You just scored for your basketball team!
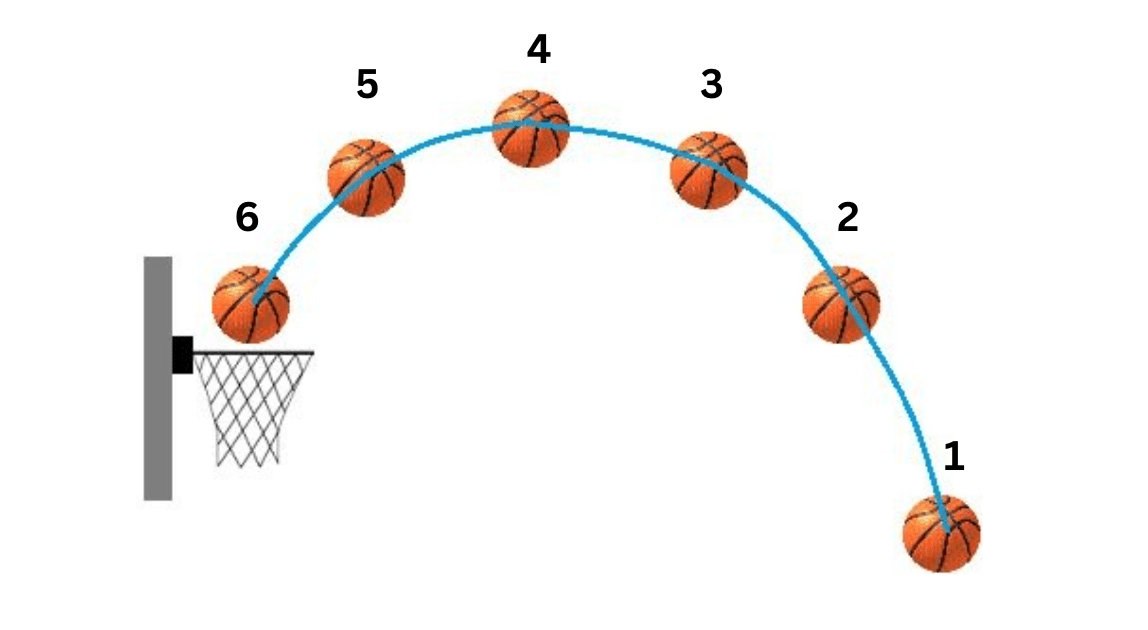
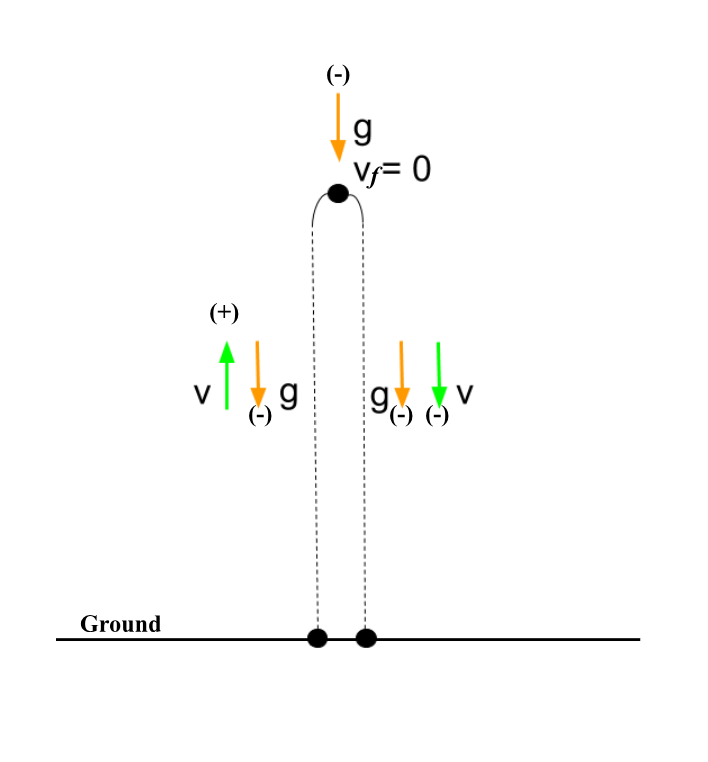
Where is the vertical velocity of this basketball = 0?
4
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical?
Horizontal = left to right (the horizon) = X
Vertical = up and down = Y
What is the force we purposefully ignore in our projectile motion calculations?
Air resistance
You want to subtract 2 from 90 and then divide that value by 4. What is wrong with inputting the following expression into your calculator?
