Muhammad was born in __________________
Mecca
Identify and fully define the five pillars of Islam
Profession of Faith (shahada). The belief that "There is no god but God, and Muhammad is the Messenger of God" is central to Islam.
Prayer (salat). Muslims pray facing Mecca five times a day: at dawn, noon, mid-afternoon, sunset, and after dark.
Alms (zakat). In accordance with Islamic law, Muslims donate a fixed portion of their income to community members in need.
Fasting (sawm). During the daylight hours of Ramadan, the ninth month of the Islamic calendar, all healthy adult Muslims are required to abstain from food and drink.
Pilgrimage (hajj). Every Muslim whose health and finances permit it must make at least one visit to the holy city of Mecca, in present-day Saudi Arabia.
Identify the first four caliphs.
Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman and Ali
Identify and explain some aspects in Islamic art and architecture.
All mosques have minarets which are used by muezzin who sing to call people to pray (known as the adhan). Most mosques make use of calligraphy, arabesques, and geometric patterns instead of images of people because that would be considered a form of idolatry.
Identify at least three different functions served by the House of Wisdom and where was it located.
In the early 800s, Caliph al-Ma'mun opened in Baghdad a combination library, academy, and translation center. There, scholars of different cultures and beliefs worked side by side translating texts from Greece, India, Persia and elsewhere into Arabic.
The hijrah refers to Muhammad's journey from ____________ to ___________ in 622 AD.
from Mecca to Yathrib (Medina).
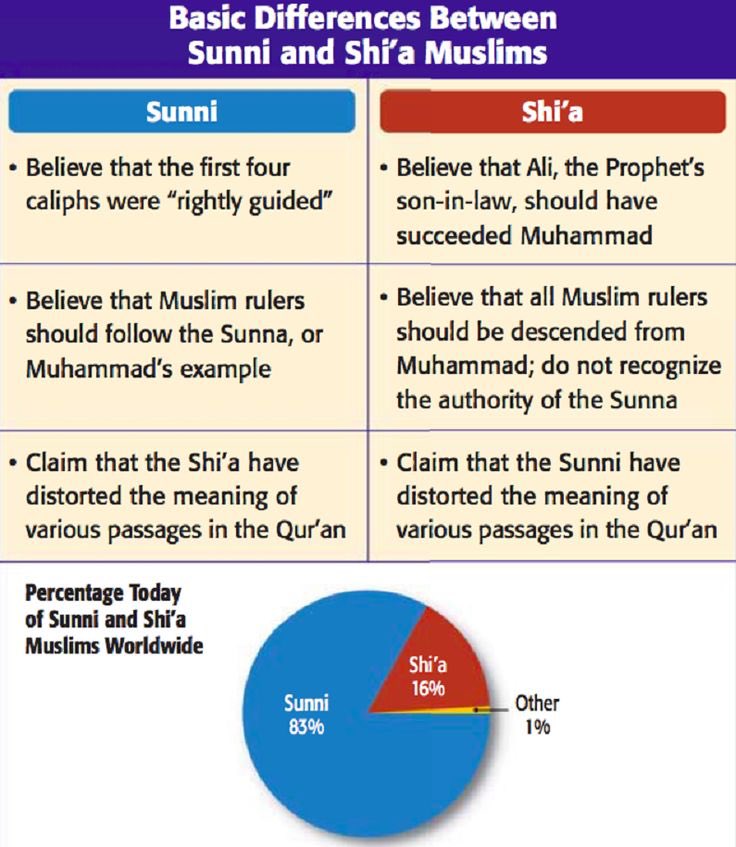
Identify some of the basic differences between the Sunni and Shia sects of Islam.
Identify a few policies of the Umayyad dynasty.
They established their capital at Damascus
Conquered North Africa, converted the Berbers to Islam, and invaded Spain (which they called Al-Andalus)
They established a great mosque at Cordoba
Identify and describe a few aspects of commerce in the medieval Islamic world.
Muslims traded with the rest of the world through the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean
They traded mainly: Sugar, Salt, Textiles, Spices, Slaves, Gold, and Horses
Instead of bringing physical currency on long business trips they used sakk (checks) which were redeemed at banks throughout the empire.
The astrolabe was a scientific instrument that determines your location in the middle of the sea so traders could go on long voyages.
Who was Al-Khwarizmi and what contributions did he make to scholarship in the medieval Islamic world?
Al-Khwarizmi, a mathematician born in Baghdad in the late 700s, studied Indian rather than Greek sources. He wrote a textbook in the 800s explaining "the art of bringing together unknowns to match a known quantity." He called this technique al-jabr - today called algebra.
The Umayyad Dynasty moved its capital to __________________ in the 7th century.
The Abbasid Dynasty established its capital at __________________,
Umayyad capital at Damascus; Abbasid capital at Baghdad.
Describe Sufism and identify a few Sufis.
Sufis like Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Rūmī and Rābiʿa al-ʿAdawiyya al-Qaysiyya pursued lives of poverty and devotion to a spiritual path. Sufi practice focuses on the renunciation of worldly things, purification of the soul and the mystical contemplation of God's nature. Followers try to get closer to God by seeking spiritual learning known as tariqa
Describe some aspects of the Abbasid government.
The Abbasids developed a strong bureaucracy to conduct the large empire’s affairs which included
A treasury kept track of the money flow
A special department managed the business of the army
Diplomats were sent to courts in Europe, Africa, and Asia to conduct imperial business
The Abbasids taxed land, imports and exports, and Non-Muslims’ wealth
The Vizier (The prime minister) advised the Caliph
Caliph sat behind a screen during gov't meetings to advise Vizier
Identify and describe the different levels of the social hierarchy in Islamic society.
