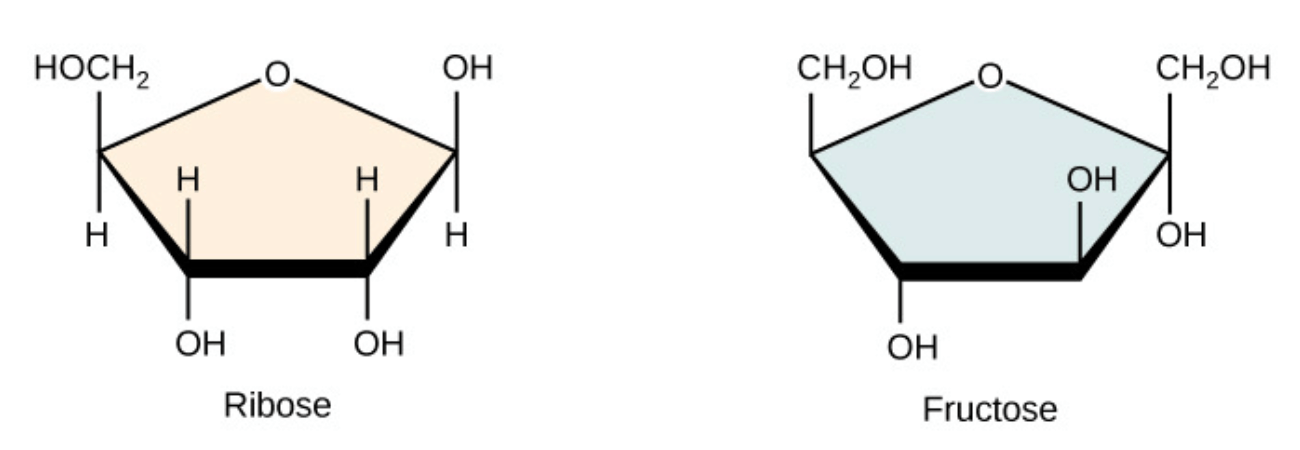
What are monosaccharides?
This type of chemical bond share electrons equally between each atom.
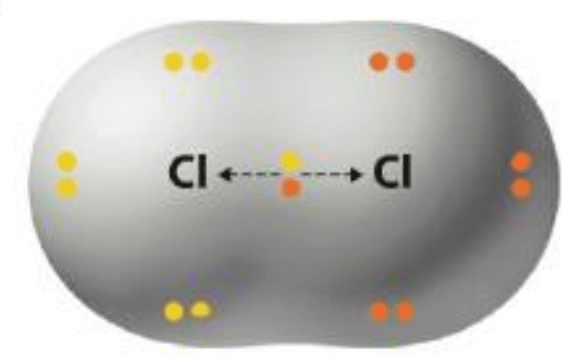
What are non-polar covalent bonds?
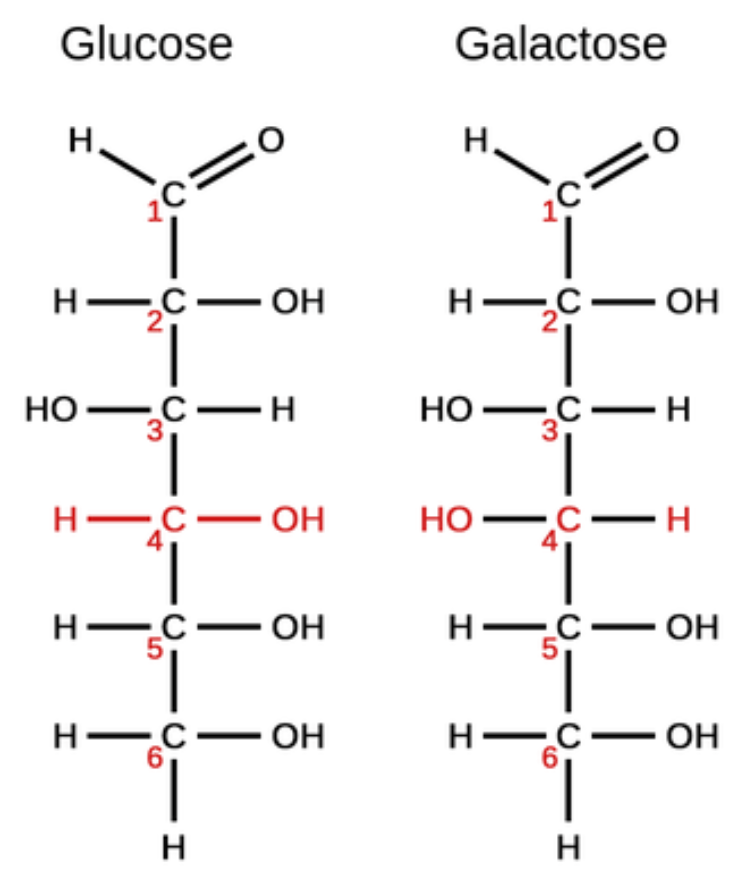
These are organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structures.
