What are the functions of the cell membrane?
1) organization
2) Transportation of substances into/out of cell
What is the name of the scientist that discovered cells in oak bark/cork?
Robert Hooke
What is the name of transport that requires no energy?
Passive Transport
Example?
What membrane-bound organelles contain digestive enzymes? (and have a lower pH!)
Lysosomes!
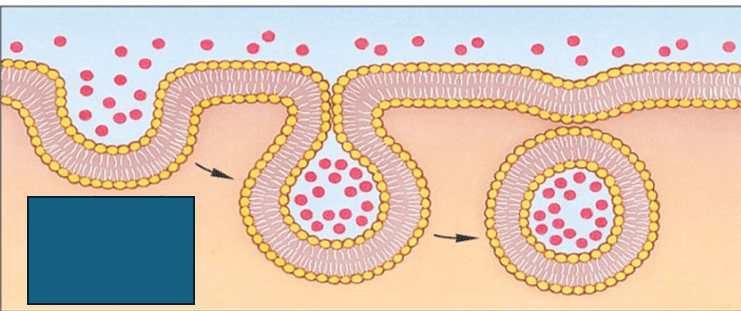 What is this a picture of?
What is this a picture of?
Endocytosis- the process of a cell bringing something IN through the membrane.
What is the name of structure A? 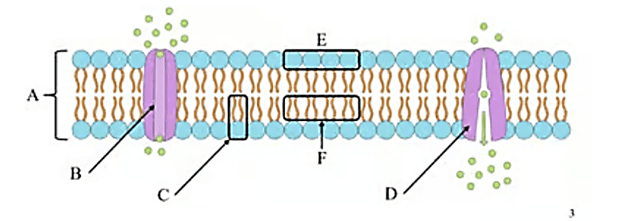
Phospholipid bilayer
What is the name of the jelly-like fluid inside the cell that contains the organelles?
Cytoplasm
What substances easily cross the cell membrane?
Water, oxygen, carbon dioxide
What type of transport requires energy?
Active Transport
What organelle acts as a supportive network inside the cell?
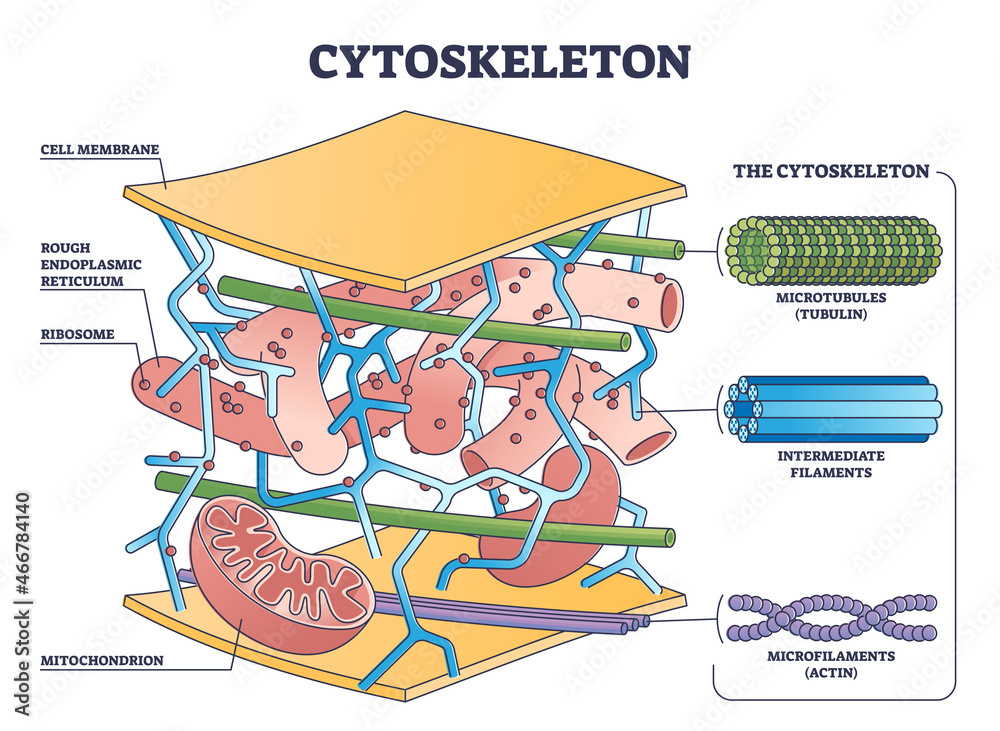 Cytoskeleton!
