A higher radius of curvature results in a more _______ bone
flatter /straighter 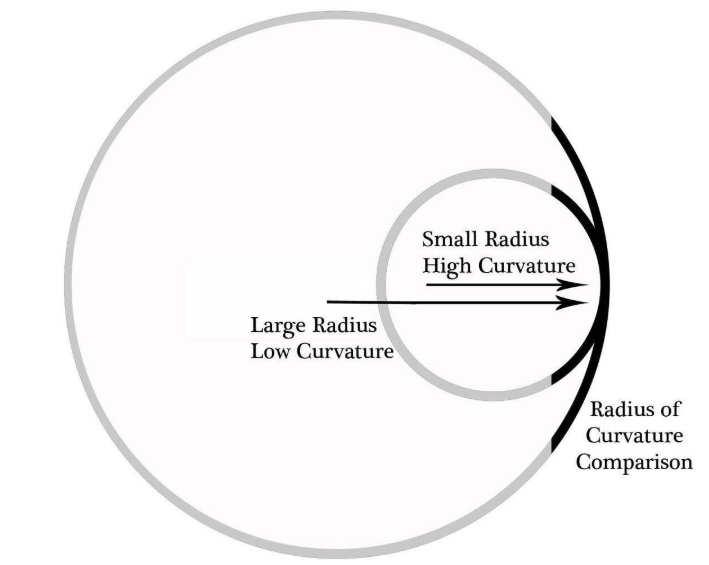
approved for use in single level ALIF and open tibial shaft fractures
rhBMP-2
consequence of a starting point which is too lateral given a specific nail design/geometry
Varus
Name 4 intra articular metaphyses
- proximal humerus
- proximal femur
- proximal radius
- distal fibula
(if osteomyelitis is seen in these areas by definition there is an associated septic joint)
AO/OTA classification system designation given to the femur
3
injury associated with this positive xray finding
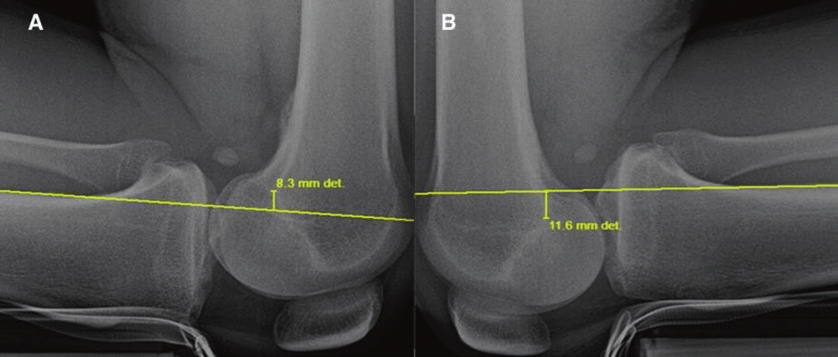
PCL injury
bending rigidity of a solid nail is equal to this proportion
what is radius to the 4th 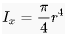
