This class of organic compound contains nitrogen.
(1) aldehyde
(2) alcohol
(3) amine
(4) ether
What is Amine?
Tip: You can think of the N in amiNe as Nitrogen!
This formula represents an alkane.
(1) C2H2
(2) C2H4
(3) C3H4
(4) C3H8
What is C3H8 ?
Soap is made through this reaction, which involves breaking fats with a base.
What is saponification?
A molecule of any organic compound contains at least one atom of this element.
What is carbon?
This is the molecular formula for the following structure.
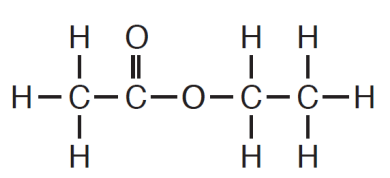
What is C4H8O2 ?
Count how many carbons, hydrogens, and oxygens.
This compound is classified as an ether.
(1) CH3CHO
(2) CH3OCH3
(3) CH3COCH3
(4) CH3COOCH3What is CH3OCH3 ?
This formula represents a saturated hydrocarbon.
(1) butane
(2) ethene
(3) heptene
(4) pentyne
What is (1) butane?
Remember:
- Only alkanes are saturated!
- Alkenes & Alkynes are unsaturated.
The reaction between an alcohol and an organic acid produces this class of compound.
What is esterification?
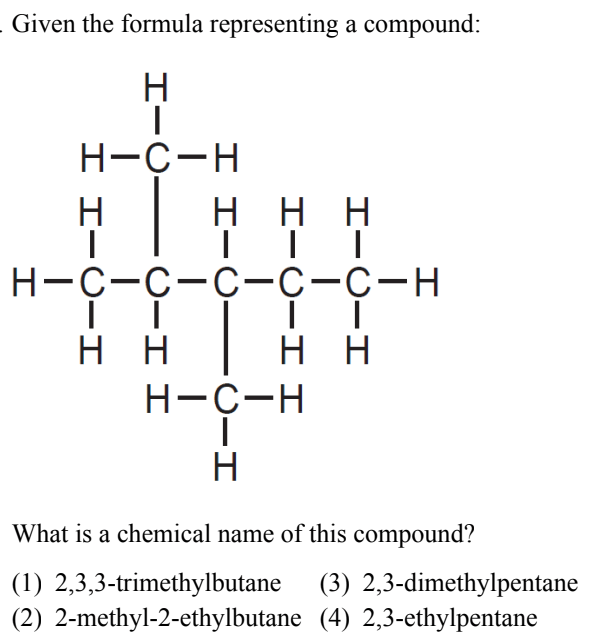
What is (3) 2, 3- dimethylpentane?
This is the empirical formula for the following structure.
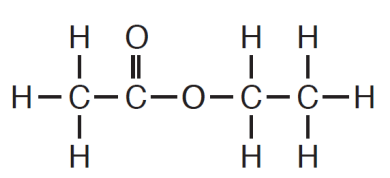
The molecular formula is C4H8O2.
The empirical formula is C2H4O1.
These two compounds, an alcohol and an ether, have the formula C₂H₆O but differ in this way.
(1) the same functional group and the same physical and chemical properties
(2) the same functional group and different physical and chemical properties
(3) different functional group and same physical and chemical properties
(4) different functional group and different physical and chemical properties
What are (4) different functional groups and different physical and chemical properties?
The molecular formula C₃H₄ represents this type of hydrocarbon with at least one triple bond.
What is an alkyne?
This reaction involves one atom replacing another in a hydrocarbon.
What is a substitution reaction?
Draw the structural formula for 2-butene.
Structural formula for 2-butene:
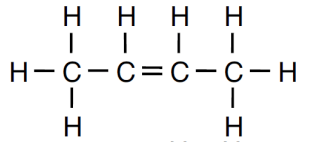
This element is present in ethyl ethanoate and makes it an organic compound.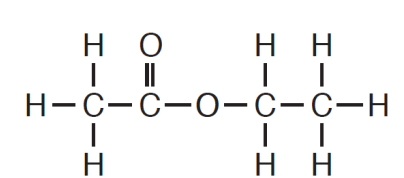
What is carbon?
Remember: Organic compounds ALWAYS contain carbon.
Butanal, butanone, and diethyl ether have different properties because they differ in this molecular characteristic.
(1) numbers of carbon atoms
(2) numbers of oxygen atoms
(3) types of functional groups
(4) types of radioactive isotopes
What are (3) types of functional groups?
This element can form ring, chain, and network structures, making it the backbone of organic chemistry.
What is carbon?
What type of reaction is represented by this equation?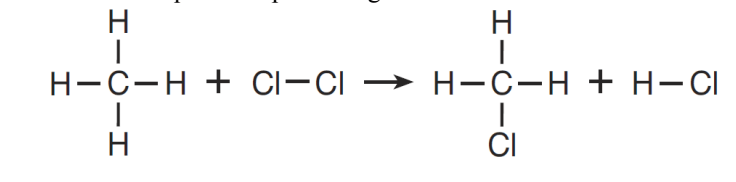
What is Substitution?
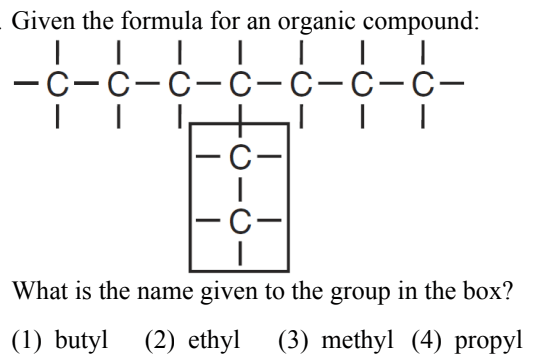
What is (2) ethyl
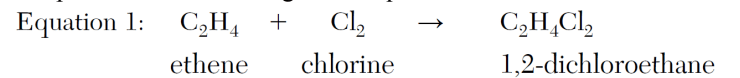
Identify the class of organic compounds to which the product of equation 1 belongs.
What is polymerization?
Polymerization: little things add up to become something greater!
This is the name given to the class of organic compounds to which ethyl ethanoate belongs.
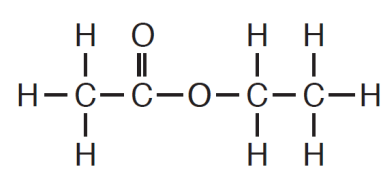
What is an ester?
These compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
What are isomers?

Explain, in terms of chemical bonds, why the hydrocarbon in Equation 1 is unsaturated.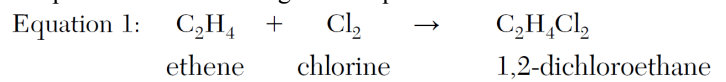
Ethene, C2H4, is an alkene. Alkenes have double bonds and are unsaturated.
This compound is an isomer of C2H5OC2H5.
(1) CH3COOH
(2) C2H5COOCH3
(3) C3H7COCH3
(4) C4H9OH
What is (4) C4H9OH.
Remember: Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures!
(Same amount, just looks different)
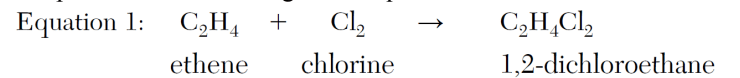
Draw a structural formula for the product of equation 1.
1,2- dichloroethane
