According to cell theory, where do cells come from?
Previously existing cells
Identify this stage of the cell cycle.
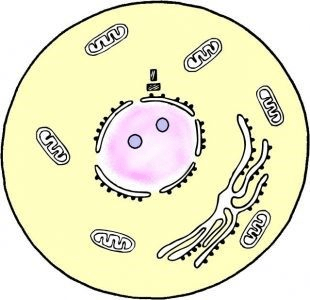
Interphase (a single nucleus is present)
Name the cell structure that joins two sister chromatids of a chromosome together.
Centromere
What is the difference between apoptosis and cancer?
Apoptosis is programmed cell death and cancer is the unregulated division of cells with damaged DNA.
What is the cell cycle? As a whole, what does it explain?
The cell cycle is the life cycle of a cell. It explains how cells make more cells.
What are the four phases of mitosis?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Fill in the blank:
The "rope" that is attached to the centromere of a chromosome is called the __________.
The "anchors" that move to opposite ends of the cell are called the __________.
Spindle Fiber
Centrioles
Cancer cells are formed when there is significant damage to a cell's DNA. Name two carcinogens (things that cause cancer).
Tobacco Products
Ultraviolet Radiation from the Sun
X-Rays
Asbestos
What is the cell cycle used for in single-celled organisms?
Asexual Reproduction
Explain what happens in a cell during anaphase.
Sister chromatids are being separated.
Name a cell structure besides DNA that is present through the entire cell cycle.
Plasma Membrane
Centrioles
How is the cancer cell cycle different from the normal cell cycle (how are cancer cells different from normal cells)?
Cancer cells have significant damage to their DNA and they go through rapid, unregulated cell division.
Why is it important that DNA is duplicated during interphase of the cell cycle?
The cell needs to create two copies of DNA to create two new cells.
Draw the different stages of mitosis.
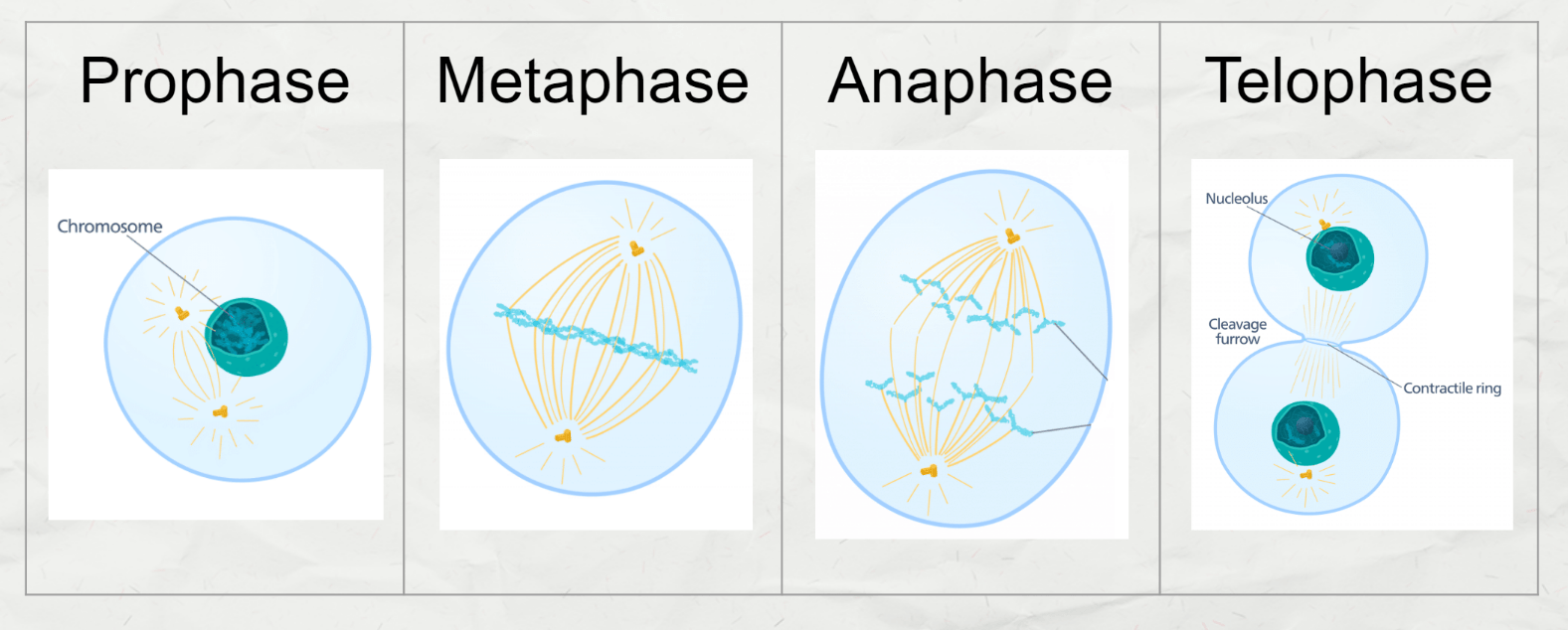
The DNA of a cell changes into different forms throughout the cell cycle. Name these forms of DNA in an order that reflects the cell cycle.
