This type of chemical reaction adds water, in the presence of an enzyme, to break bonds to turn polymers back into monomers.
hydrolysis
This type of bond is found inside of water molecules and causes partial charges on the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. BE SPECIFIC!
polar covalent bond
The monomer for carbohydrates. Means one sugar or simple sugars.
monosaccharide
3 functions of lipids
long term energy storage
insulation - temperature regulation
protection
The monomer for proteins.
amino acids
The monomer for a nucleic acid. Give the 3 parts.
nucleotide
- phosphate, sugar, nitrogen base
This type of chemical reaction extracts water, in the presence of an enzyme, to build bonds & make polymers.
dehydration synthesis
This type of bond is responsible for the special chemical properties that emerge from water when water molecules are bonded together.
hydrogen bond
2 functions of carbs
structure & protection
glycerol & fatty acids
3 functions of proteins
storage
transport
structure
enzymes
movement
The function of nucleic acids.
holds the instructions for genetic info
instructions for how our bodies should work & act
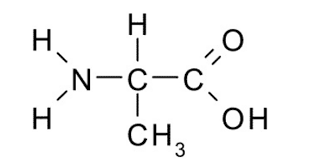
Identify the functional group(s) present in the molecule shown. Give the name of the group(s).
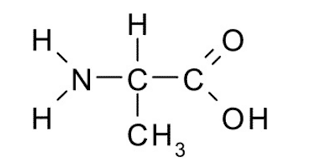
amino & carboxyl
These properties of water are responsible for the vertical movement of water against gravity in a plant (transpiration)
cohesion & adhesion
Which can we digest? Starch or cellulose? Why?
starch
we have the enzymes to do so
Identify 2 characteristics of saturated fats.
solid at room temperature
harmful to body
no double bonds in tails
comes from animals
type of bonds - primary structure of proteins
covalent bonds
single or double bonds?
purines
double
Identify the functional group(s) present in the molecule shown. Give the name of the group(s).
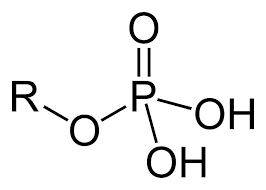
phosphate
This property of water allows an organisms body to dissolve important molecules and nutrients in order to move them around the body.
water is a great solvent
cellulose
we don't have enzymes to do so
Identify 2 characteristics of unsaturated fats.
liquid at room temperature
good for the body
double bonds in tails
comes from plants or fish
type of bonds - secondary structure of proteins
covalent bonds
hydrogen bonds
cytosine, uracil, and thymine? purines or pyrimidines
single or double rings?
pyrimidines
single rings
Identify the functional group(s) present in the molecule shown. Give the name of the group(s).
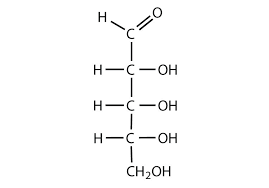
carbonyl & hydroxyl
This property of water allows for evaporative cooling. Helps to produce sweat.
heat of vaporization
starch = alpha glucose
cellulose = beta glucose
Main function of phospholipids. Where are they found?
cell membrane
plasma membrane
lipid bilayer
type of bonds - tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins
disulfide bridges
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
Type of molecule?
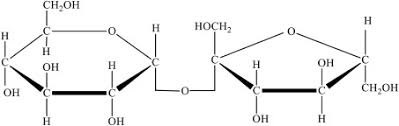
carbs
Identify the molecule with glycosidic linkages. A or B?
A.
B.
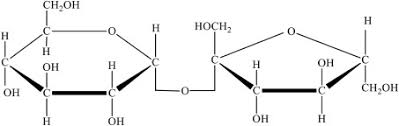
B. carbohydrates
This property of water allows for insulation and temperature regulation of bodies of water during the winter time.
density of water
expansion of water
Which two polysaccharides (polymers of carbs) are used for energy storage in plants and animals?
starch (plants)
glycogen (animals)
Type of molecule?
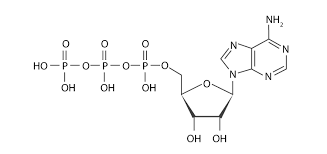
nucleotide
What determines the difference between one amino acid and another?
the r groups
Type of molecule?
lipid