OIL RIG
This is the capacity to do work and bring about some sort of change.
What is energy?
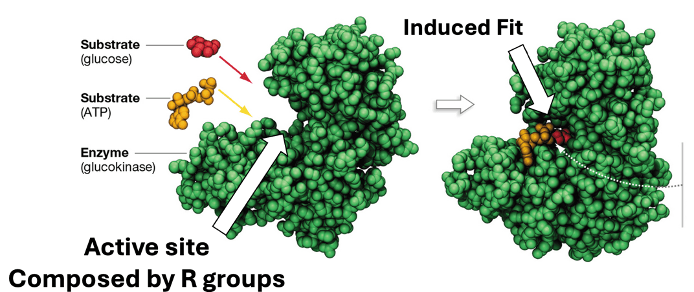
What is an enzyme?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-enzyme-structure-and-function-375555_v4-6f22f82931824e76b1c31401230deac8.png)
In this reaction, the yellow line represents this.
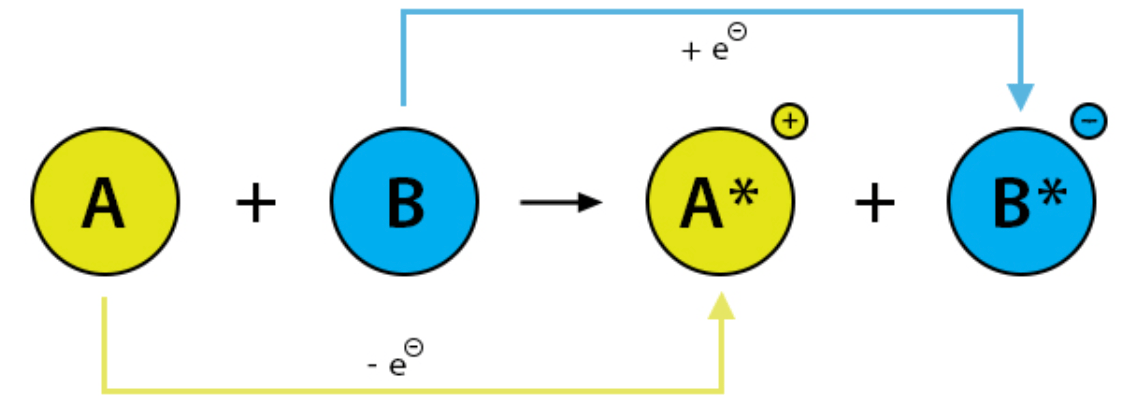
What is oxidation?
**Molecule A is losing electrons**
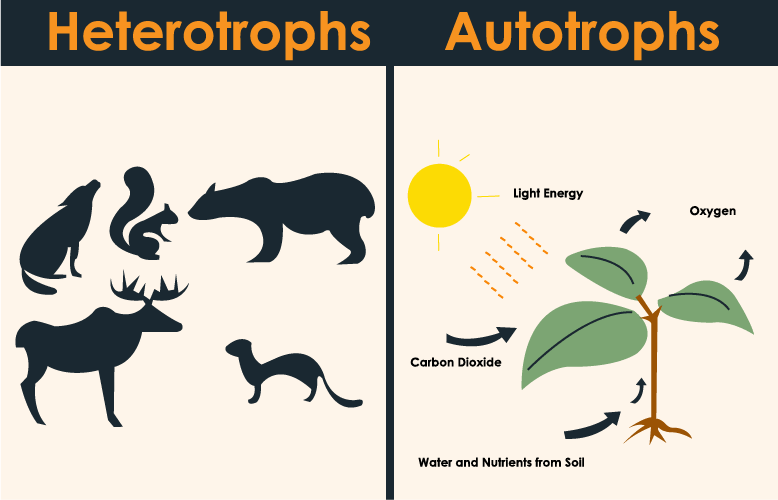
Also known as producers or self-feeders, these are organisms that produce organic compounds from inorganic materials.
What are autotrophs?
