Name 3 risk factors for tetralogy of fallot
Family history.
Having a virus during pregnancy including Rubella
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy.
Eating poorly during pregnancy.
Smoking during pregnancy.
Mother's age is older than 35.
Down syndrome or DiGeorge syndrome in the baby.
What day of gestation does human heart development begin and what happens on that day?
20th day
fusion of the outer endocardial tubes into a single tubular structure, the cardiac tube
What are the 3 leading causes of mortality following repair of Tetralogy of Fallot?
arrhythmia, heart failure, and complications from reoperations
What is the gold standard of imaging studies for Tetralogy of Fallot?
Echocardiogram
What kind of scan is this?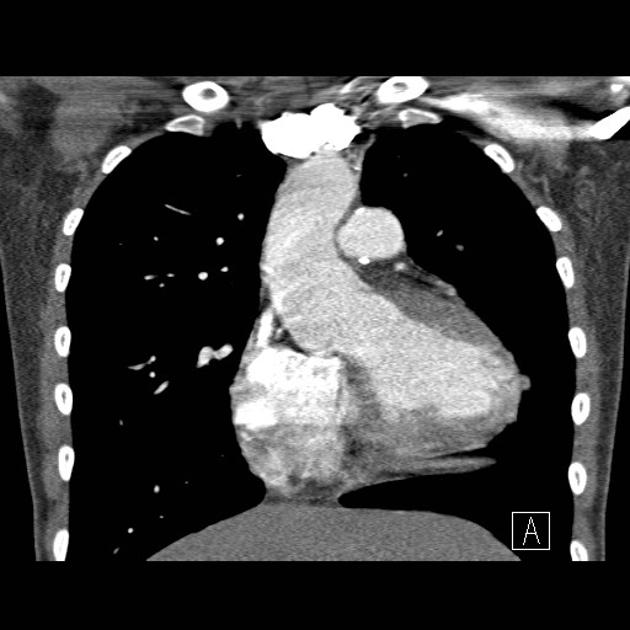
CT
What are common symptoms of Tetralogy of Fallot
Blue or gray skin color
Shortness of breath and rapid breathing, especially during feeding or exercise
Trouble gaining weight
Getting tired easily during play or exercise
Irritability
Crying for long periods of time
Fainting
True or False: The exact embryological process that contributes to Tetralogy of Fallot is known.
False. An association is seen where an anterior and cephalad deviation of the infundibular septum that results in a misaligned ventricular septal defect, with an overriding aortic root causing a subsequent right ventricular outflow obstruction.
Do women who have complete repair of tetralogy of Fallot have similar or different outcomes compared to general obstetric population?
Similar
Increased pregnancy complications are related to the level of pulmonary hypertension and the severity of the pulmonary regurgitation with right or left ventricular dysfunction
What is a common sign of tetralogy of Fallot on an XRay? Describe it.
Boot-shaped heart - normal-size heart silhouette, with an upturned apex and a concave main pulmonary artery segment
What time of imaging is this and what is seen?
