There are ____ pairs of cranial nerves that emerge from the brain. Most are mixed, some are sensory.
12 pairs.
What is the Cauda Equina?
The lumbar and sacral spinal nerves that hang below the end of the spinal cord, before they exit from the vertebral canal.
What are the 2 division of the autonomic nervous system? What is the function/purpose of each?
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Sympathetic division dominates during stressful situations; responses prepare body to meet physical demands. Fight or Flight
Parasympathetic division dominates in relaxed situations to permit normal functioning.
These help form the blood-brain barrier.
Astrocytes
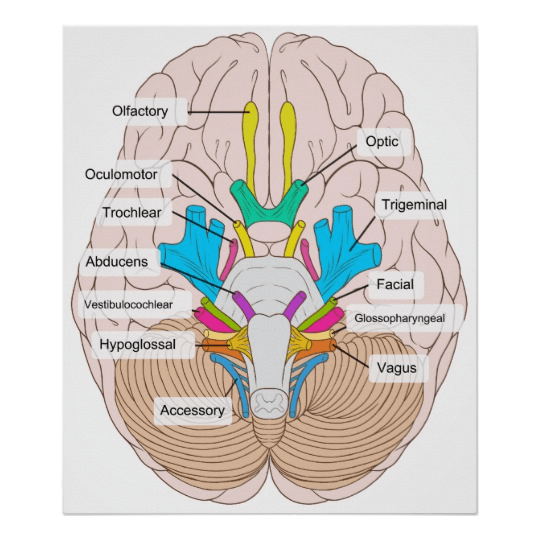
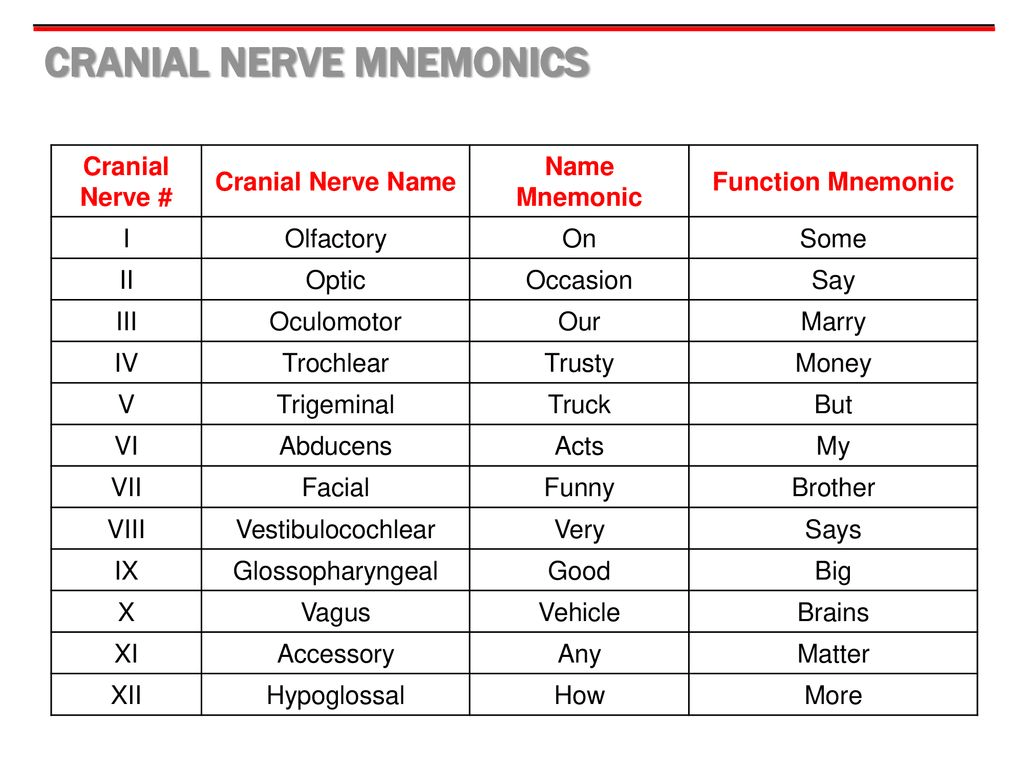
Name the 12 cranial nerves.