this metal frequently used in orthopedic implants has a modulus of elasticity that most closely approximates cortical bone
titanium
this technique used when reaming for a prophylactic nail decreases intramedullary pressures
Venting
most common level for vertebral artery to enter transverse foramen
C6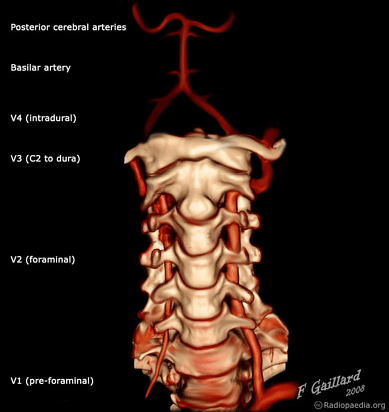
Age and weight in which you can consider rigid antegrade nailing compared to other methods for fixing pediatric/adolescent femur fractures
11-12yrs, >50kg (100lbs)
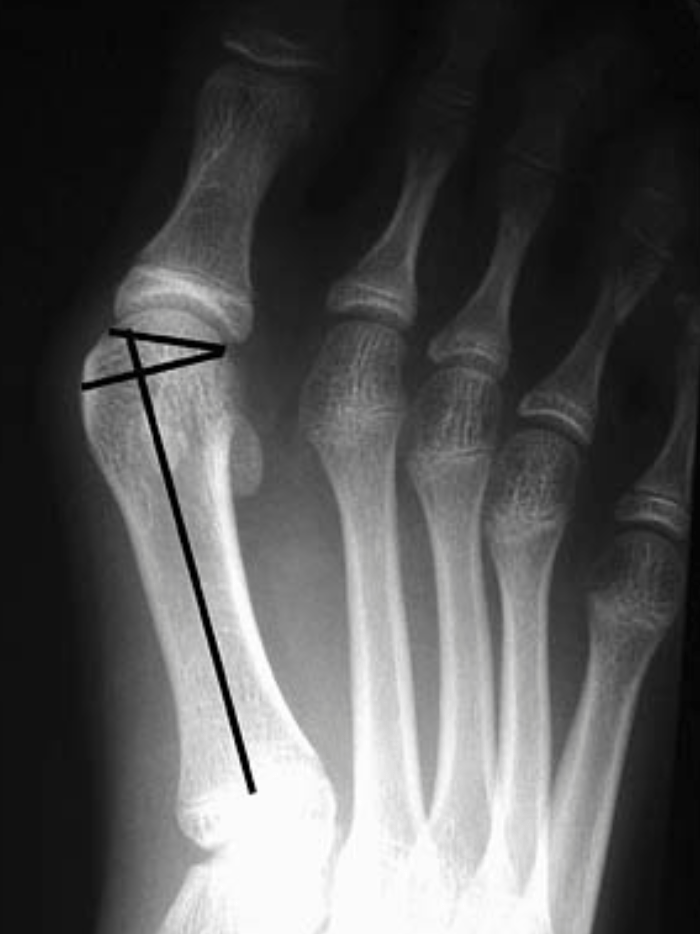
what is the distal metatarsal articular angle (DMAA)?
normal is <15 degrees
in the normal individual with spinopelvic harmony this is geometrically related to 2 additional radiographic parameters
PT + SS
galvanic corrosion
