What is an IP Address? What is the purpose?
A number assigned to any item that is connected to the Internet. IP addresses provide a unique number for identifying devices that send and receive information on the Internet
What is paired programming? What are the two roles?
Paired Programming-a collaborative programming style in which two programmers switch between the roles of writing code and tracking or planning high level progress
Driver- Manipulates the keyboard and the mouse
Navigator- Keeps track of the big picture. Guides towards the goal.
What is the time elapsed between the transmission and the receipt of a request.
Latency
Defined as the website names that use words and letters to describe them
Domain names
What is a difference between Analog and Digital Data?
Analog Data= smooth data
Digital Data= Choppy copy
What is a Packet?
Small chunks of information that have been carefully formed from larger chunks of information. How information is sent over the internet. The internet traffic process in which information is broken into smaller packets that are sent along different routes, and reassembled at their destination
Which of the following best describes the protocols used on the Internet?
The protocols of the Internet are open and used by all devices connected to the network
Type of attack that consists of creating an email and/or websites that look exactly like a legitimate one to try to induce people to introduce sensitive information
Phishing attacks
What’s the function of the DNS (Domain Name Service)?
Translating the site name in text format to a numeric IP address
Which value is greater: 135 or 10000111?
135= 10000111
What is a computer network?
A computer network is any group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data.
Which of the following Internet protocols is used to request and send pages and files on the World Wide Web?
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
Which of the following is true of how the Internet has responded to the increasing number of devices now using the network?
Moore's Law- The protocols of the Internet were designed to SCALE as new devices are added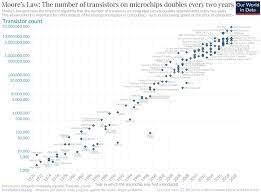
Which part of a domain name is the top-level domain (TLD)?
The far right side of the domain name
8 bits is enough to represent 256 different numbers. How many total bits do you need to represent 513 different numbers
10 bits
What is Fault Tolerance?
The Internet having a lot of redundancy and duplication built into it makes it have this trait
Your computer uses 4 bits to represent decimal numbers (0, 1, 2, 3 and so on) in binary. What is the SMALLEST number for which an overflow error occur?
16
What is a measure of bit rate - the amount of data (measured in bits) that can be sent in a fixed amount of time?
What is Bandwidth
What does URL stand for?
Uniform Resource Locator
What is the difference between lossy vs lossless compression?
Lossy: Compression that removes data that can’t be returned to its original format
Lossless: Compression that removes data that can be returned to its original format
How does HTTP represent a level of abstraction?
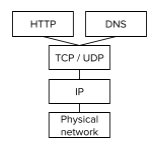 HTTP is built on top of TCP/IP and other layers of protocols. At this higher level, we do not need to know how the lower levels work exactly.
HTTP is built on top of TCP/IP and other layers of protocols. At this higher level, we do not need to know how the lower levels work exactly.
Which of the following is true of intellectual property?
Creative Commons enables content creators to freely distribute their otherwise copyrighted work.
What is difference between TCP and UDP?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)- quality
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)- speed
What’s the syntax of second-level domains?
In ASCII, the uppercase letter "G" is represented by the decimal (base 10) value 71. What would be the letter Q written in the decimal (base 10) value?
81= 01010001