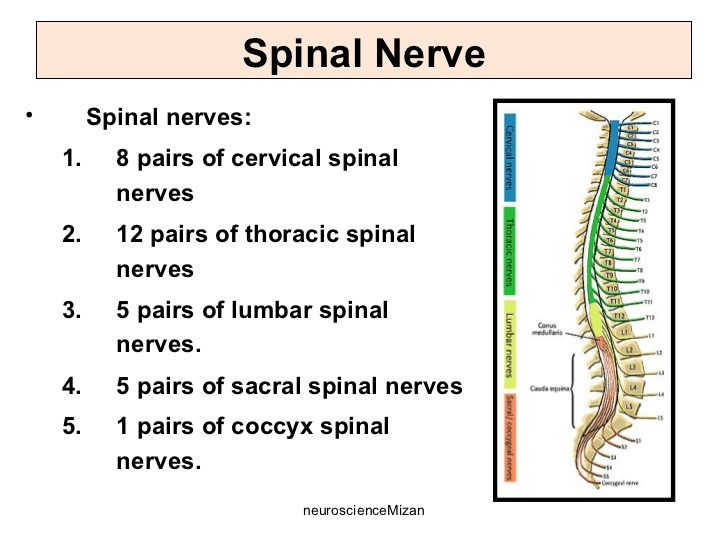
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31
An ANS pathway has how many neurons that synapse in a ganglion?
Preganglionic neurons- From the ____ to the ____
Postganglionic neurons- From the ___ to the ____
2
CNS to the Ganglia
Ganglia to the effectors
This regulates body temperature and appetite.
This is the 'matter' on the surface of the spinal cord..
Hypothalamus
Pia Matter
Name the function of cranial nerves 1-3.
Olfactory-
Optic-
Oculomotor-
Olfactory- sense of smell
Optic- sense of sight
Oculomotor-movement of the eyeball, constriction of pupil in bright light or for near vision.
Review the steps of the Reflex arc- the pathway of impulses.
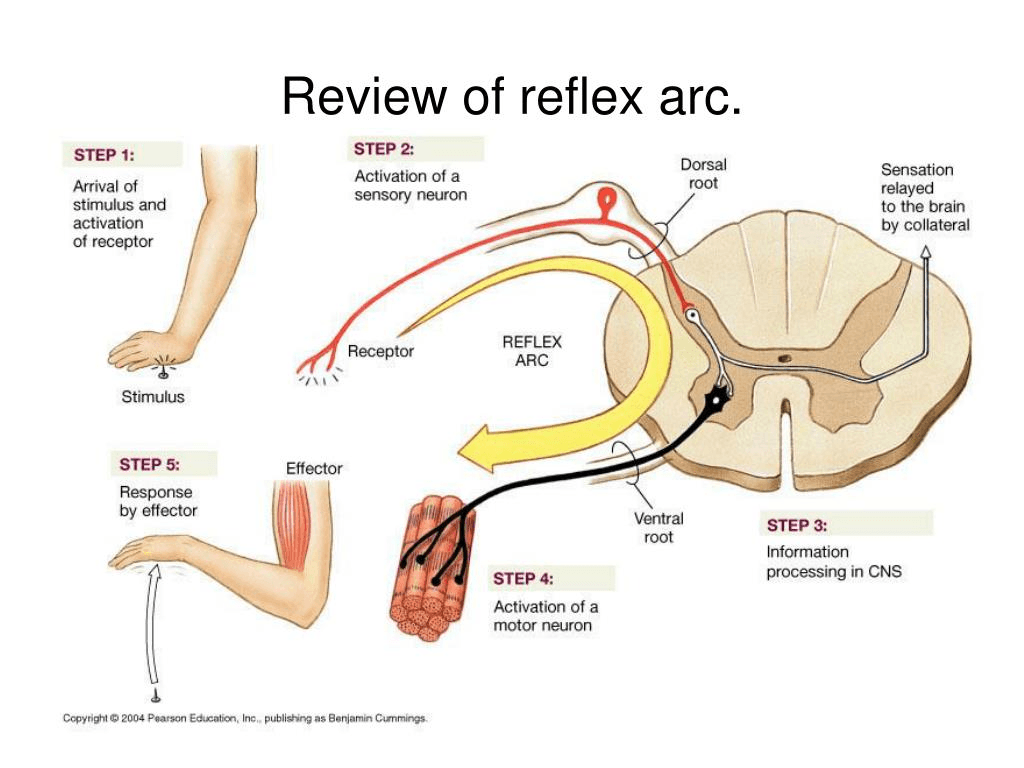
Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter released by all preganglionic neurons- both sympathetic and parasympathetic. It is inactivated by what?