Cytoskeleton!
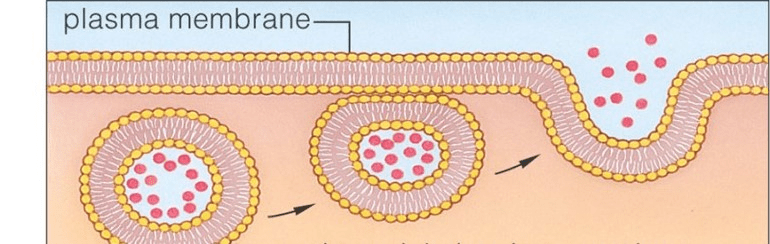 What is this a picture of?
What is this a picture of?
Exocytosis- the cell removing waste!
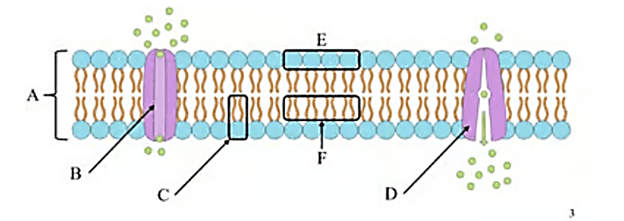 What is the name of Structure B?
What is the name of Structure B?
Channel Protein
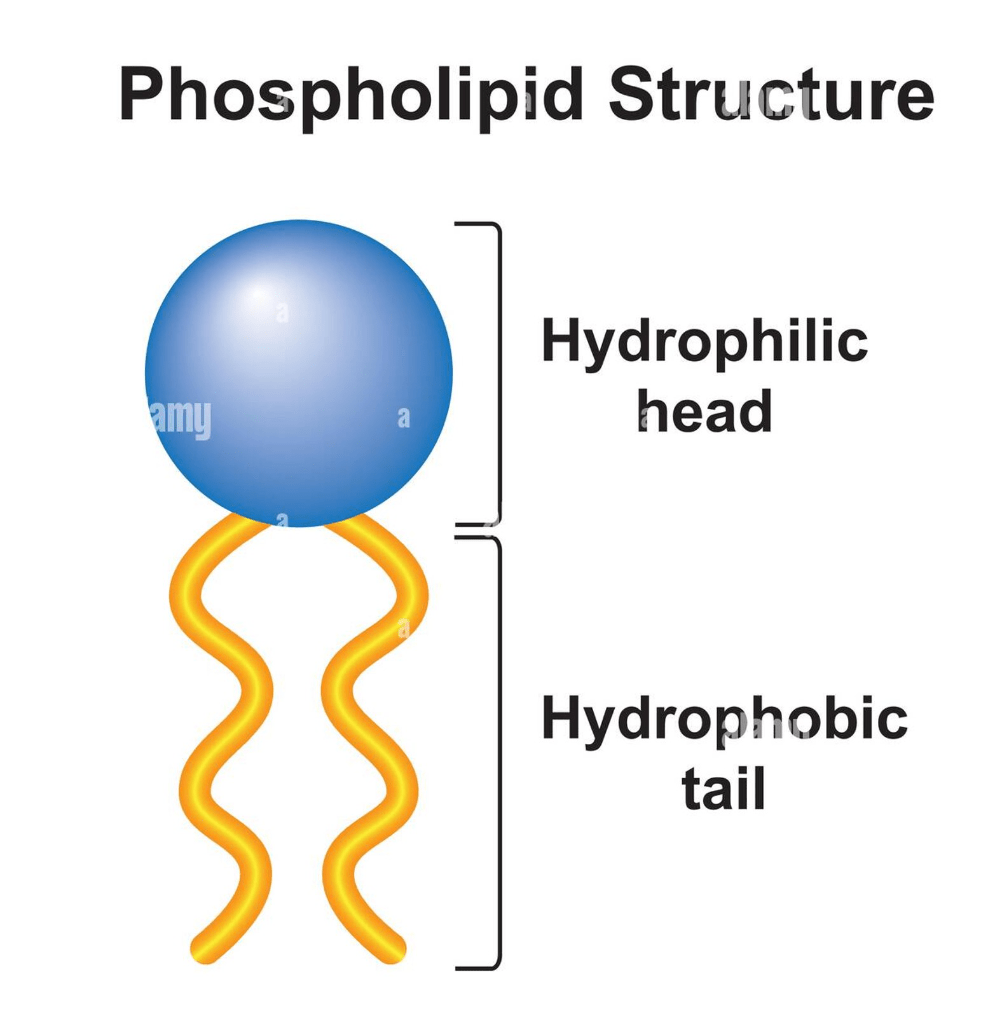
What part of the phospholipid is hydrophilic?