What are isomers?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hydroxylfunctional-56a129e05f9b58b7d0bca5df.jpg)
Alcohols contain this functional group, which is highly polar and makes compounds more soluble in water.
What is a hydroxyl group?
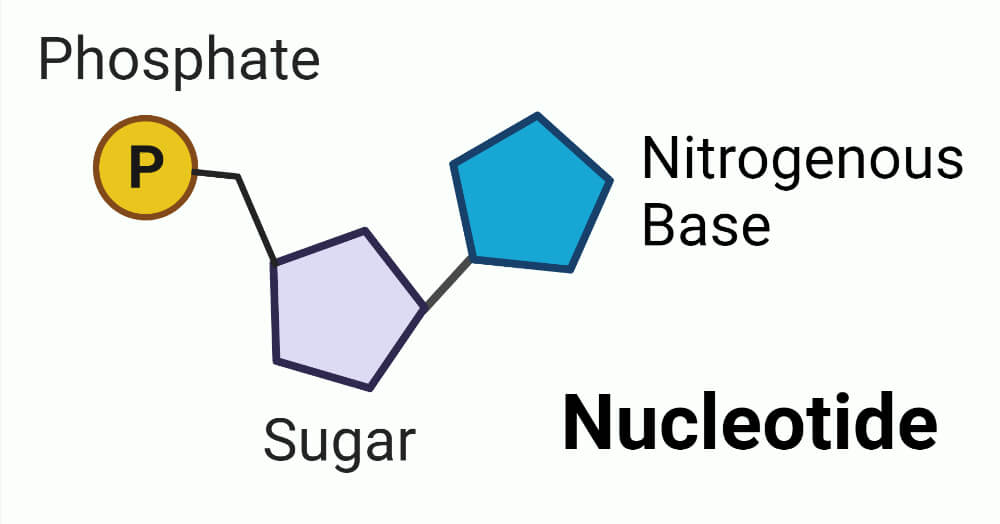
These molecules contain a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a pentose sugar.

What are nucleotides?
These carbohydrates are important for cellular communication, recognition and signaling.
What are oligosaccharides?

This type of chemical bond involves partial charges on each atom due to unequal sharing of electrons.
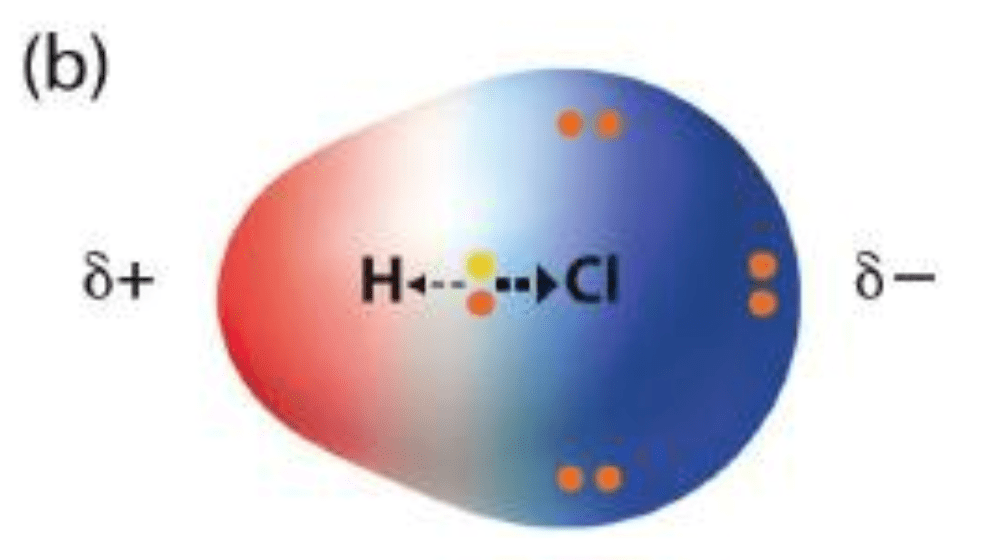
What are polar covalent bonds?
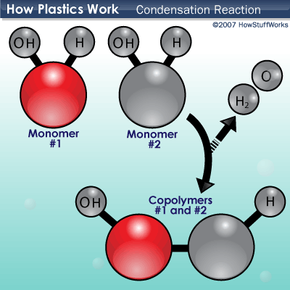
The synthesis of macromolecules occurs through these kind of reactions.
