Most common causes of Croup
What is Parainfluenza, RSV, Adenovirus
9 month old with nasal discharge and congestion past 3 days presenting to the ED with fever of 101.5, barking cough, increased respiratory efforts.
PE significant for mild subcostal retractions and inspiratory stridor at rest
What is croup?
Causes of wheezing in childhood apart from asthma
What is bronchial edema (infection, inhalation of irritant gases), aspiration of foreign body or gastric contents, cystic fibrosis, PCD, intrinsic airway lesions ( endobronchial tumors), vocal cord dysfunction
Definitive diagnosis of bacterial tracheitis
What is direct visualization of the air way via laryngoscopy and tracheobronchoscopy.
Treatment for mild croup
What is single dose of oral dexamenthasone (0.15mg-0.6mg/kg)
Most common cause of inspiratory stridor and infants. Often aggravated by swallowing problems & gastroesophageal reflux.
What is Laryngomalacia [floppy larynx]
3 y/o is evaluated for recurrent wheezing. Symptoms have been present for 6 months. Seen in the ED 2 weeks ago. He received albuterol & 3 day course of PO steroids. No resolution to sxs. Denies fhx of asthma, allergic rhinitis, or eczema. P/E remarkable for inspiratory stridor most prominent on the anterior neck. CXR unremarkable. What is likely causing his current sxs?
What is vocal cord dysfunction?
Triggers include excercise, asthma, smoking, intubation and anxiety. Dificulty brething is most common compliant. Pts also present with wheezing, through tightness, chocking sensation, dysphonia, cough and GER or dysphagia. P/E remarkable loudest on anterior neck and CXR is normal.
Foreign body objects most commonly dislodge in this anatomical area
What is right mainstem bronchus?
1- y/o M with down syndrome. Presenting to the clinic with complains of excessive day time somnolence and behavioral changes. Teachers are concerned about school performance and excessive nap taken during school hours. Mother admits to hearing loud snoring at night, which has gotten progressively worse. BMI is > 95th percentile. P/E is remarkable for hypertrophic, bilateral tonsils. What is the definitive test for evaluation of this child's symptoms?
What is polysomnogram?
14 year old boy with exercise induced bronchoconstriction asks for advice about preventing his symptoms. What strategy is preferred according to the 2007 NHLBI EPR 3 asthma guideline?
What is administering short acting B2 agonist just before exercise?
Benign tumor caused by HPV- 6 and HPV -11 associated with hoarse voice/ cry and biphasic stridor
What is Juvenile pharyngeal papillomatosis?
12 year old with rapid onset fever of 104.5, appears anxious, difficulty swallowing for 3 days, neck pain, decreased oral intake.
Physical exam noticeable for saliva pooling, enlarged anterior cervical LN
What is retropharyngeal abscess
Pt with recurrent otitis media, history of chronic sinusitis and bronchiectasis and this CXR present 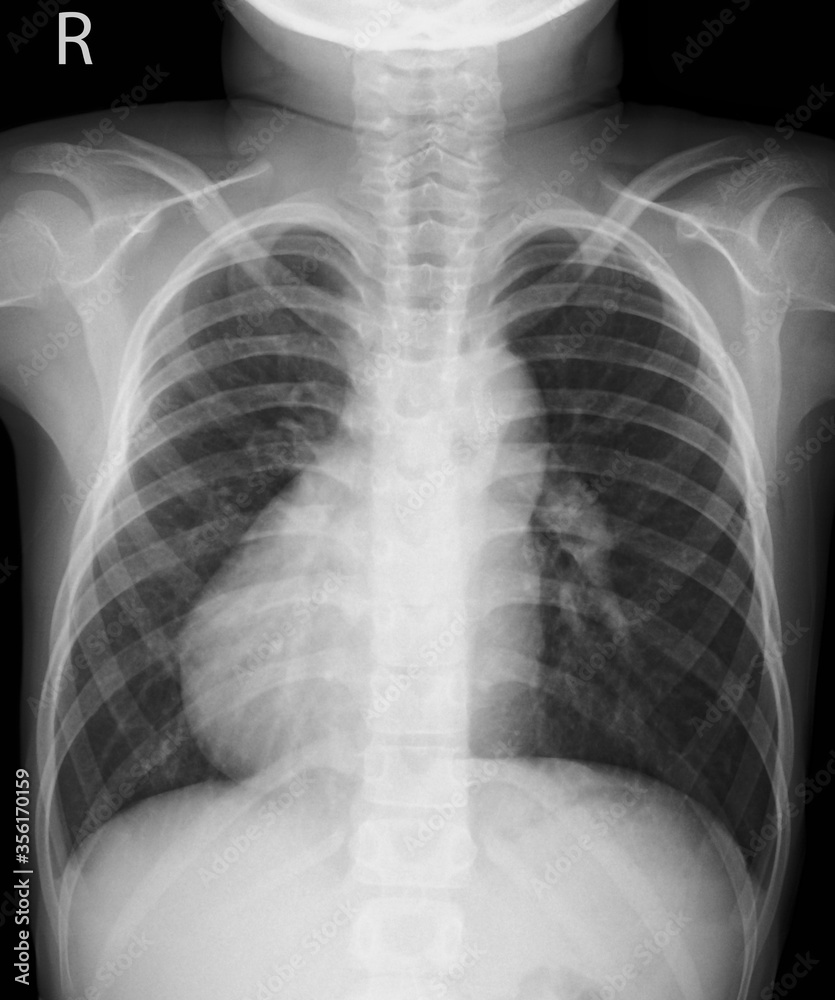
What is primary ciliary diskinesia?
