What is the primary difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation, while longitudinal waves oscillate parallel to it.
Describe the difference between a longitudinal wave with a large amplitude and one with a small amplitude.
In a longitudinal wave with a large amplitude, the compressions are more dense and the rarefactions are less dense. In a longitudinal wave with a small amplitude, the compressions are less dense than in high-amplitude waves, and the rarefactions are more dense.
The musical note A above middle C has a frequency of 440 Hz. If the wavelength is measured to be 0.80m, what is the speed of the wave?
350 m/s
The angle of _________ is equal to _____________.
You make a transverse wave by shaking the end of a long rope up and down. Explain how you would shake the end of the rope to make the wavelength shorter.
To make the wavelength shorter, you would increase the frequency of shakes
What happens when waves come into contact with a boat? Explain if the wave move the boat to a different position.
Waves carry energy without transferring matter from place to place. Waves may move the boat up and down and maybe even back and forth, but they do not change its location.
The _______ is the highest point on a transverse wave, and the ____ is the lowest point.
crest / trough
If 100 waves pass a given point in 4 seconds, what is the wave's frequency?
25 Hz
How is your brain fooled into seeing a broken straw?
The brain interprets the light waves that enter the eye as if they have traveled in a straight line, which can cause you to see the portion of the straw in the water as if it were in a different location.
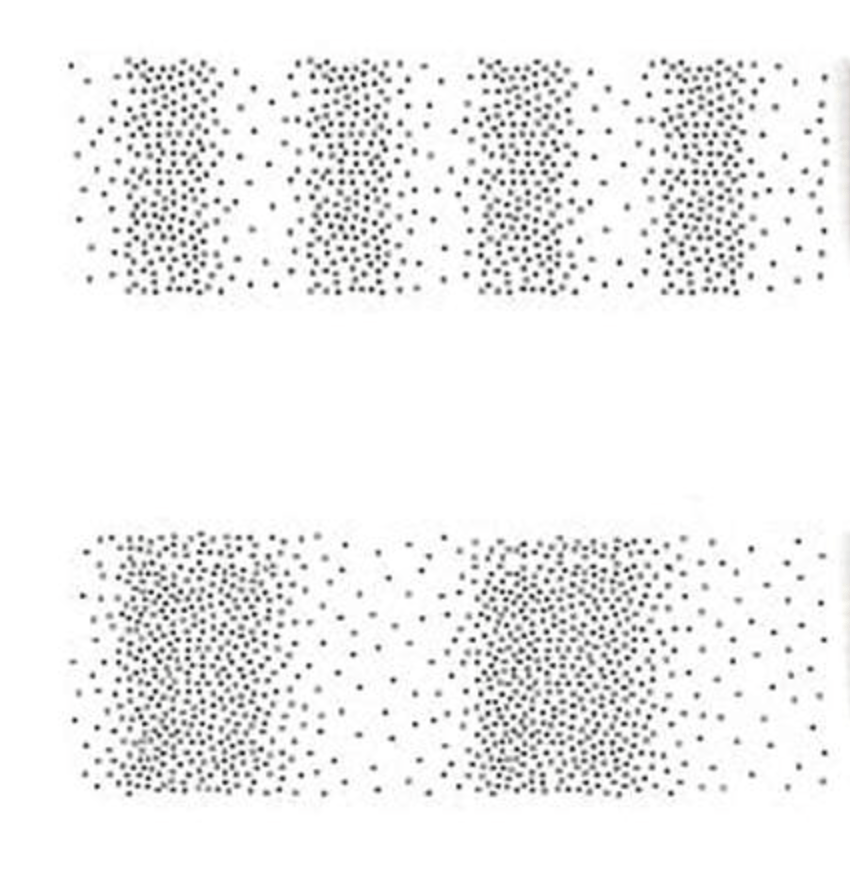
Which of the longitudinal waves has a higher frequency?
The first one
Contrast how you would move a spring to make a transverse wave with how you would move a spring to make a longitudinal wave.
You would move the spring forward and backward, creating compressions, to make a longitudinal wave. You would move the spring left and right, like a rope, to make a transverse wave.
