Explain why the rate of disappearance of NO and the rate of formation of N2 are not the same in the reaction, 2CO(g) + 2NO(g) → 2CO2(g) + N2(g).
The rate of disappearance is twice as fast as the rate of formation due to the 2:1 ratio of NO and N2.
Consider the reaction for the decomposition of hydrogen iodide at 448 Celsius. The initial concentration of HI (g) is 1.00 M. Once an equilibrium was established, the concentration of HI (g) was measured to be 0.078 M. Calculate the equilibrium constant (Kc).
35
If the reaction quotient Q has a larger value than the related equilibrium constant K, will there be more products or more reactants?
More reactants.
Ka
What is the acid-dissociation constant
pOH = 10.15
OH^- = 7.08x10^-11
In the reaction H2O2(aq) → H2O(l) + ½ O2(g), the initial concentration of H2O2 is 0.2546 M, and the initial rate of reaction is 9.32×10–4 M s–1. What will be [H2O2] at t = 35 s?
0.2546 M
The C in ICE
What is change?
Which of the following is true for a chemical reaction at equilibrium?
a. Only the forward reaction stops
b. Only the reverse reaction stops
c. Both the forward and the reverse reactions stop
d. The rate constants for the forward and the reverse reactions are equal.
e. The rates of the forward and the reverse reactions are equal.
The rates of the forward and the reverse reactions are equal.
Kb
What is the base-hydrolysis constant
A certain brand of root beer has a hydrogen concentration of 1.9x10^-5 M. What is the pH and the pOH of this root beer?
pH = 4.72
pOH = 9.28
In the reaction A → products, we find that when [A] has fallen to half of its initial value, the reaction proceeds at the same rate as its initial rate. Is the reaction zero order, first order, or second order? Explain.
Since the rate is not changing as a function of time, the reaction must be zero order.
Nitrogen Dioxide can break down into nitrogen monoxide and oxygen. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is Kc = 0.40. If the equilibrium concentration of NO2 (g) is 0.20 M and the equilibrium concentration of NO (g) is 1.0 M. What is the equilibrium concentration of O2 (g)?
0.016 M
A chemical equilibrium may be established by starting a reaction with -----
a. Reactants only
b. Products only
c. Equal quantities of reactants and products
d. Any quantities of reactants and products
e. All of the above
All of the above
when Ka lowers what happens to pKa?
Dr. Pepper has a [H+] = 1.4x10^-5 M. What is the pH?
pH = 4.85
A first order reaction, A → products, has a rate of reaction of 0.00250 M s–1 when [A] = 0.484 M. What is the rate constant, k, for this reaction?
k = Rate/[A] = 0.00250 M s–1/0.0484 M = 5.17×10–3 s–1.
The E in ICE
What is equilibrium?
The equilibrium constant for the acid-ionization of mercaptoethanol (HSCH2CH2OH) is 1.91x10^-10
HSCH2CH2OH(aq) <--> H^+(aq) + SCH2CH2OH^-(aq)
Which of the following is true regarding this equilibrium?
a. The reaction is product favored
b. The reaction is reactant favored
c. Equilibrium lies far to the right
d. Equilibrium lies far to the left
B and D.
when Kb increases what happens to pKb
pKb decreases
What happens to pOH when pH increases
pOH decreases
In the first-order decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide at 335 K,
N2O5(g) → 2 NO2(g) + ½ O2(g)
if we start with a 2.50-g sample of N2O5 at 335 K and have 1.50 g remaining after 109 s, (a) What is the value of the rate constant k? (b) What is the half-life of the reaction? (c) What mass of N2O5 will remain after 5.0 min?
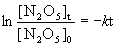
Since the concentration units cancel out, we can work directly in grams for this problem.
(a) [N2O5]0 = 2.50 g, [N2O5]t = 1.50 g, t = 109 s, so
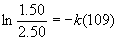
so k = 4.69×10–3 s–1
(b) t½ = 0.693/k = 0.693/4.69×10–3 = 148 s.
(c) t = 5.0 min = 300. s, so
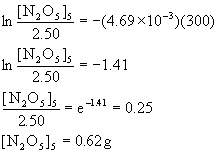
the I in ICE
Initial concentration
Increasing the temperature of an endothermic reaction results in ----
a. more products and fewer reactants
b. more reactants and fewer products
c. more reactants and products
d. fewer reactants and products
e. no change in the quantities of reactants and products
A
A 0.0050 M solution of butyric acid, HC4H7, has a pH = 4.0. Calculate Ka
2.0x10^-6
14.00