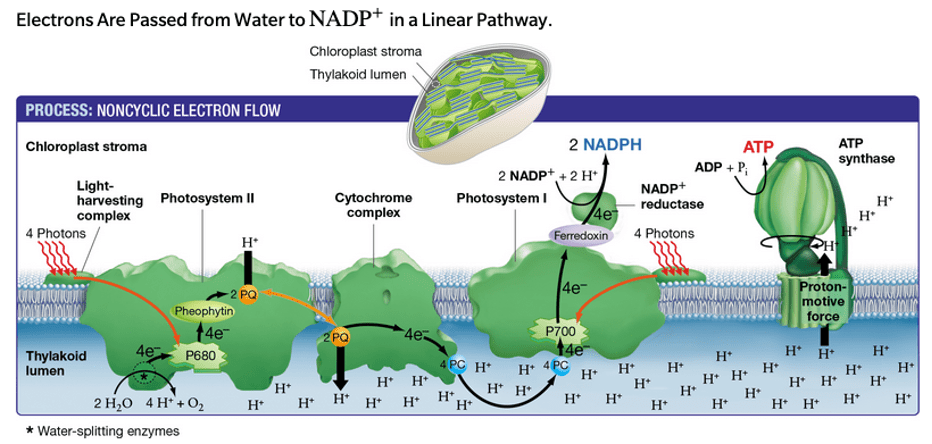
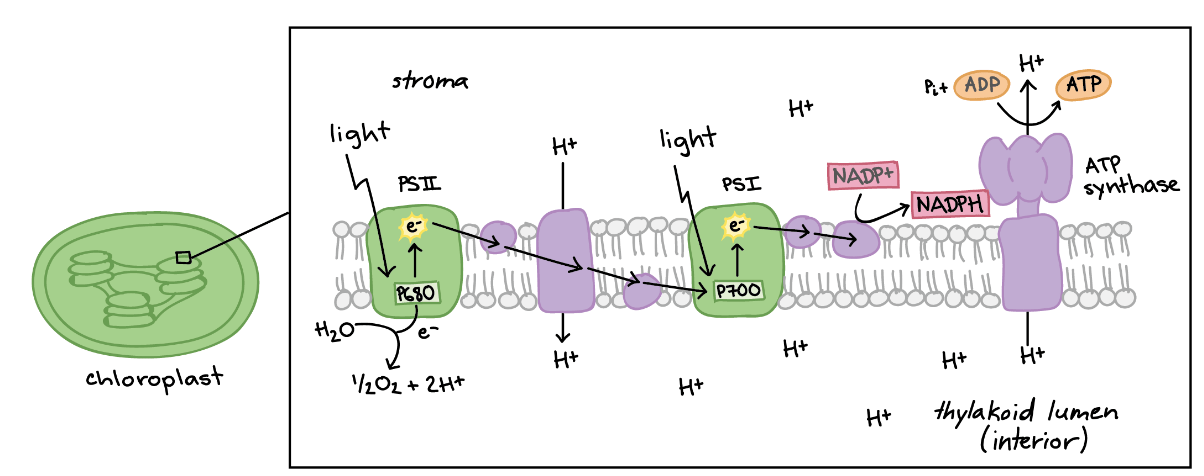
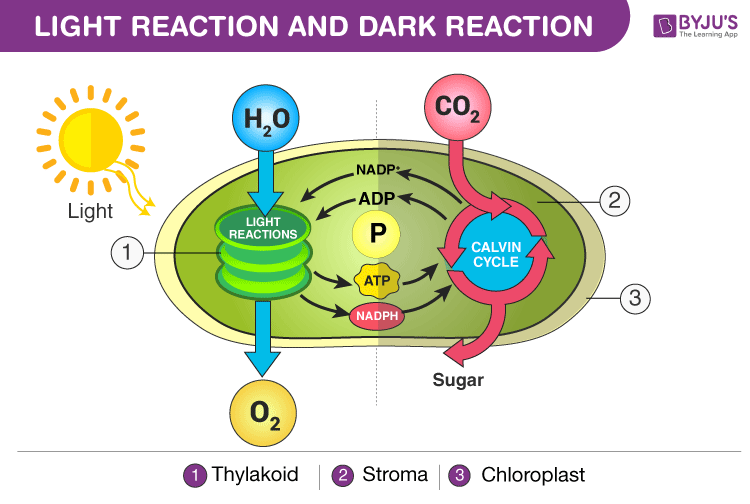
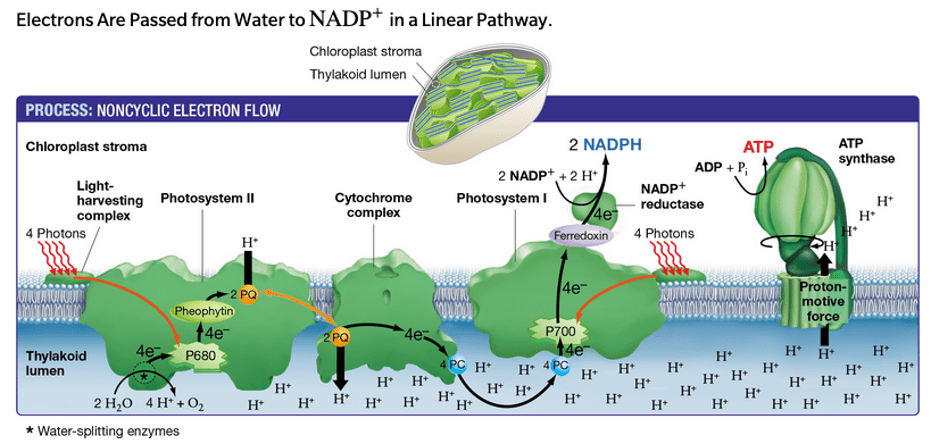