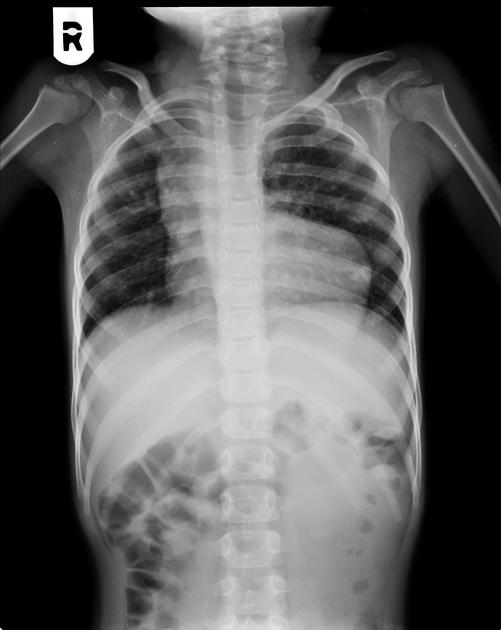
XR
boot-shaped heart configuration
What are some factors that describe the etiology of Tetralogy of Fallot (name 2)
untreated maternal diabetes
maternal intake of retinoic acid
Phenylketonuria
Chromosomal anomalies (trisomies 21, 18, 13)
Microdeletions of chromosome 22q11.2,
Alagille syndrome with JAG1/NOTCH2 mutations
Based on the diagram, name the 4 anatomical malformations characteristic to Tetrology of Fallot
Pulmonary stenosis – When the valve located between the lower right heart chamber and pulmonary artery narrows, limiting blood flow from the heart to the lungs
Right ventricular hypertrophy – The muscle of the right ventricle becomes thickened as the heart’s pumping action works harder than normal. Like any other muscle, it gets thicker and stronger when exercised. This can make the heart stiff and weak over time.
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) – A hole in the wall between the bottom heart chambers (left and right ventricles). This hole allows blood to cross from one side of the heart to the other, limiting blood flow and decreasing the body’s supply of oxygen-rich blood.
Overriding aorta – With malalignment of the muscle, the aorta (the main blood vessel going to the body) sits over the VSD, receiving blood from both of the pumps. This results in a mix of low-oxygen and high-oxygen blood from the right and left ventricles.
What is a short-term complication of tetralogy repair that is accompanied with a risk of ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation/flutter, and intra-atrial reentrant tachycardia
Arrhythmia
Name 3 diagnostic tests and their function/purpose?
Oxygen level measurement
Echocardiogram
ECG or EKG
Chest X-ray
Cardiac catheterization - not commonly used but can help to assess the level of obstruction, pulmonary stenosis or hypoplasia, coronary artery anatomy, and the presence of collaterals and accessory septal defects
What imaging modality is this? Is this a corrected or uncorrected Tetralogy of Fallot?
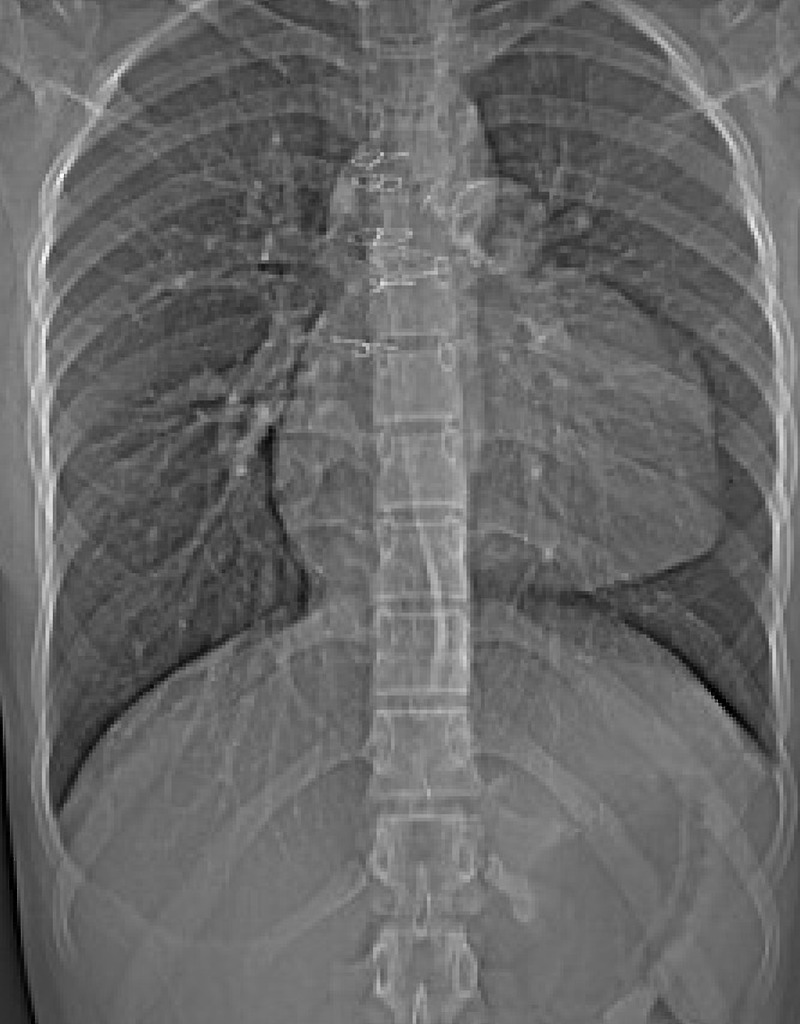