What are condensation (dehydration) reactions?
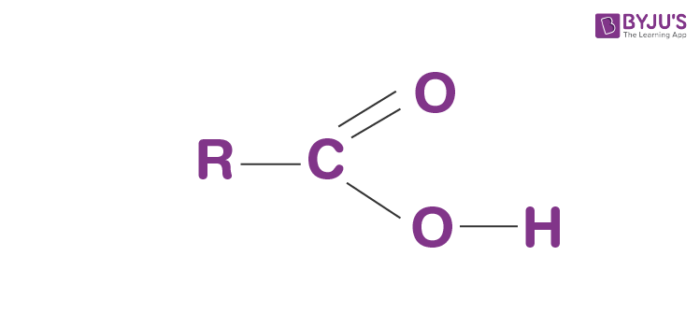
These functional groups act as an acid and tend to lose protons in solution.
What are carboxyl groups?
Bonus: what is the difference between a carboxyl and carbonyl group?
These molecules are simple to identify once you take a close look at their functional groups.
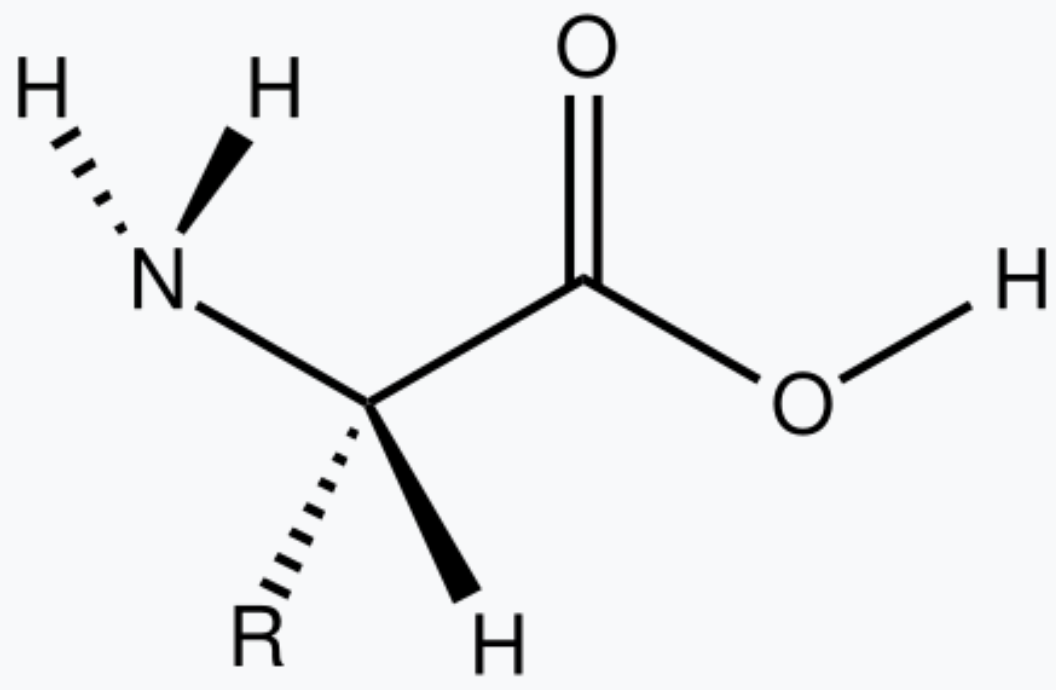
What are amino acids?

Polysaccharides are connected by this type of covalent bond.
What are glycosidic bonds?

This type of chemical bond involves the complete transfer of one or more valence electrons, resulting in full charges.
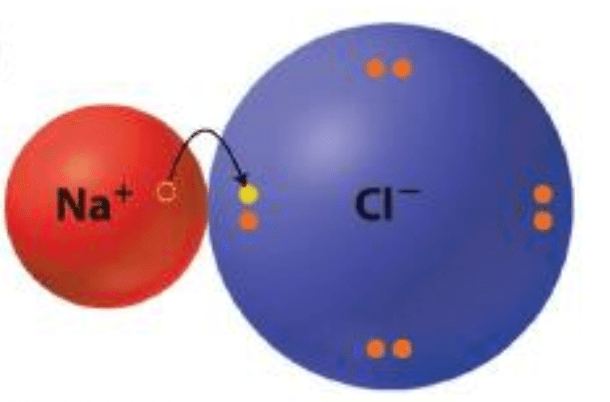
What are ionic bonds?