These are the 4 reactants of the light-dependent phase of photosynthesis.
What are sunlight, water, NADP+, and ADP?
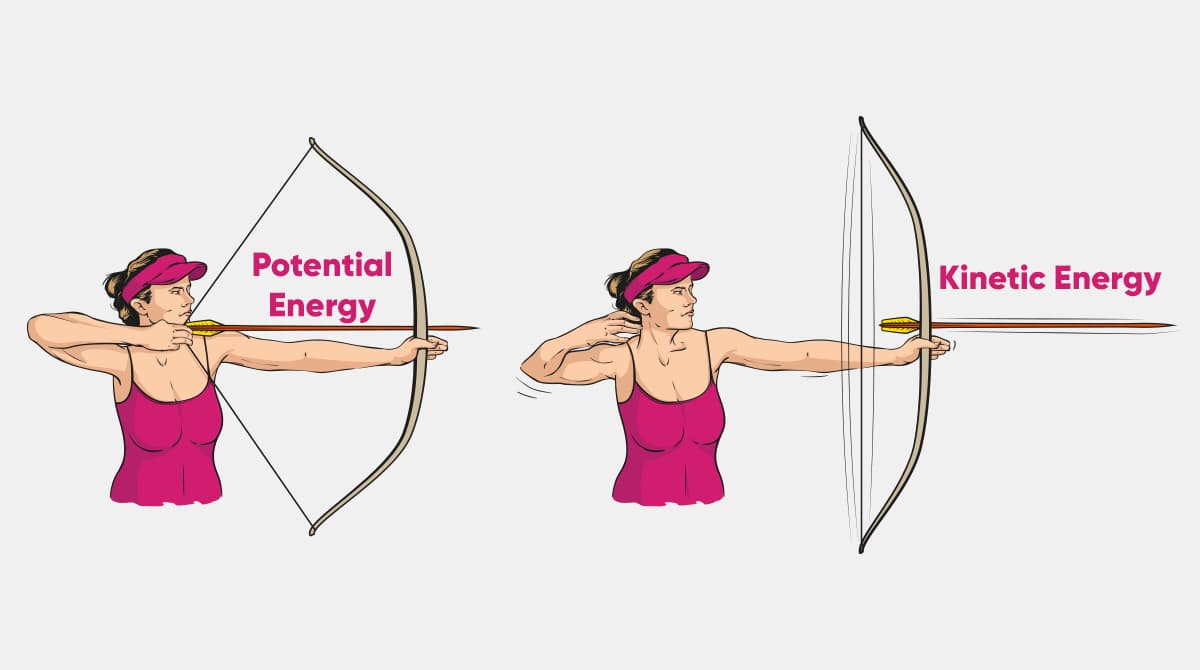
The energy stored in glucose is an example of this.