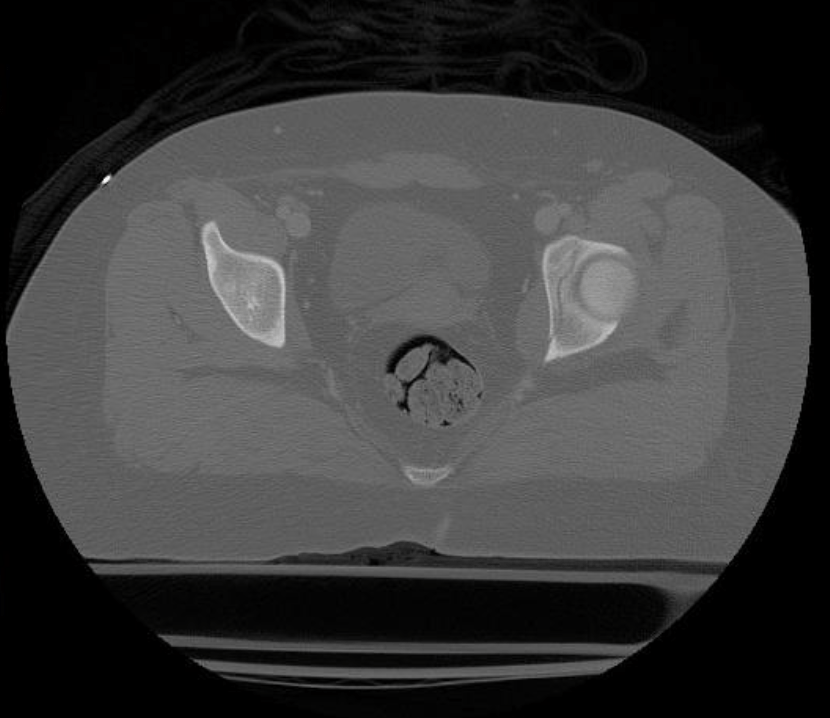
name the column and wall best evaluate in the R hip on this xray
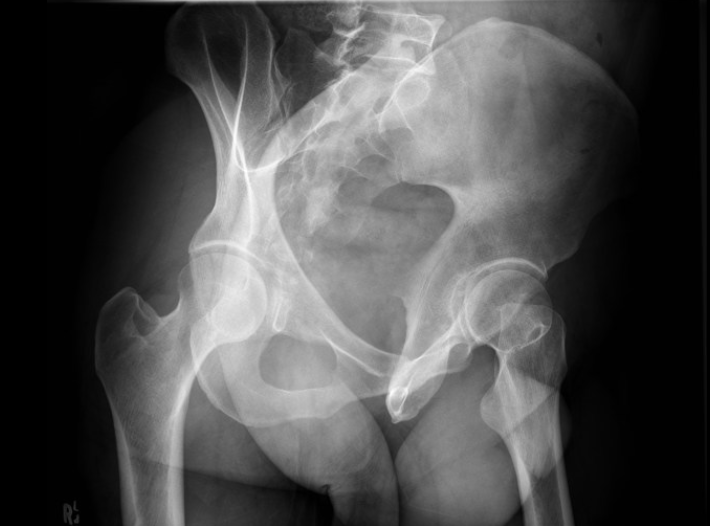
posterior wall
anterior column
vascular structure at risk with piriformis entry nail
medial femoral circumflex artery
Compared to their geriatric counterparts, young, high energy femoral shaft fractures with associated femoral neck fractures are more likely this orientation (include classification designation)
Vertical, Pauwels III
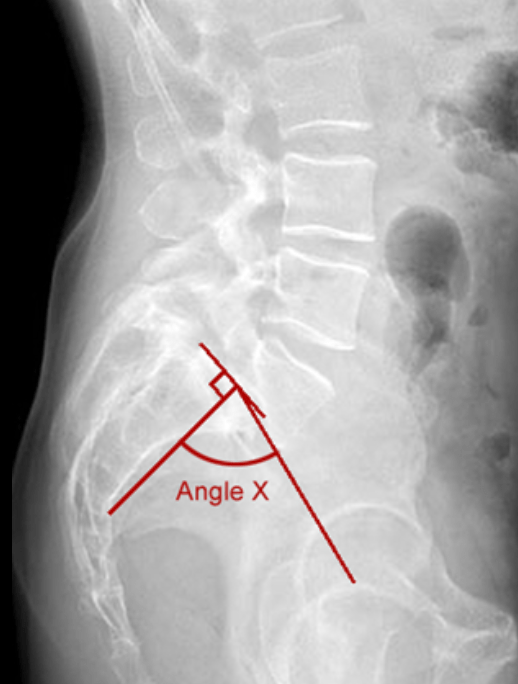
What is the Southwick slip angle?
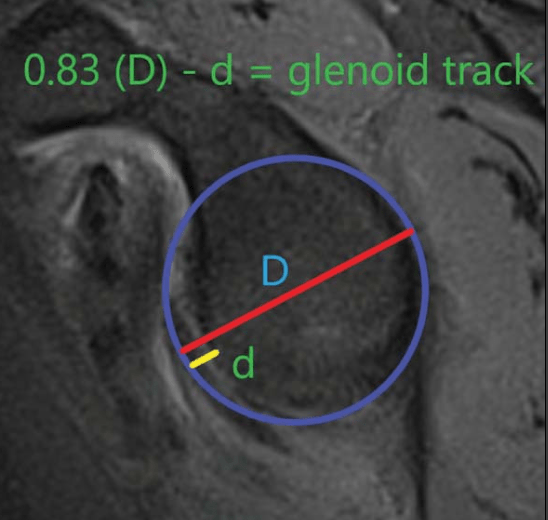
circle line method for calculating glenoid track
0.83D - d
in this stress over strain curve, the slope in the elastic zone
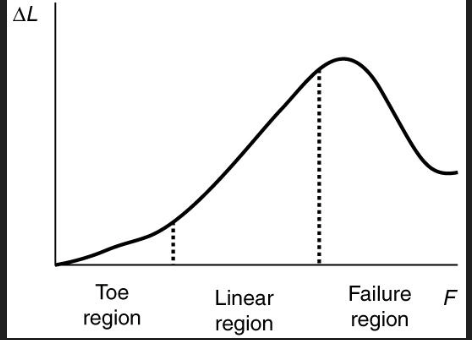
what is young's modulus of elasticity?