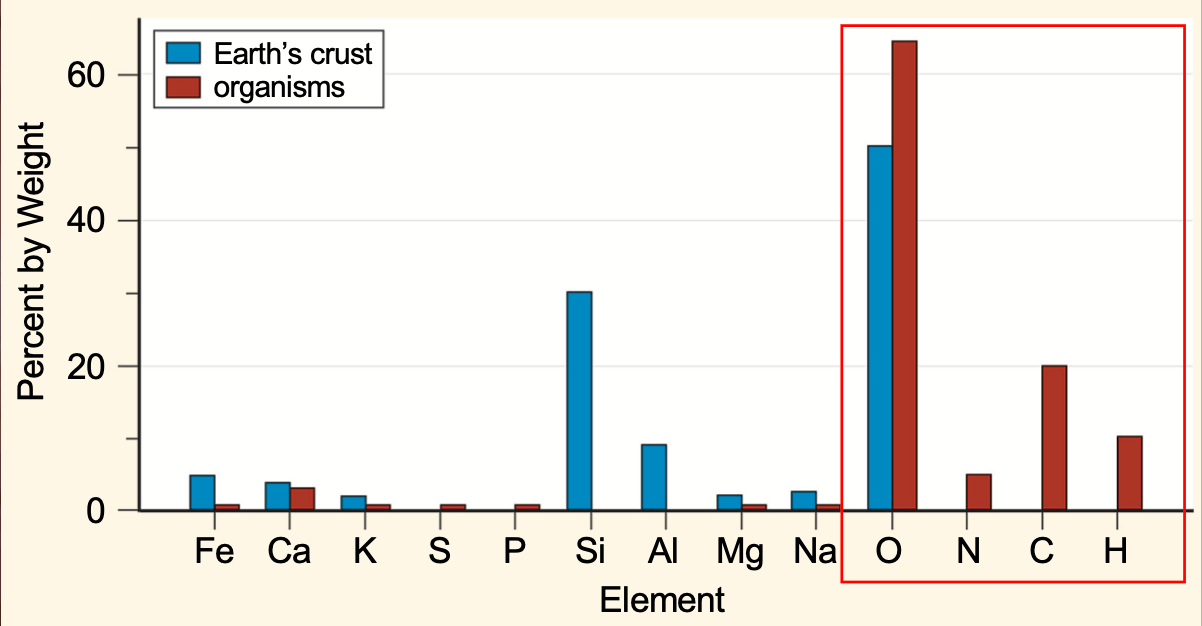
These 4 elements are the most abundant in earthlings.
What are oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen?

These functional groups form bonds that contribute to protein structure.
What are sulfhydryl groups?

These molecules can be identified by counting the number of carbons, hydrogens, and oxygens.
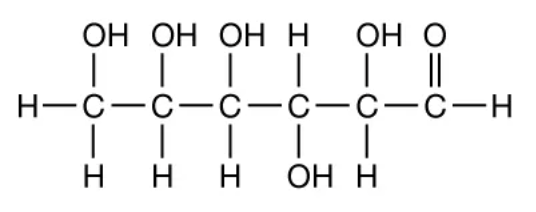
What are carbohydrates?
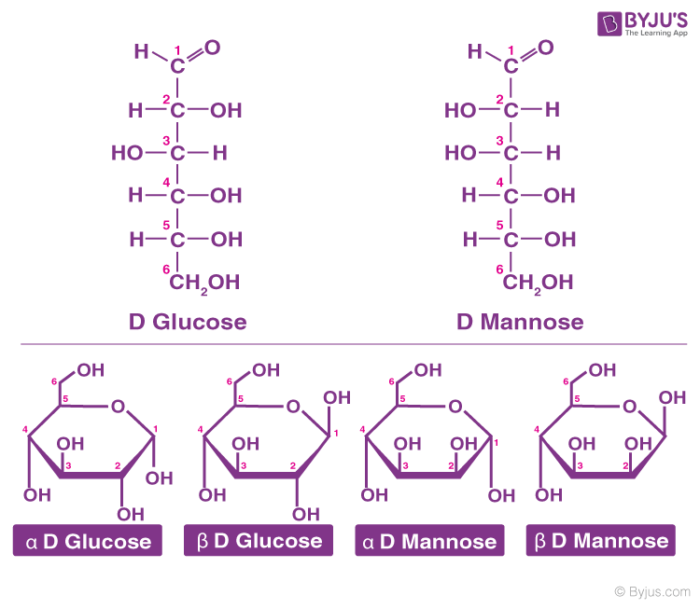
Bonus: what is the ratio of C to H to O?
This polymer of carbohydrates forms the structural support for fungal cell walls and exoskeletons.
What is chitin?