What is potential energy?
Enzymes have this affect on the activation energy of a reaction.
What is reduces activation energy?
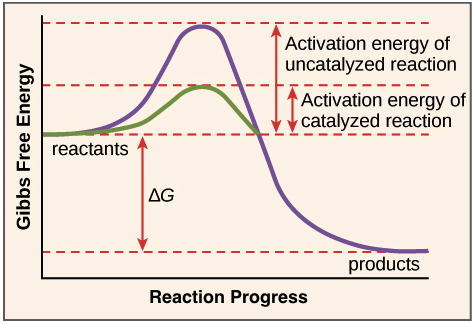
**∆G doesn't change!!**
In this reaction, the blue line represents this.
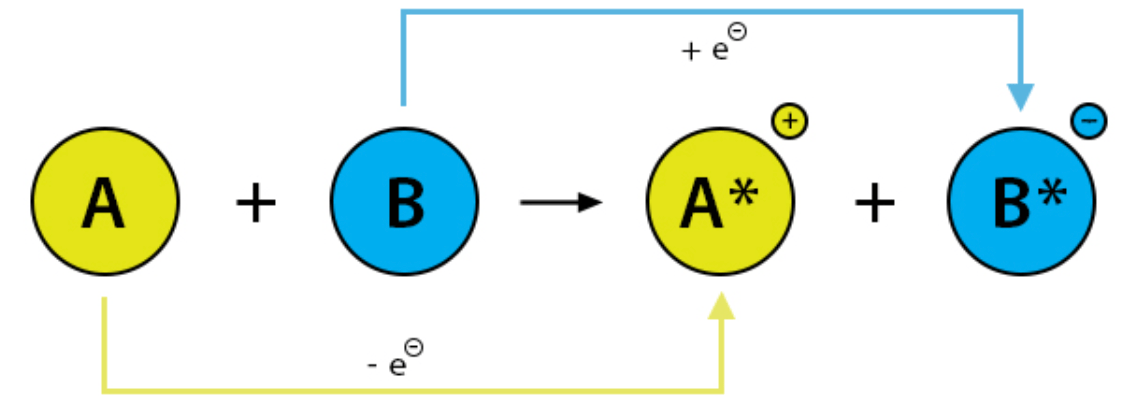
What is reduction?
**Molecule B is gaining electrons**
Photosynthesis is considered this type of process.
(Hint: with respect to ∆G)
What is endergonic?
These are the 4 products of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis.
What are heat, oxygen, NADPH, and ATP?
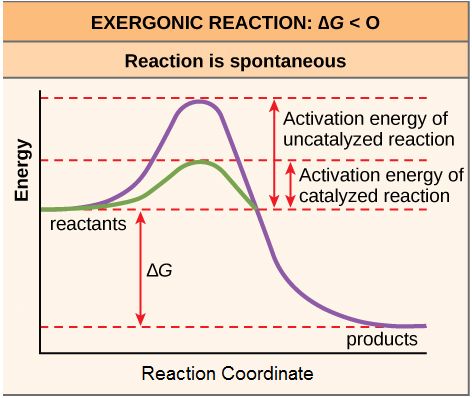
The following graph depicts this type of reaction.
