A change in the physical properties of a substance.
What is a physical change?
The major component (higher concentration) in a homogeneous (evenly mixed) solution.
What is the solvent?
write the electron configuration for Ca
5 electron groups: 4 bonding 1 lone pair (include bond angle)
eg:Trigonal bipyramidal
mg: Seesaw <120, <90
phosphate
PO43-
when a chemical substance is transformed into one or more different substances
what is a chemical change?
The minor component in a homogeneous solution.
what is the solute?
express 254,998 m in Km, Mm, and mm.
Km- 254.998 Km
Mm-2.54998 x10-1 Mm
mm- 244998x103 mm
6 electron groups: 5 bonding,1 lone pair
eg; octahedral
mg: Square pyramidal, <90
sulfite
SO32-
The reactant that results in the least amount of product.
What is the limiting reactant?
The measure of a concentration of a solution.
what is molarity?
write the lewis structure for BBr3
and determine the central atom's eg and mg.

eg: trigonal planar
2 electron groups
linear, 180
Dihydrgen phosphate
H2PO4-
Anything that is left over after the reaction. (NOT limiting)
What is excess reactant?
One conducts electricity when dissolves in a solution, one does not.
what is the difference between an electrolyte and a non-electrolyte?
Complete and balence the reaction: CrB2(aq) + Na2CO3 (aq)
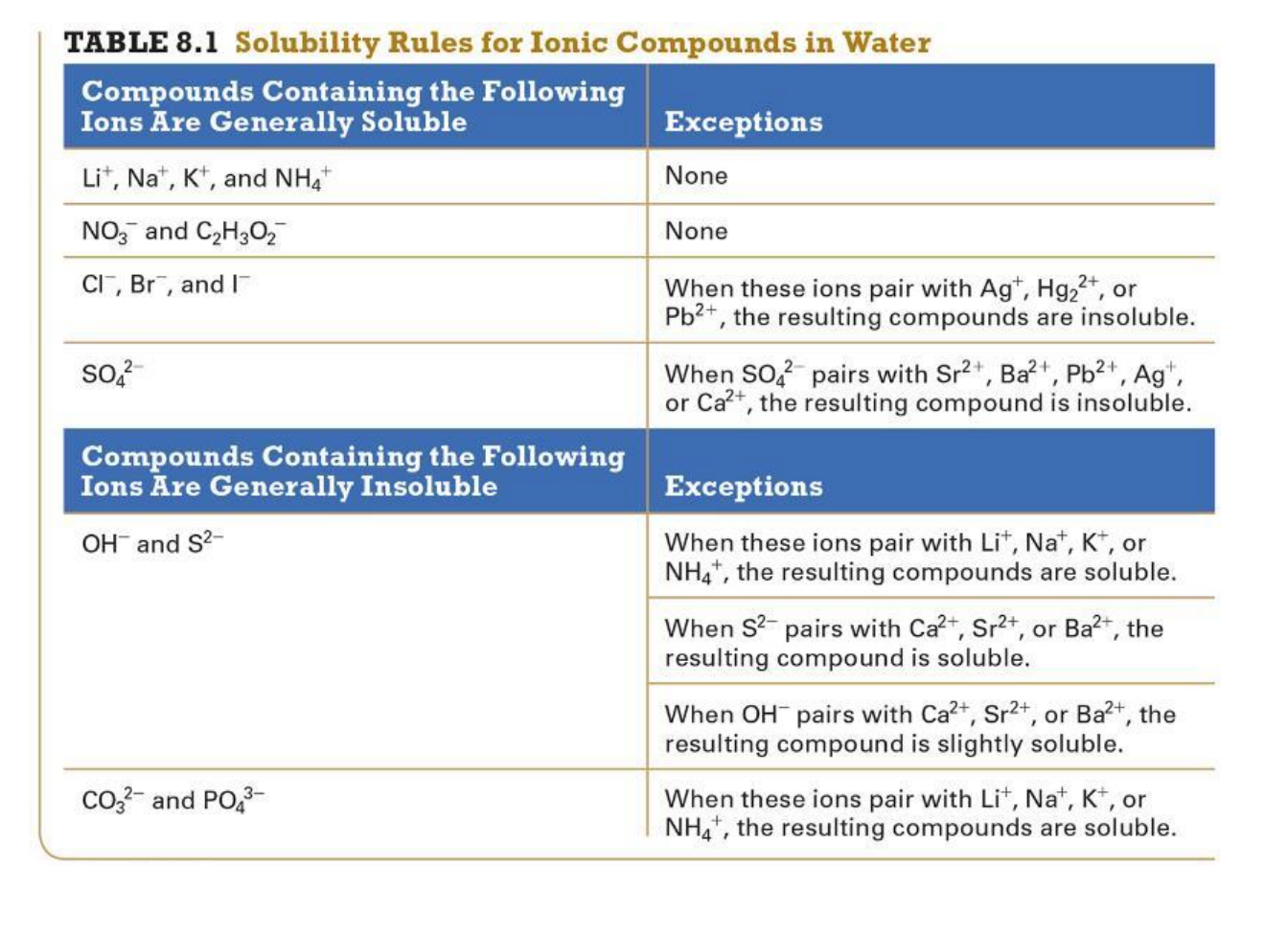
This table is on page 330.
CrB2(aq) + Na2CO3 (aq) ---> CrCO3 (s) + 2NaBr (aq)
4 electron gropus; 2 bonding 2 lone pairs
eg; tetrahedral
mg : bent
nitrite
NO2-
Amount of product that can be made based on limiting reactant.
What is a theoretical yield?
A solution in which a large fraction of the dissolved solute exists as ions
What is a strong electrolyte?
to what volume should you dilute 50.0 mL of a 12 M HNO3 solution to obtain a 0.100 M HNO3 solution?
6.0 L
3 electron groups; 1 lone pair 2 bonding
eg; trigonal planar
mg; trigonal pyramidal ,109.5
carbonate
CO32-