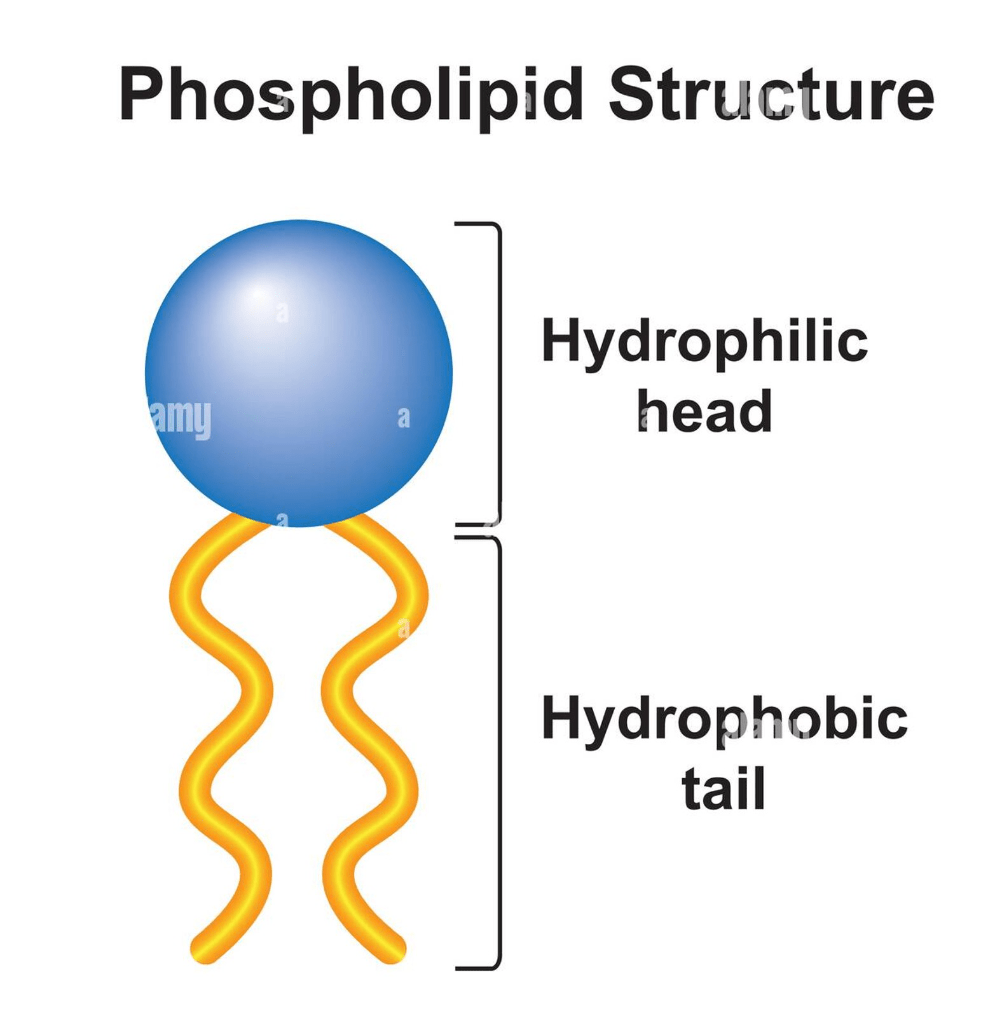 The head
The head
What is the movement of particles from high to low concentration called?
Diffusion
What is an example of active transport?
Carrier proteins!
What is the function of the mitochondria?
converts food to energy for our cells!
 Is the following an example, is water moving IN or OUT of the cell?
Is the following an example, is water moving IN or OUT of the cell?
IN
What is the name of structure C? 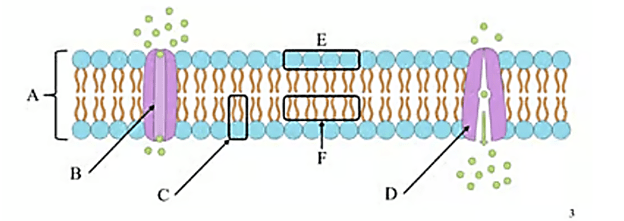
Phospholipid
What is the scientific name for the two-layered cell membrane?