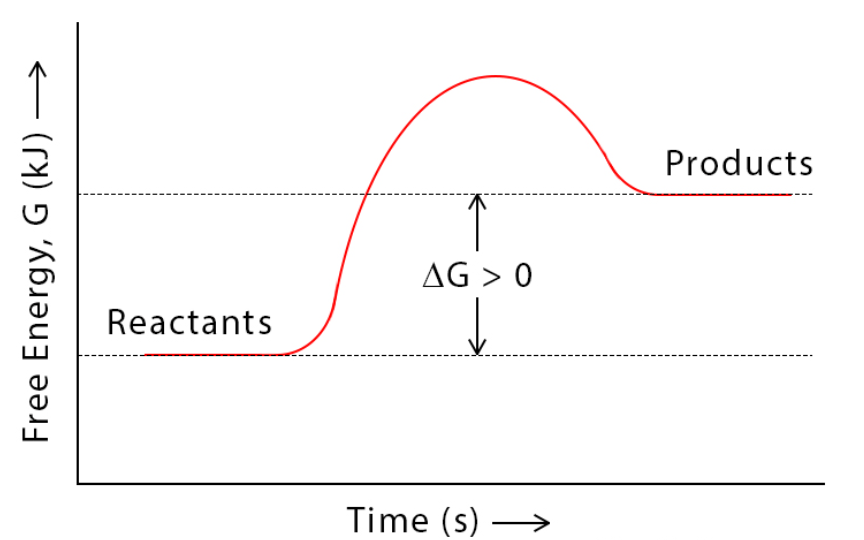
What is endergonic?
These are the reactants of catalyzed reactions.
What are substrates?
This is what is occurring to NAD+ in the following reaction.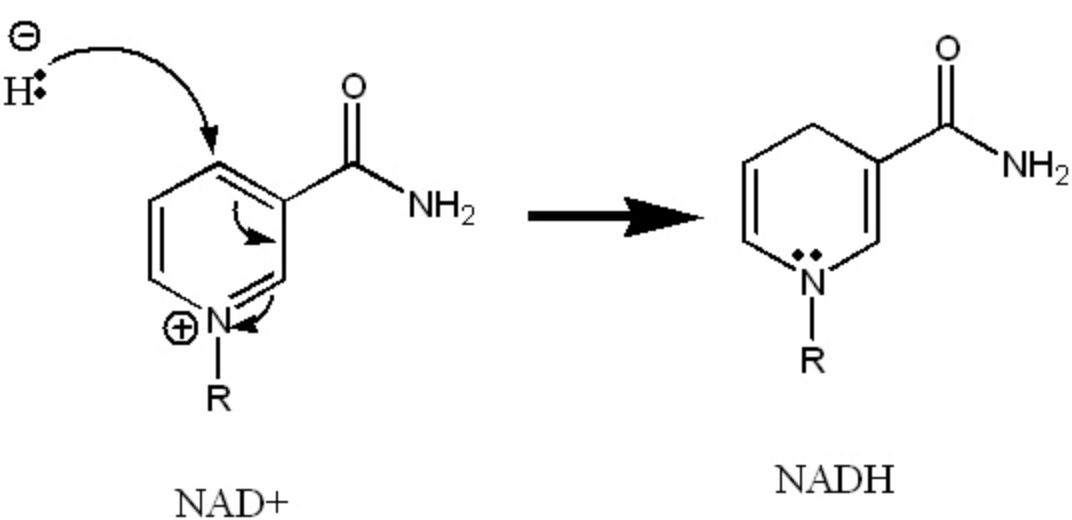
What is reduction?

Positive --> negative = gaining electrons
RIG --> Reduction Is Gaining
These are the two major pathways that comprise photosynthesis.
What are light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle?