90-2/4
Your calculator follows order of operations ... PEMDAS
90-2/4
90-2/4= 90-0.5 = 89.5
(90-2)/4
(90-2)/4 = 88/4 = 22
Imagine two scenarios:
1. You drop a ball straight down from a certain height
2. You throw a ball horizontally from the same height
Which one hits the ground first?
They hit at the same time
(Remember the bullet dropped versus fired from a gun video?)
In projectile motion, the horizontal and vertical motions are ______ each other.
A) independent of
B) dependent on
C) equal to
A) independent of
The vector resulting from adding two or more vectors is called the ____.
Resultant
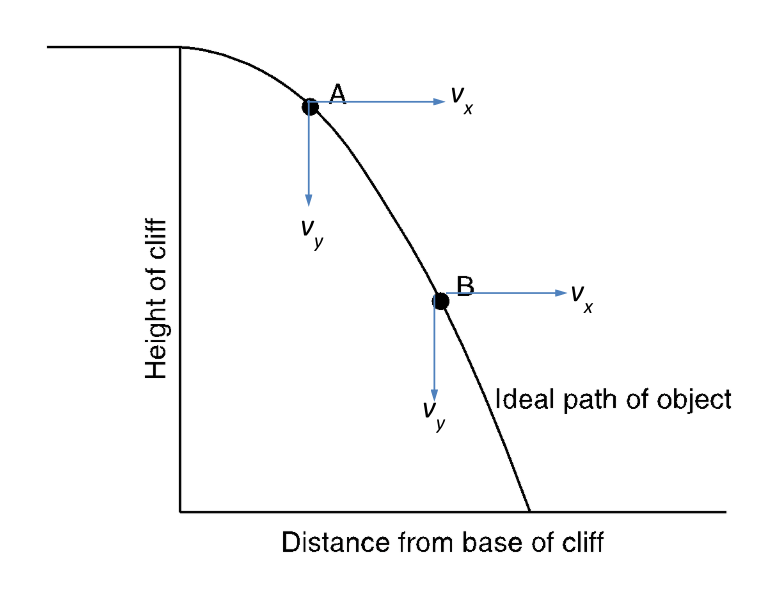
For this horizontally-launched projectile, at what point (A or B) is the ball moving faster vertically? What about horizontally?
Bonus: what is wrong with the picture above?
Vertically: vy B > vy A
Horizontally: vx B = vx A
Bonus: downward arrow for vy B should be longer than arrow for vy A (bigger arrow = larger velocity)
What is the resultant of these three vectors?
A: <<1,2>>
B: <<-3,-3>>
C: <<1,-5>>
A+B+C = <<1-3+1,2-3-5>> = <<-1, -6>>
What are the x and y components of vector u? 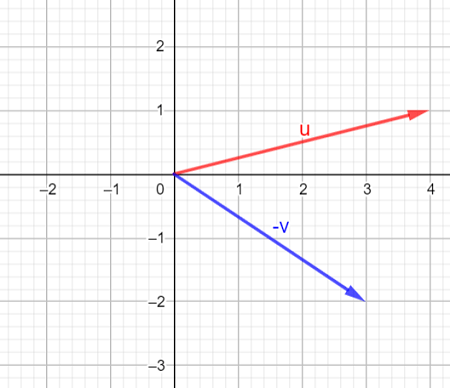
What is the magnitude of vector u?
x component = 4, y component = 1
mag=sqrt((4)^2+(1)^2)=4.123
A baton twirler is moving horizontally at a constant speed and tosses their baton straight up into the air while continuing to move at the same speed. When the baton comes back down, the horizontal location of the twirler will...
A) Be behind the baton
B) Be directly under the baton
C) Be in front of the baton
D) Depend on the speed at which the baton was released
B) Be directly under the baton
(Watch 1:38-1:47)
A projectile's path is called its ____.
Trajectory
For a projectile launched at an angle, flight time depends only on ____ velocity.
(Vertical or horizontal)
Vertical
Come to the board and draw the resultant of these two vectors. Use tip to tail addition.
What is the magnitude of the resultant vector?