Muslims
Anybody who is a muslim
could range from a king to a farmer
Converts
People who converted to Islam
“People of the book”
The Jewish people and Christians
They were respected, but lived in an Islamic Society
Slaves and Non-Muslims
Criminals
prisoners of war
Who was Ibn Sina (known as Avicenna) and what were his scholarly contributions?
Among the great sages of Islamic medicine, Ibn Sina is the best known in the West. Considered as the successor to Galen, his great medical treatise, the Canon was the standard textbook on medicine in the Arab world and Europe in the 17th century. It contained a thorough list of all known disorders alongside the best known treatments or cures at the time.
Muslims from North Africa, known as Berbers conquered __________________, and formed an extraordinary Muslim state called __________________. It was here in the tenth century, where the city of __________________ became a center of Muslim culture.
Spain; Al-Andalus; Cordoba
What is this and why did Muhammad feel it was important to Islam?

After creating a religious following in Yathrib (Medina), Muhammad led an invasion of Mecca to take over the Ka'aba because it was built by Abraham and the same god that spoke to Abraham was the god that spoke to Muhammad. The Arabs were defiling the Kaaba by putting their idols inside of it, so Muhammad wished to remove the idols and claim it for Islam.
Why did the Umayyad dynasty decline?
A failed revolt by Husayn (Ali's second son) inspired a second more successful revolt led by the Abbas family. The Abbasids then create their own dynasty.
How did Muslims treat conquered nonMuslims (namely Christians and Jews)?
Because the Qu'ran forbade forced conversion, Muslims allowed conquered peoples to follow their own religion. Christians and Jews, as "people of the book," received special consideration. They paid a poll tax each year in exchange for exemption from military duties. They entered into agreements called dhimma, that subjected to them to various restrictions.
Why was Ibn Rushd (also known as Averroes) heavily criticized by other Muslims?
In the 1100s, Averroes, who lived in Cordoba, was criticized for trying to blend Aristotle's views with those of Islam. He agreed with many of Aristotle's views, such as the belief that the world had no beginning, despite having a creator. However, Ibn Rushd argued that Greek philosophy and Islam had the same goal to find the truth.
The Dome of the Rock, located in __________________, is the earliest surviving Islamic monument built in 691, believed to be the spot where Muhammad ascended to heaven.
Jerusalem
What is this monument, where is it located, and what is its significance to Islam?
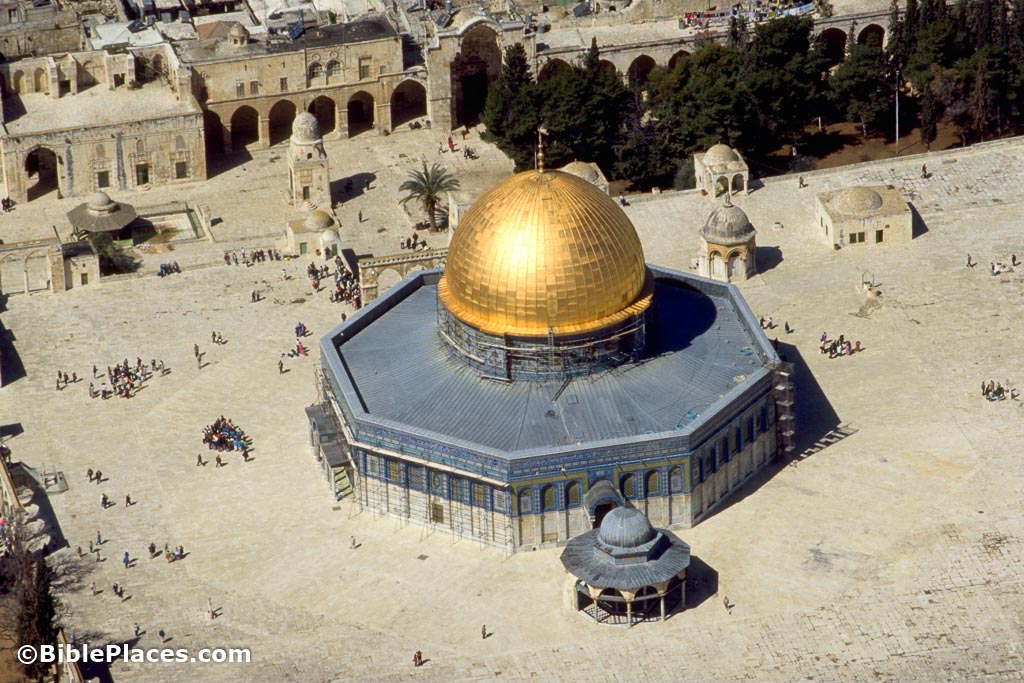

The Dome of the Rock mosque is the earliest Islamic monument built and it marks the spot in Jerusalem where supposedly Muhammad ascended to heaven and conversed with God in what has been called the "Night Journey."
Why did the Abbasid dynasty decline? What role did the Fatimids play in this decline?
Independent Muslim states sprang up, and local leaders dominated many smaller regions. The Fatimid caliphate was formed by Shi'a Muslims who claimed descent from Muhammad's daughter Fatima. The caliphate began in North Africa and spread across the Red Sea to western Arabia and Syria.
What was the status of women in Islamic society?
The shar'ia gave Muslim women specific legal rights concerning marriage, family, and property. Thus, Muslim women had more economic and property rights than European, Indian, and Chinese women of the same time period. Nonetheless, Muslim women were still expected to submit to men. The Qu'ran says, "Men are the managers of the affairs of women."
Who was Al-Zarahwi and what were his contributions to treating cataracts?
A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of the eye. The use of a couching tool to remove the cataract and let light into the pupil was a method created by Al-Zarahwi that bears close relation to modern methods today.