Definitive diagnosis for vocal cord dysfunction
What is laryngoscopy
Shows laryngeal adduction during inspiration and abduction during expiration
Treatment for patient with suspected retropharyngeal infection and signs of severe airway obstruction
What is: secure airway followed by surgical incision and drainage
2 year-old boy brought into an urgent care facility for new-onset wheezing. Cough is appreciated but no fever, rhinorrhea. He has mild tachypnea and steroids are started. In spite of several treatments, he continues to wheeze. CXR are obtained. What is your next step in management?
What is urgent endoscopic removal?
6 y/o F recently started school presents to your office with c/o a wet cough for 6 weeks. After careful history, you find there are no other symptoms present. On exam, there are continuous rhonchi throughout all lung fields. She is given treatment of inhaled bronchodilator in the office with no change to exam. What is the diagnosis
What is protracted bacterial bronchitis?
3-week-old infant was born at term with a birth weight of 7lb 4 oz. Newborn screening (IRT/DNA) for cystic fibrosis comes back positive. What is next step in diagnosing?
What is sweat chloride testing?
20-month-old referred to ED with high pitched, barky cough and mild respiratory distress, following few day course of URT symptoms with low grade fever. Respiratory virus film array is positive for parainfluenza. What findings would you expect on this xray?
What is loss of normal shoulders of subglottic airway?
What is subglottic tracheal narrowing?
6 y/o F recently started school presents to your office with c/o a wet cough for 6 weeks. After careful history, you find there are no other symptoms present. On exam, there are continuous rhonchi throughout all lung fields. She is given treatment of inhaled bronchodilator in the office with no change to exam. Dx with protracted bacterial bronchitis. What is your treatment
What is 2-4 week course of amoxicillin/clavulanate or 2nd/3rd cephalosporin?
4 differential diagnosis of upper airway obstruction in newborns
What is:
choanal atresia, Micrognathia (pierre robin, treacher collins, digeorge), Laryngeal webs/cleft/ atresia, vocal cord paralysis/paresis ( weak cry, unilateral or bilateral), congenital subglottic stenosis, nasal encephalocele, macroglossia
Unilateral mucupurelent nasal dischage past week with mouth breathing in 2 year old
What is foreign body
Indications for performing sweat test
What is:
Resp: Chronic or recurrent cough/ pneumonia, Recurrent bronchiolitis,,Recurrent or persistent atelectasis
GI: meconium ileus, mec plug, atresia malabrsorption, hepatic cirrhosis, pancreatitis,
MISC: rectal prolapse, FTT, Fhx of cystic fibrosis, nasal polyps, recurrent sinusitis, aspermia, absent vas deferens
Causes of false positives in cystic fibrosis
adrenal, eczema, ectodermal dysplasia, hypothyrodism, malnutrition, dehydration, prostaglandin E1 administration, mucopolysaccharidosis, hypothyroidism, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Treatment for moderate to severe croup
What is dexamethasone 0.6mg/kg
What is racemic epinephrine
What is supportive care: oxygen or humidified ai, antipyretics and encourage fluid intake