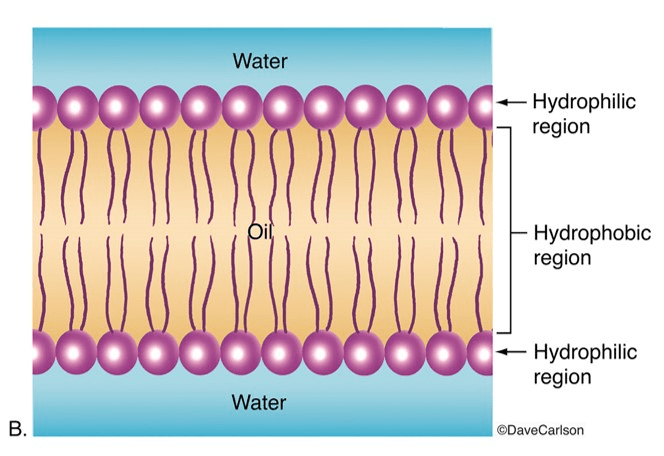 Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipid bilayer
The movement of WATER through a semipermeable membrane is called...
Osmosis
What is an example of passive transport?
diffusion, osmosis, channel proteins
What is the function of the rough/smooth Endoplasmic reticulum?
Rough = makes protein
Smooth = makes lipids
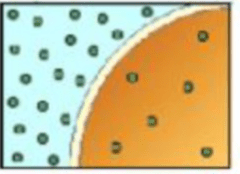 In this example, is water moving IN or OUT of the cell?
In this example, is water moving IN or OUT of the cell?
OUT
What is the name of structure D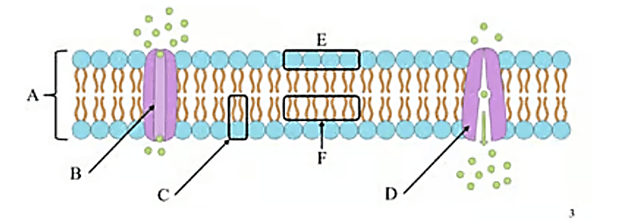 ? Is it hydrophobic, or hydrophilic?
? Is it hydrophobic, or hydrophilic?
Active Transport Protein
What type of membrane allows some substances to cross, but not others?
A selectively permeable membrane
In the context of solutes moving in/out of cells, does water want to move where there is a (higher/lower) concentration of solutes?
Water wants to move where there is a HIGHER concentration of solutes
What type of energy is required for active transport?
ATP!
What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Converts sunlight to energy!
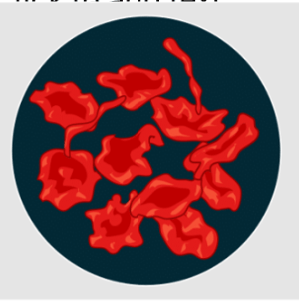 Are these cells hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic?
Are these cells hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic?
Hypertonic
What is the name of structure E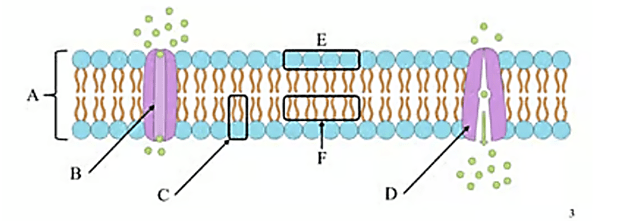 ? Is it hydrophobic, or hydrophilic?
? Is it hydrophobic, or hydrophilic?
Phospholipid head, (hydrophilic)
Draw a phospholipid, and label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic region
What are 3 cell structures that are found in PLANT cells, but not animal/human cells?
Chloroplasts, central vacuole, cell wall
The plasma membrane contains channels that help move materials from one side to the
other. What are these channels made of?
 Proteins!!
Proteins!!
What organelle is the "UPS" System of the cell, and finishes the formation and packaging of cellular products?
Golgi Body (Apparatus)
What is the name of this Hippo? 
Moo Deng
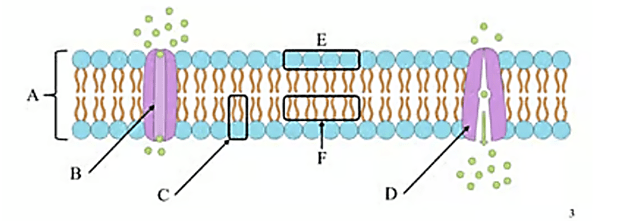
What is the name of structure F? Is it hydrophobic, or hydrophilic?
Lipid tails (hydrophobic)