Chromatin turns into chromosomes in prophase. chromosomes turn into sister chromatids in anaphase. Sister chromatids turn back into chromatin during telophase.
How are cancer cells harmful to living things?
Cancer cells have no function and divide rapidly. Cancer cells reduce or remove the function of whatever tissue (body part) they are attached to which eventually kills the living thing.
Explain how multicellular living things use the cell cycle to grow and heal itself.
Multicellular living things use the cell cycle to grow by creating more cells to add to their body. They use the cell cycle to heal by creating replacement cells for any damaged cells.
Create a detailed diagram of the entire cell cycle. Identify the three main parts of the cell cycle and list what happens in each of these stages.
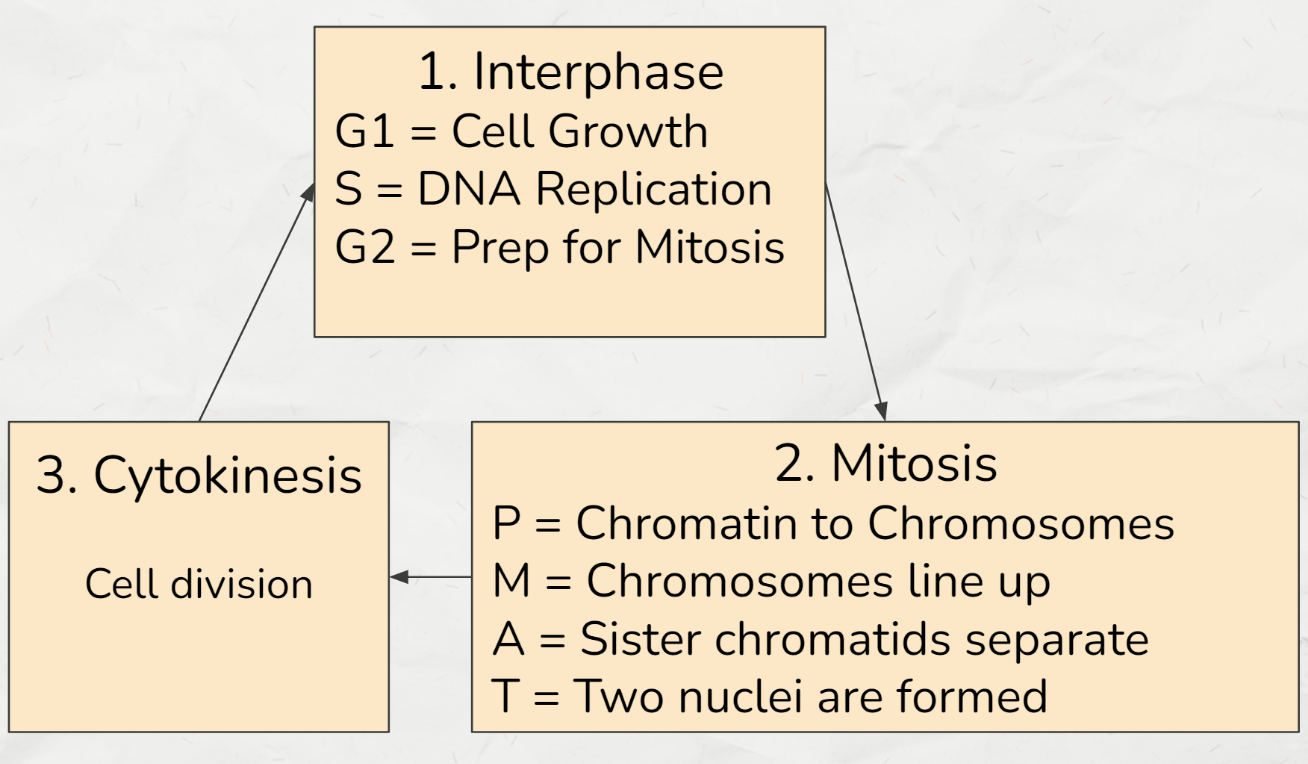
Label the given image.
