The size of a eukaryote compared to a prokaryote.
What is larger?
The cell membrane is mainly made of these molecules.
What are phospholipids?
It is the movement of molecules from areas of greater concentration to areas of lower concentration.
What is diffusion?
"8"
What is mitochondria?
The powerhouse of the cell that creates ATP for energy.
What is the mitochondrion?
The two things missing in prokaryotes.
What are a nucleus and organelles?
The hydrophobic part of a phospholipid.
What is the tail?
It is the diffusion of water through channel proteins embedded in the cell membrane.
What is osmosis?
"6"
What are the centrioles?
They contain digestive enzymes for breaking down and recycling cell contents.
What are lysosomes?
The biggest limiting factor of cell size.
What is surface area?
Most of the specific functions of a cell membrane are carried out by them.
What are proteins?
The name for the difference between the high and low concentrations.
What is concentration gradient?
"4"
What is the cytoskeleton?
Proteins in cells are removed and recycled by them.
What are proteasomes?
The liquid present throughout the cell.
What is cytoplasm (cytosol)?
These will respond to specific chemical signals.
What are receptor proteins?
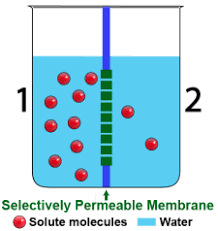
The direction water will travel through the membrane.
What is to the left?
"7"
What is smooth ER?
The two forms of DNA.
What are chromatin and chromosomes?
Cells were first observed by this person.
Who is Hooke?
The part of the cell membrane that will determine blood type.
What are carbohydrates?
A solution where there is a greater concentration of water outside the cell.
What is hypotonic?
They are cylindrical structures made of cytoskeleton fibers (microtubules) that direct the movement of chromosomes during cell division.
What are centrioles?
They contain the green pigment chlorophyll needed to perform photosynthesis in plants.
What are chloroplasts?