In a longitudinal wave, a ____ is an area where the particles are spread apart and a ____ is an area where the particles are close together.
rarefaction / compression
Calculate the frequency of a water wave that has a wavelength of 0.5 m and a speed of 4 m/s.
8 Hz
How light would respond differently when striking an object that is not transparent than when striking an object that is transparent, such as a glass window.
Light that strikes an object that is not transparent would reflect. It would not also refract as it might when striking a transparent object.
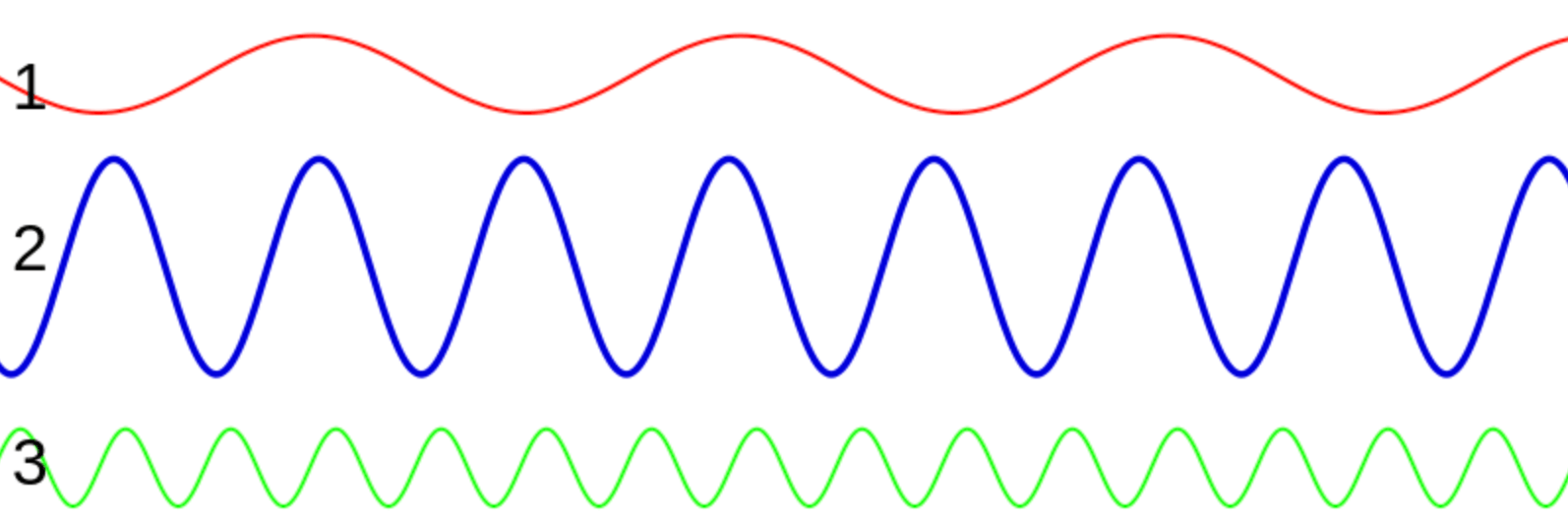
The mechanical wave with more energy is
Number 2
Examples of mechanical waves are: (list 3)
sound waves, earthquakes, coil spring.
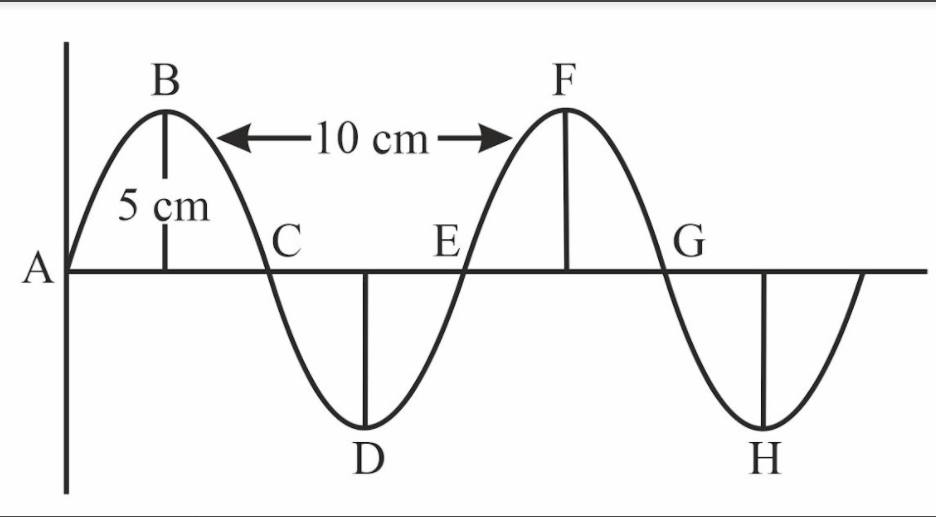
What is the wavelength in this image?