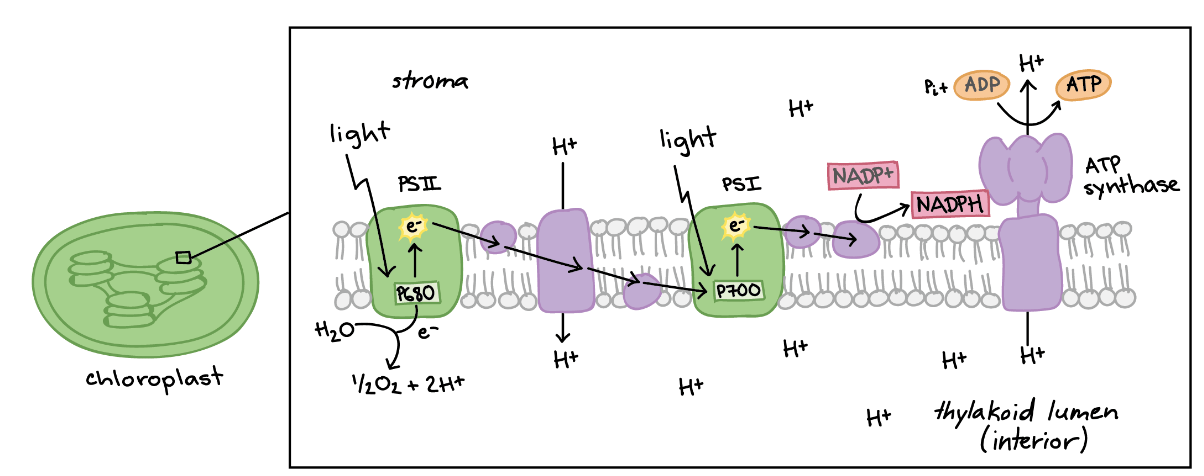
This is the green protein on the left, also known as P680.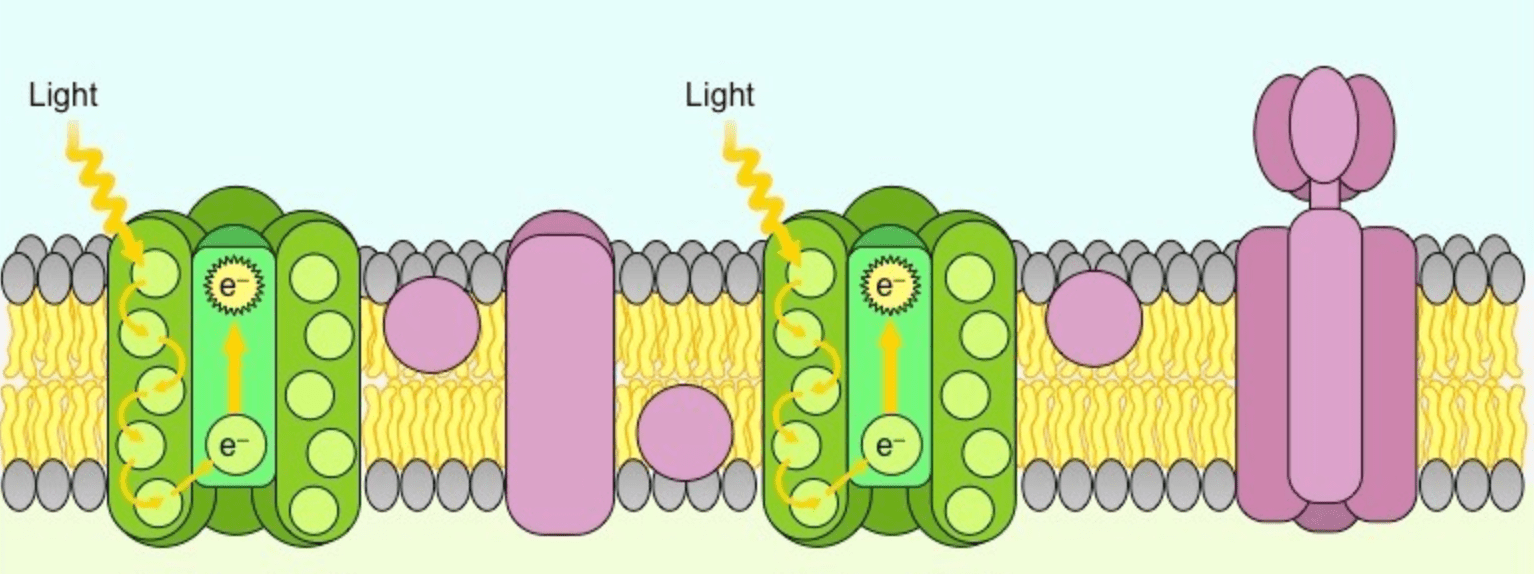
What is Photosystem II?