What neurotransmitter is released by most sympathetic postganglionic neurons at the synapses with the effector cells?
Cholinesterase in postganglionic neurons.
Norepinephrine
Which nerves ( contributed to by C3-C5) supply the diaphragm?
These lobes initiate voluntary movement...
Phrenic Nerves
Frontal Lobes
Name the function of cranial nerves 4-7.
Trochlear-
Trigeminal-
Abducens-
Facial-
Trochlear- movement of eyeball
trigeminal-sensation of the face, scalp, teeth. contraction of chewing muscles.
abducens-movement of the eyeball
facial-sense of taste, contraction of facial muscles; secretion of saliva.
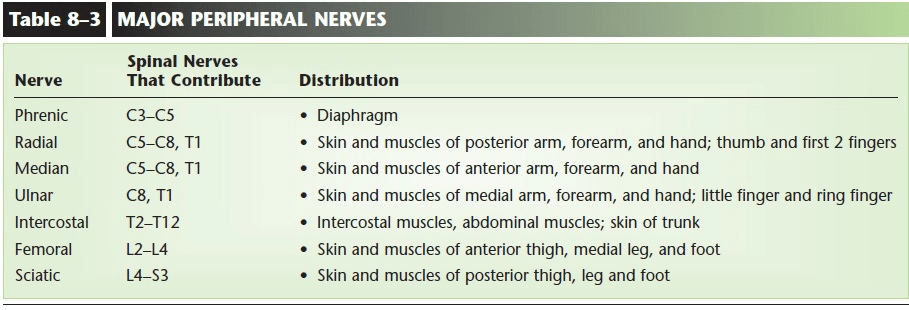
Name a few of the major nerves, the spinal nerves that contribute to those, and the distribution of them.
Example:
Sciatic Nerve- L4-S3- skin and muscles of posterior thigh, leg and foot.
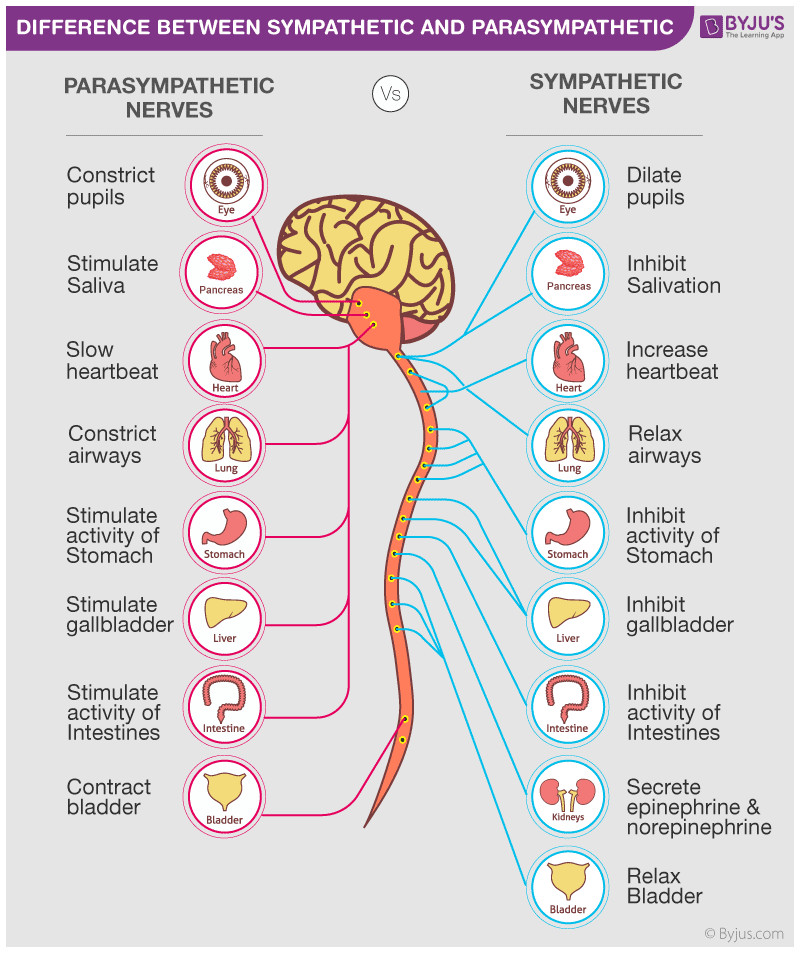
Compare the actions of the parasympathetic nerves and sympathetic nerves. Think Sympathetic is fight or flight- so which systems would be more important? What might happen to the heart with a Sympathetic reaction? Then what happens when the parasympathetic nerves take back over?