10 cm
An FM radio station broadcasts radio waves with a frequency of 96,000,000 Hz. What is the speed of these radio waves if they have a wavelength of 3.1 m?
300,000,000 m/s
Describe What are two situations in which a wave will diffract?
A wave diffracts when it passes around an object or through a narrow opening.
Which waves can carry matter?
None, waves carry energy
Identify a mechanical wave that is also a longitudinal wave.
Sound
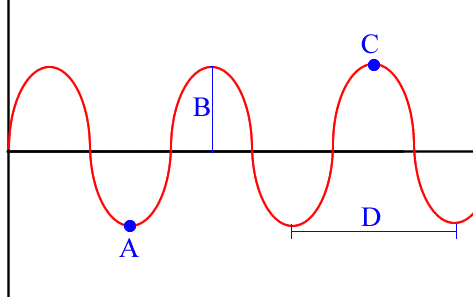
On this wave diagram, what is A?
Trough
An ocean wave travels a distance of 300 meters in 25 seconds. Calculate the speed of the wave.
12 m/s
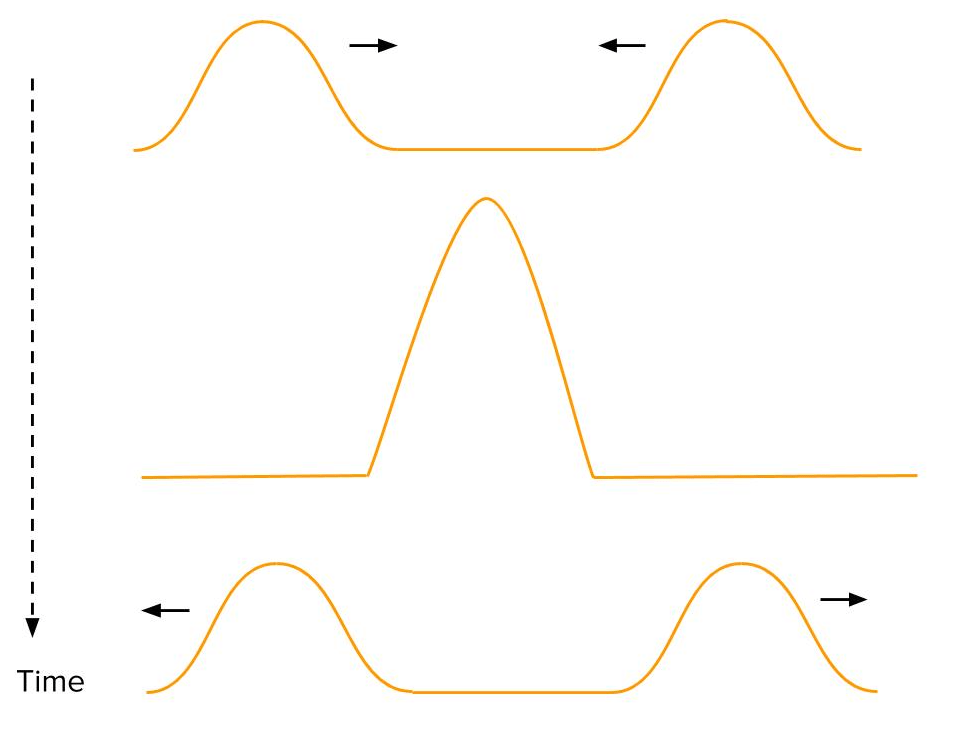
The two waves will undergo _________________ when they meet.
Constructive interference
Do all waves need a medium to travel?
Not all, electromagnetic waves can travel in a vacuum