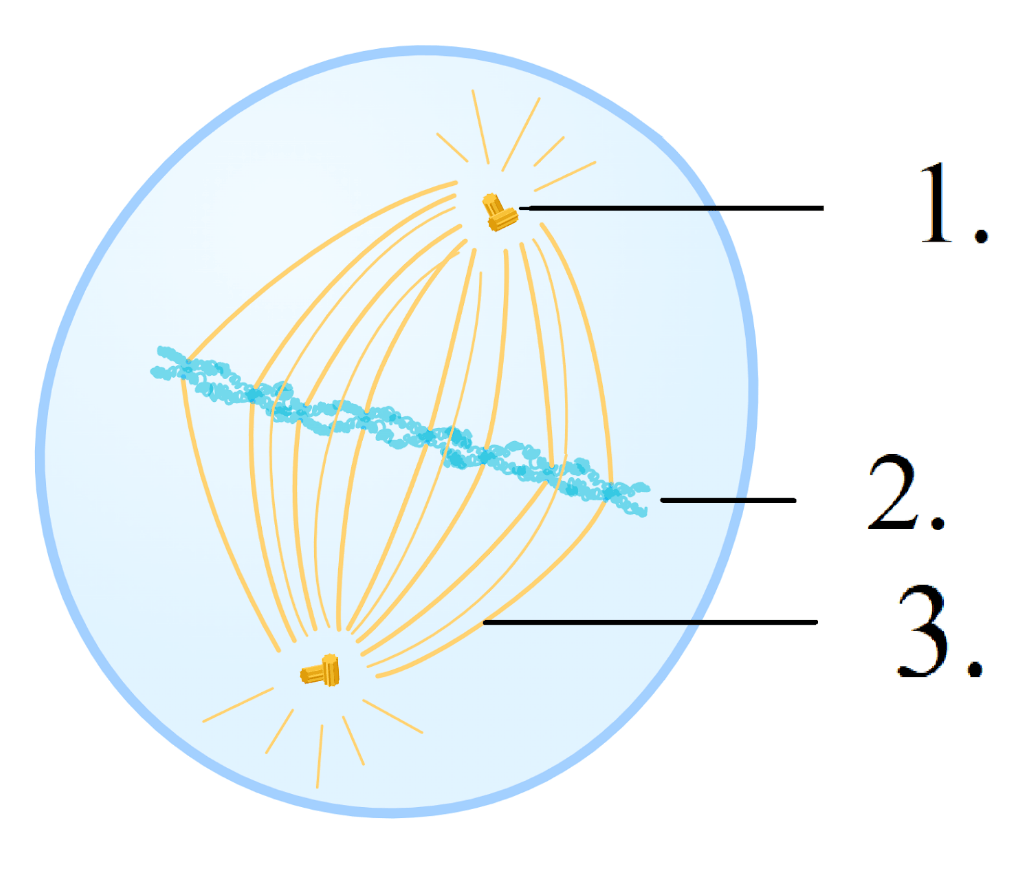
1. Centriole
2. Chromosomes
3. Spindle Fiber
Explain how the following terms link together, the cell cycle, cyclins, apoptosis, and cancer (Hint: what would happen if cells did not have cyclins or go through apoptosis when needed).
The cell cycle is the process of how cells create more cells. Cyclins regulate the cell cycle by ensuring that the DNA of cells is good enough for cell division. If there is significant damage to DNA, cyclins make the cell go through apoptosis. This process prevents the creation of cancer cells.