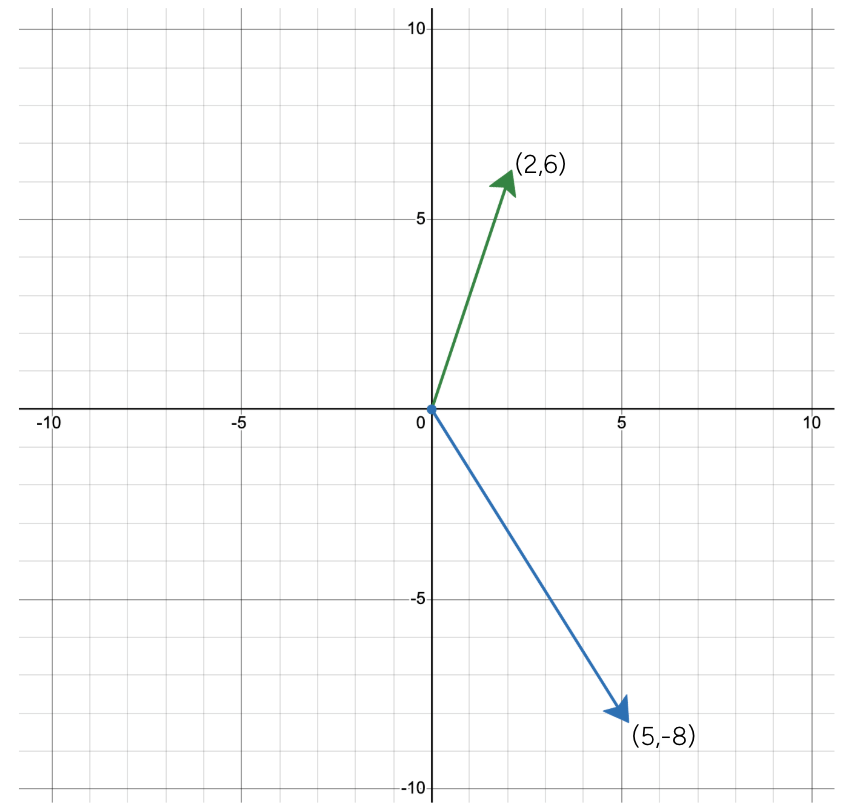
Resultant:
<<7, -2>>
mag = sqrt((7)^2+(-2)^2)=7.28
Name 3 different examples of projectiles.
Answers may vary.
If you throw a lacrosse ball to your friend, 1) What forces are acting on the ball as it leaves your hand? 2) What forces act on it as it flies through the air?
1) As it leaves your hand: force of your throw
2) As it is in the air: gravity, air resistance (but ignoring this for computations)
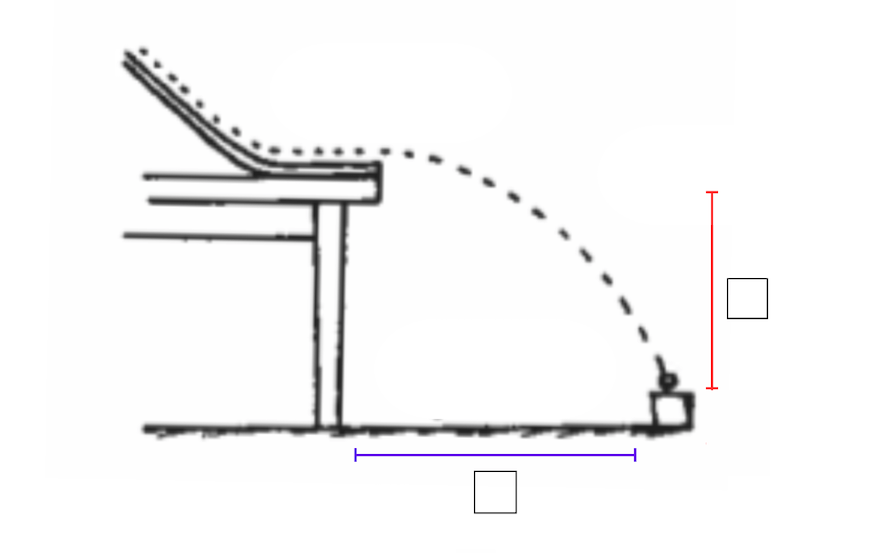
This is a drawing of the projectile from our Ball in Can lab.
Correctly label the two quantities (blue and red) using the following quantity list:
ax , ay (g) , dx , dy , t , vx , v0y , vfy
Blue = dx
Red = dy
A car drives off a cliff at a horizontal velocity of 50 m/s and covers a certain horizontal distance (dx) before it hits the ground.
What happens to the horizontal distance travelled if the car drives off the same cliff at only 10 m/s?
The car covers less horizontal distance (exactly 1/5th the distance).
dx = vx * t
If vx is less, dx is less.