( measure of stiffness, higher measure = stiffer material)
% increase in metabolic cost for unilateral AKA vs control
44-47%
narrowest diameter thoracic and lumbar pedicles respectively
T4, L1
These are 3 main deforming forces in a subtrochanteric femur fracture with responsible offenders
Abduction/ER - gluteal muscles
Varus - abductors
Flexion - IP
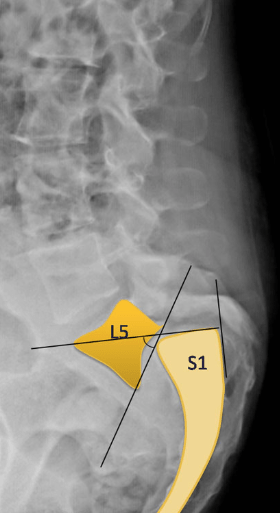
slip angle
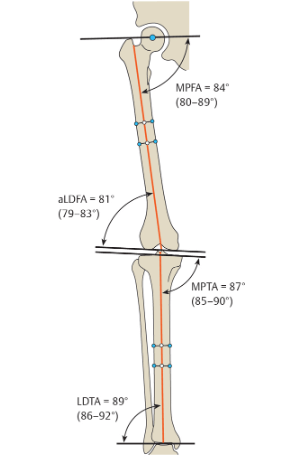
normal lateral distal tibial angle (aLDTA)
what is 89 degrees
mechanism of action of nitrogen containing bisphosnates
inhibiting farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS), an enzyme involved in the mevalonate pathway
DAILY DOUBLE
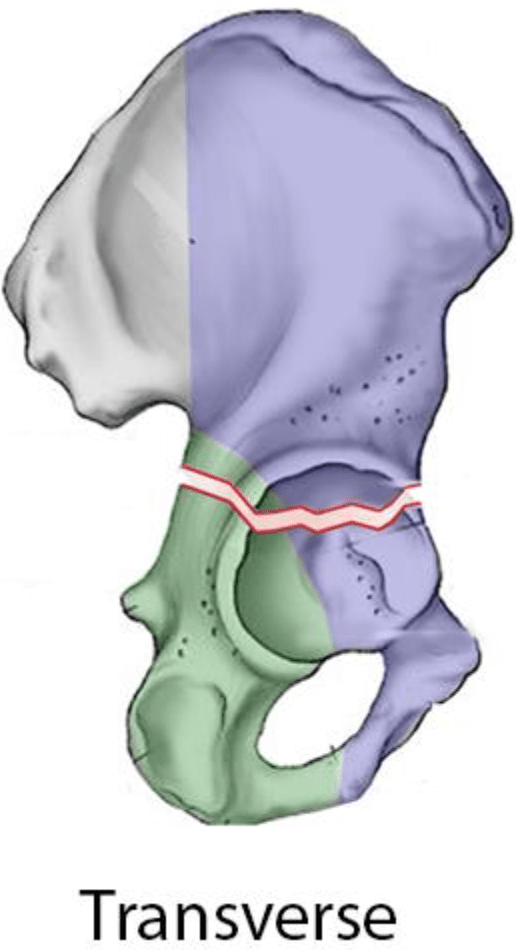
only elementary acetabular fracture pattern to involve both columns
transverse
