Name the lobes that make up the Cerebrum of the brain.
The Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe, Occipital lobe, and Temporal lobe.
The speed of neural conduction between neurons will result in difficulties in speaking, vision, and balance if the ________________ insulating the axons is damaged or removed.
Myelin or Myelin Sheaths
Do dendrites receive impulses and travel down the neuron or send impulses to other neurons?
receive
What does the central nervous system consist of?
the brain and spinal cord
What does the PNS contain?
The peripheral nerves, all sensory and motor neurons, cranial and spinal nerves.
Which lobe gives your emotional response and allows us to know what we are doing or our consciousness?
The Frontal lobe
What structures receive impulses from neighboring cells or sensory receptors?
dendrites
What is the function of the axon?
What is to send the impulse to the next neuron?
What is the cerebrum responsible for?
voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, and memory
What is the electrochemical process of depolarization and repolarization along a nerve fiber; how neurons transmit information.
Nerve Impulse
Which part of the brain if injured can make it difficult to see or identify colors?
Occipital Lobe
What is #5 pointing to?
Nodes of ranvier
What is it called when a neuron is NOT sending impulses? Is the neuron polarized or depolarized during this time?
What is the resting potential. Polarized
Where is the cerebellum located?
at the back of the brain, between the cerebrum and brain stem
Two types of effectors that receive motor input are:
muscles and glands
The lobes that are located laterally and help in hearing and equilibrium are what?
Temporal Lobe
What is the job of a motor neuron?
to send signals to the effectors (muscles and glands) to respond to the stimulus
The space between an axon of a neuron that is communicating with a dendrite of another neuron is called a ________________
Synapse
An automatic subconscious response to stimuli is called what?
A Reflex
What are the three layers of the meninges called and where are they located?
Pia Mater (bottom layer closest to brain and spinal cord)
Arachnoid mater (middle layer)
Dura Mater (outer layer closest to skull and vertebrae)
Which part of the brain controls your heart beat and breathing? (State the name of the structure.)
brain stem
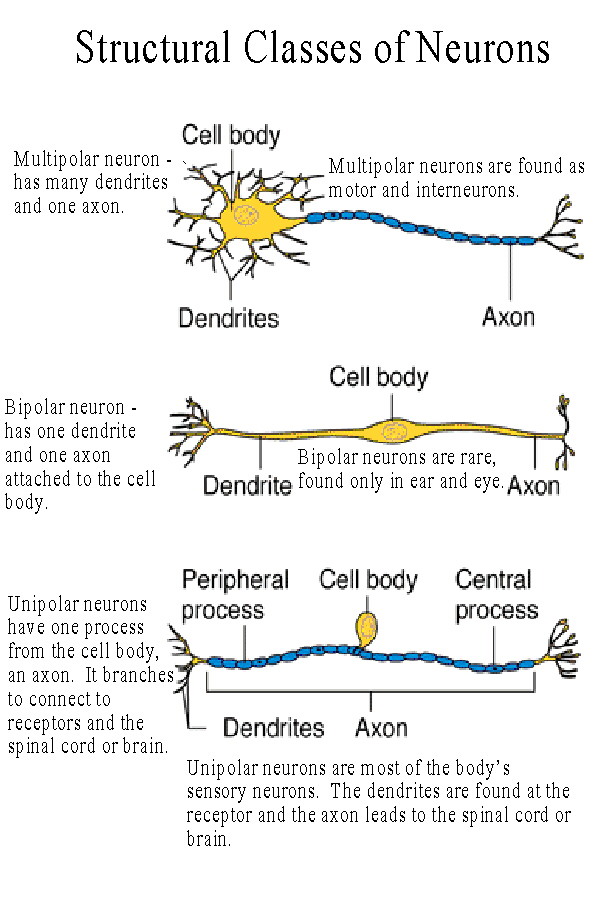
What are the three main classes of neurons based on their structure?
bipolar, multipolar, unipolar
This part of the neuron stores then releases neurotransmitters into the synapse.
Vesicles in the Axon Terminal
What is the difference between gray matter and white matter?
What is grey matter is not myelinated and white matter is.
grey matter = cell bodies and does integration; white matter = mylenated axons
Draw and label a neuron - include axon, dendrite, axon terminals, cell body, schwann cells and Nodes of Ranvier