(Draw this out on the board using a visual with different paths for vx = 50 m/s and vx = 10 m/s)
A projectile is launched at an angle with an initial vertical velocity of 30 m/s.
Draw this trajectory and label the initial and final vertical velocity values. Also label the velocity at the highest point.
v0y= 30 m/s
vmax height = 0 m/s
vfy= -30 m/s
You are going to do a beautiful dive off of the high dive, but oh no! The diving board is slippery, and you slip and fall off of the board, so now you are free falling toward the pool below you.
If you hit the pool at a velocity of -44 m/s, determine:
a. Time to impact with the pool (t)
b. The vertical distance you fell (dy)
t = 4.49 sec
dy = -98.78 m
Bonus: Why is this distance negative?
You are a cheerleader with your bestie, and you two have choreographed a crazy stunt. You throw her straight up in the air! You throw her upwards with an initial velocity of 12 m/s.
Calculate the time for your friend to reach maximum height.
- What is the maximum height your friend reached?
1. vy = v0y + at
At max height, vy=0
0 = 12 + (-9.8)(t)
t = -12/-9.8 = 1.22 sec
2. dy = voyt+1/2at2
dy = 12(1.22)+(1/2)(-9.8)(1.22)^2 = 7.35 m
Bonus: What do you get for dy if you use 1.22448979592 (the full decimal for -12/-9.8) for time instead of rounding it to 1.22?
Why do we use g instead of a for acceleration during projectile problems?
g = special case of a due to gravity = -9.8 m/s2
Taken from study guide:
If a ball rolls off the edge of the table and hits the ground 1 meter away, how far away would a ball with 3 times the mass go, if it’s rolling at the same velocity?
A) 0.3 m
B) 1.0 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 9.0 m
B) 1.0 m
Three projectiles, A, B, and C, were launched from, and returned to, level ground. Given the initial horizontal and vertical velocity values below, which projectile has the longest flight time?
Projectile A
v0x = 40 m/s
v0y = 20 m/s
Projectile B
v0x = 50 m/s
v0y = 10 m/s
Projectile C
v0x = 30 m/s
v0y = 25 m/s
Projectile C
t=(2*v_{0y})/g
Larger v0y=larger t
If you have a cannonball launched with positive v0y and positive v0x, when you increase v0y, which is true?
A) The cannonball goes farther
B) The cannonball goes higher
C) The cannonball goes both farther and higher
D) Not enough information
C) The cannonball goes both farther and higher
At the board, fill in the blank spaces below with the correct signs (+ or -) and values of each velocity component. Also, determine the time at which the projectile reaches its apex (highest point) in its trajectory.
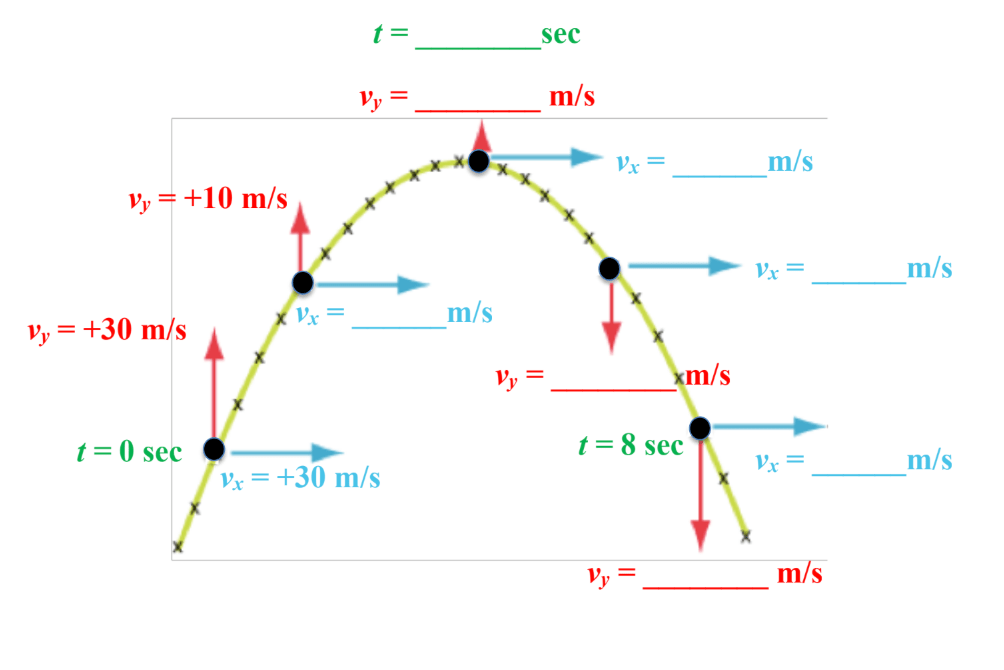
Done in class, refer to angle launched projectile notes
In projectile motion, we use v0y and vfy to represent the initial and final vertical (up and down) velocity.