XR
Corrected
Name 2 heart sounds heard in this case
Aortic regurgitation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uZysrKXHJMM
Aortic stenosis
Describe “Tet spells”
Decrease in systemic vascular resistance or an increase in pulmonary resistance contributing to a right-to-left shunt across the ventricular septal defect, causing marked desaturation
Decrease after 4-5 yrs of age
What is the most common indication for pulmonary valve replacement and what is used to measure severity?
Pulmonary insufficiency
Measure the regurgitant fraction on magnetic resonance or CT scan
Who would most benefit with a cardiac MRI? (think age group, what condition, etc.)
In adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot
What block is seen in this ECG/EKG?

complete right bundle branch block
What are some differential diagnosis of tetralogy of fallot
bronchiolitis, pneumonia (viral/bacterial), pneumothorax, or severe pulmonic or aortic stenosis, complete (d-) transposition of the great arteries with pulmonary stenosis; double outlet right ventricle, including Taussig-Bing anomaly; tricuspid atresia; Ebstein anomaly; and pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum, total anomalous pulmonary venous return, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, and single ventricle and truncus arteriosus
The degree of _____ determines the pathophysiology of Tetralogy of Fallot.
right ventricular outflow obstruction
What are typical ECG findings following repair?
Right bundle branch block or left bundle branch block pattern associated with wide complex tachycardia
What are the common findings on ECG/EKG of someone with Tetrology of Fallot?
signs of right atrial enlargement and right ventricular hypertrophy showing right axis deviation
prominent R waves anteriorly and S waves posteriorly
upright T wave in V1 (abnormal after 7 days of life up to 10 years of age)
qR pattern in the right precordial leads
What condition is seen here?
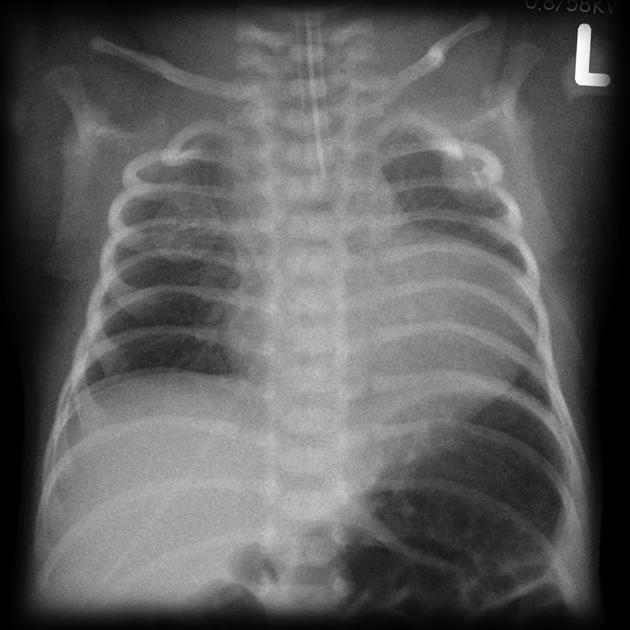
pulmonary atresia - a differential diagnosis