Which part of the brain regulates breathing and heart rate?
Which cranial nerves carry impulses to the intestines?
Medulla
Vagus nerves
Function of cranial nerves 8-12
Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear)-
Glossopharyngeal-
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal-
Acoustic- Sense of hearing; sense of equilibrium
Glossopharyngeal- Sense of taste, sensory for cardiac, respiratory, and blood pressure reflexes; contraction of the pharynx; secretion of saliva
Vagus- Sensory in cardiac, respiratory, and blood pressure reflexes; sensory and motor to larynx (speaking); decreases heart rate; contraction of alimentary tube (peristalsis); increases digestive secretions.
Accessory- contraction of neck and shoulder muscles, motor to larynx (speaking)
Hypoglossal- movement of the tongue
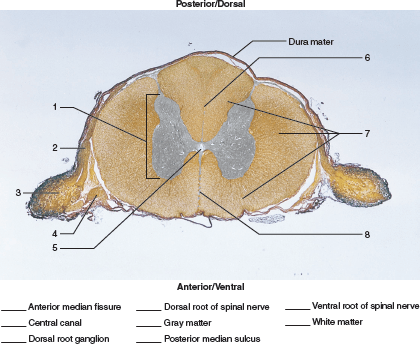
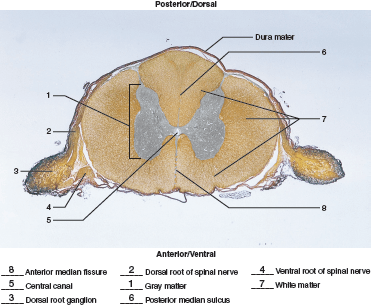
Let's review a cross section of the spinal cord. Name the parts.
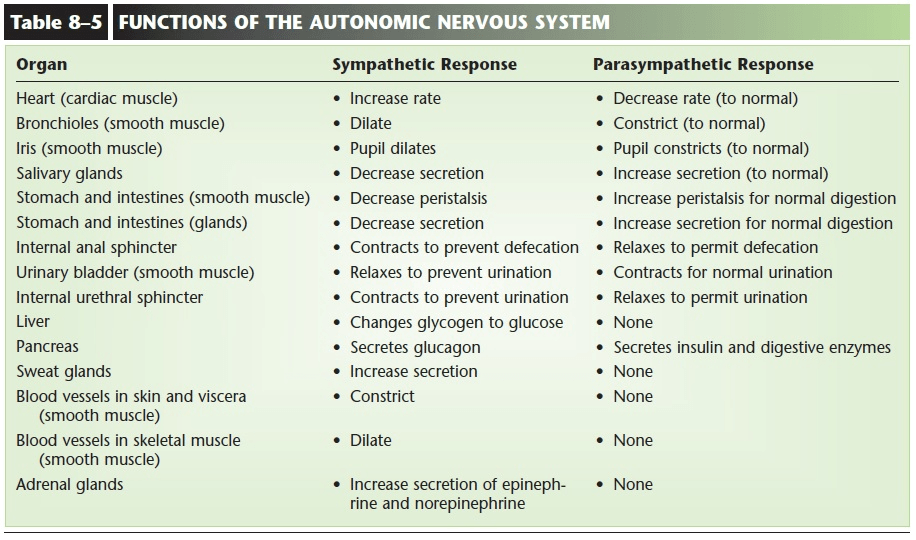
On each of these organs, name the parasympathetic and sympathetic response through the ANS.
Heart
Urinary Bladder
Adrenal glands
This fluid is the tissue fluid of the CNS...
Cerebro....spinal fluid