For the horizontal (side to side) velocity, why do we only use vx instead of vox and vfx ?
There are no forces acting horizontally (side to side) to change the velocity of the projectile, so its initial velocity is equal to its final velocity. We use vx to represent the constant horizontal velocity from start to finish.
Why is this is the correct velocity-time graph for an object thrown directly up in the air?
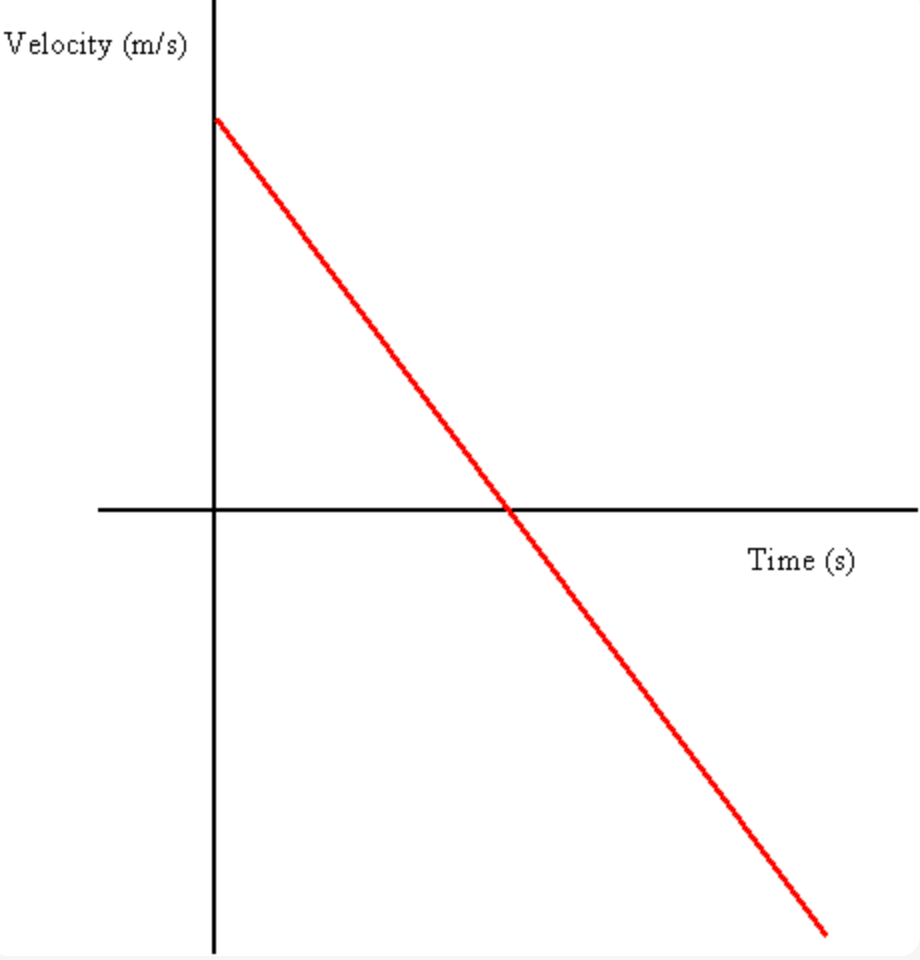
Initial velocity is positive, and -9.8 m/s2 acceleration due to gravity causes velocity to constantly decrease (slowing down as it moves upward) until it is 0 (maximum height) then negative (speeding up as it moves downward)
Bonus: what is the slope of the line?
You are golfing, and you hit the ball with a horizontal velocity of 5 m/s and an initial vertical velocity of 10 m/s. Using this information, determine the following (in this order):
a. The total time (ttotal) of flight of the projectile.
b. The range (dx) of the trajectory.
c. The maximum height (dy) reached by the golf ball.
a. 2.04 sec
b. 10.2 m
c. 5.1 m
Are these values always positive, negative, or can be either? Explain.
- acceleration (due to gravity)
- time
- distance
- velocity
a is always (-) (g=-9.8 m/s2)
t is always (+)
distance can be either (+) or (-)
velocity can be either (+) or (-)
Follow up: When is distance and velocity (+) versus (-)?