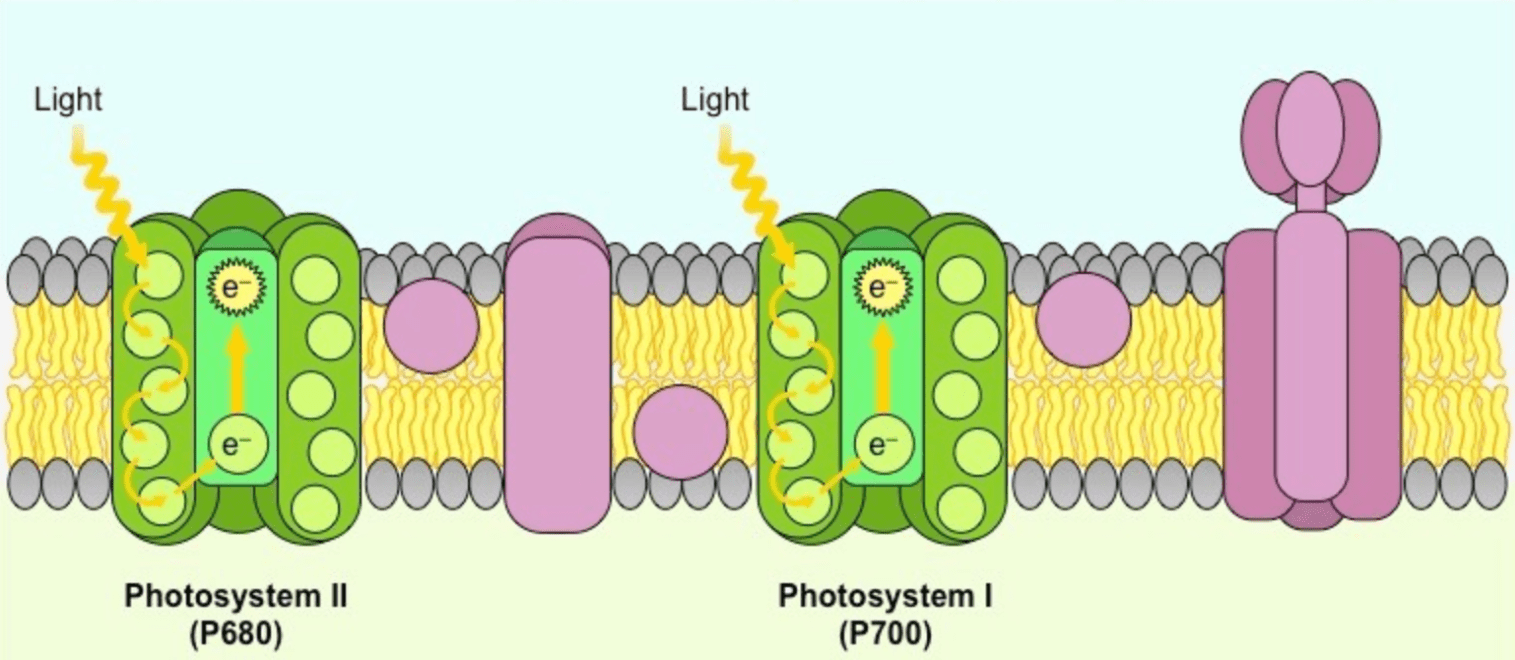
**Bonus: how do these carrier proteins differ from those of cellular respiration?**
Exergonic reactions can be identified by this change in ∆G.
What is negative?
This type of inhibition occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to the enzyme's active site.
What is competitive inhibition?

In redox reactions, electrons may be gained or lost in these two ways.
What are covalent bonds and ionic bonds?
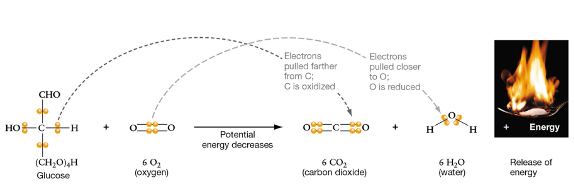
**example of electrons being moved from covalent bonds**
Ionic --> Fe3+ to Fe2+
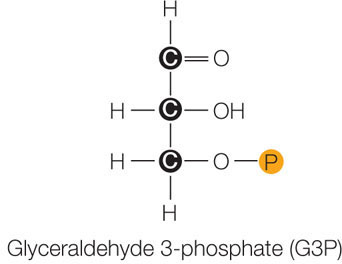
This is the organic carbon product of photosynthesis, which includes hydrogen from water and carbon from CO2.