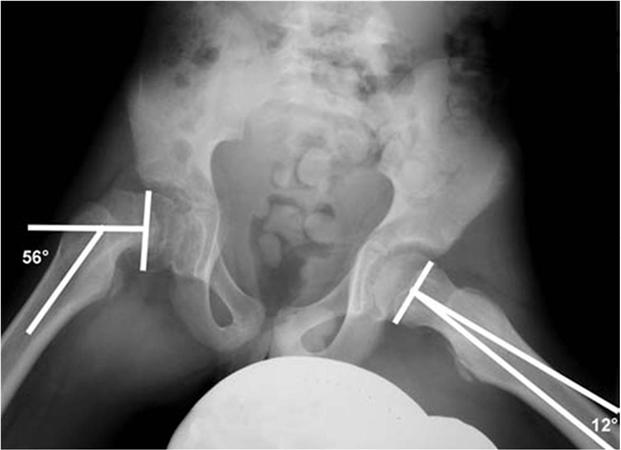
most accurate description of the angle B - angle A
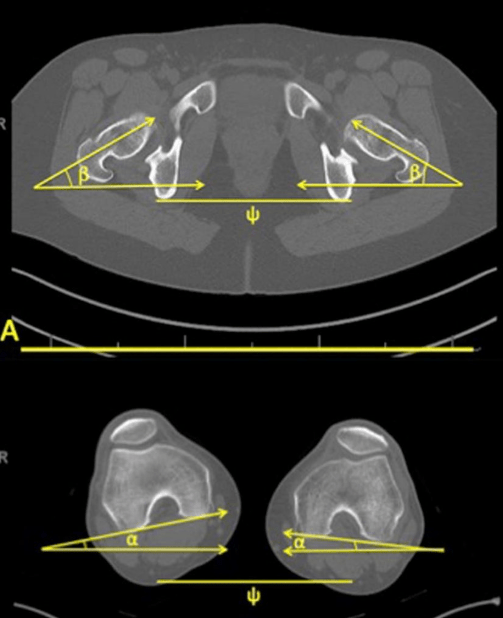
femoral ante torsion (femoral rotation)
femoral ante torsion = angle of femoral neck relative to posterior condylar axis
femoral ante version = angle of femoral neck relative to pelvic horizontal (interischial line)
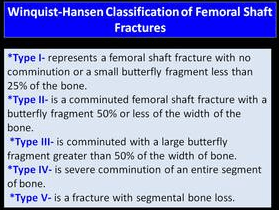
In the Windquist & Hansen classification of femoral shaft fracture, what separates Type II and Type III fracture patterns?
Amount of cortical contact
Type II <50%
Type III >50%
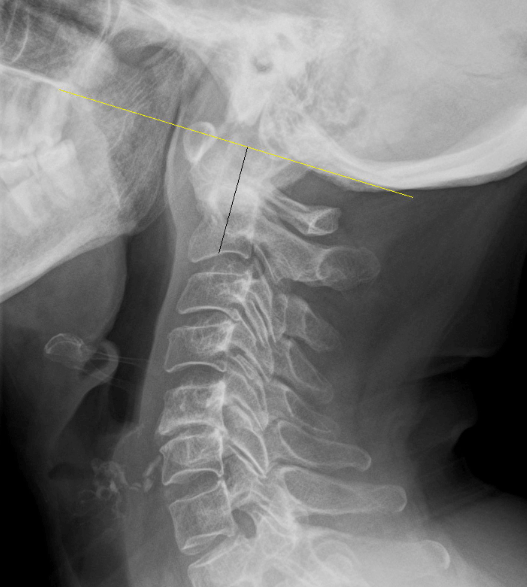
McGregor's Line
odontoid tip >4.5cm above indicates basilar invagination
name this specialized radiographic technique in imaging of the foot
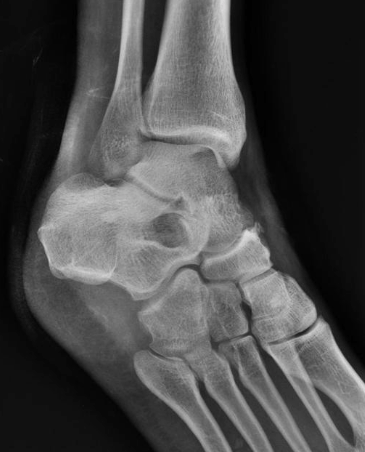
Broden's view