This macromolecule's function is to store genomic information and direct the process of protein synthesis.
What is nucleic acid?
This macromolecule is composed with the general chemical formula (CH2O)n, made up of molecules of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
What is a carbohydrate?
This monomer is a sugar that can form repeated chains and branched structures.
What is glucose (or monosaccharide)?
DNA and RNA are examples of this polymer.
What are polynucleotide chains?
The intramolecular bond in water molecules and the intermolecular bond between neighboring molecules.
What are polar covalent and hydrogen bonds?
This macromolecule is responsible for providing structural support to cells, body, and organs.
What is protein?
This macromolecule is made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a phosphate group (hydrophilic)
What is a lipid?
This monomer is divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines.
What are nucleotides?
Galactose, sucrose, and lactose are all examples of this polymer
What are polysaccharides?
The tendency of an atom to be polar and the tendency of an atom to nonpolar.
What are hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
This hydrophobic macromolecule is responsible for storing long term energy, and building up hormones like testosterone.
What are lipids?
This macromole has functional groups called carboxylic acid, amino group and are placed together with peptide bonds.
What is a protein?
This monomer has a central carbon, hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, amino group and variable R group.
What is an amino acid?
This polymer is made up of 3 fatty acid units bonded together by a glycerol molecule.
What is triglyceride?
This functional group consists of one nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
What is an amino group?
These macromolecules function to provide structural support in plant cells and certain insects.
what are carbohydrates?
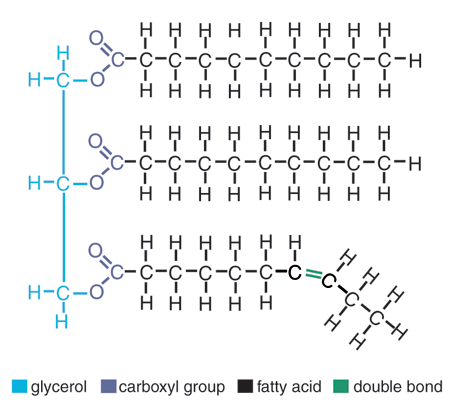
What is a lipid?
This monomer has a long, straight chain of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end and a methyl group (CH3) at the other.
They can either be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (containing double bonds between carbons) depending on the type.
What are fatty acids?
this polymer is composed of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds, forming a chain with a distinct "backbone" structure where each amino acid is connected to the next via its amino group to the carboxyl group of the previous one.
What is a polypeptide chain?
This functional group consist of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single bonded to a hydroxyl group
What is a carboxyl group?
These macromolecules play a major role in gene expression. They will synthesize the genetic information found in DNA.
What are proteins?
This macromolecule is the only one molecularly structured with a phosphate group.
What is a nucleic acid?
phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine are all examples of this monomer
What are amino acids?
Polypeptide chains arrange into these two structures during the second phase of protein folding.
What are alpha helix and B pleated sheets?
The position of this functional group in a monosaccharide can be used to categorize the sugar.
What is a carbonyl group?