What is G3P?
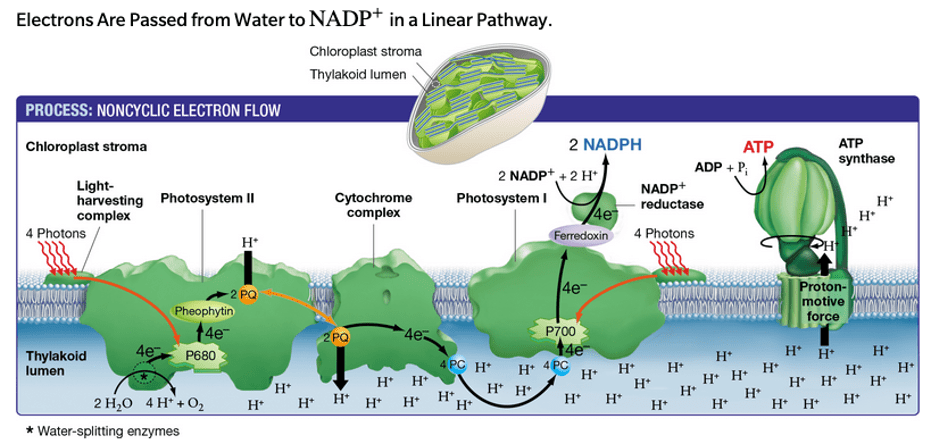
During the light-dependent phase, H+ ions return to the stroma (along the proton gradient) via this transmembrane enzyme.
What is ATP synthase?
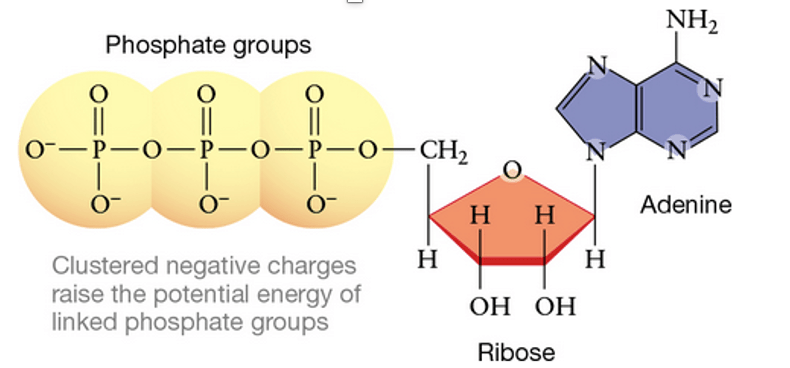
The high potential energy of ATP is a result of the four negative charges clustered in which groups?
What are phosphate groups?
This type of regulation occurs when the active site of an enzyme becomes available to the substrate when a regulatory molecule binds to a different site on the enzyme.
What is allosteric regulation?

This is the reduced form of the electron carrier used in the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis.
What is NADPH?
This is the equation for photosynthesis.
What is
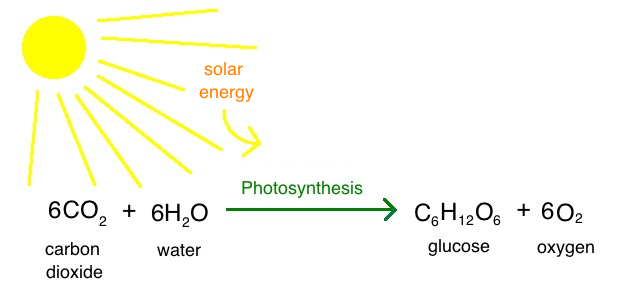 ?
?
During the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, H+ ions accumulate in this structure.
What is the thylakoid lumen?