What bone forms the largest portion of the floor of the orbit?
Maxillary bone
What are the two main layers of the synovial membrane, and what are their key features?
Intimal layer – 1–3 cells thick; contains type A (macrophage-like) and type B (fibroblast-like) synoviocytes.
Subintimal layer – loose connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves.
If a patient’s leg shows spasticity and brisk reflexes, is this more likely an upper or lower motor neurone lesion?
Upper Motor Neurone
What typical radiographic finding is seen in Osgood–Schlatter disease, and what anatomical structure is involved
Fragmentation and irregularity of the tibial tuberosity apophysis, due to traction from the patellar tendon
Why might a patient describe complementary medicines as “non-chemical,” and why is this scientifically inaccurate?
They see them as “natural,” but scientifically everything is made of chemicals, including herbal and vitamin products.
What is the name of the first cervical vertebrae (C1)?
Atlas
Which cell type in the synovium is primarily responsible for producing hyaluronic acid and lubricin, and what is their function?
Type B synoviocytes; produce hyaluronic acid and lubricin for joint lubrication and shock absorption.
Which reflex tests the L3/L4 spinal level?
Knee jerk / patellar reflex
Identify the condition
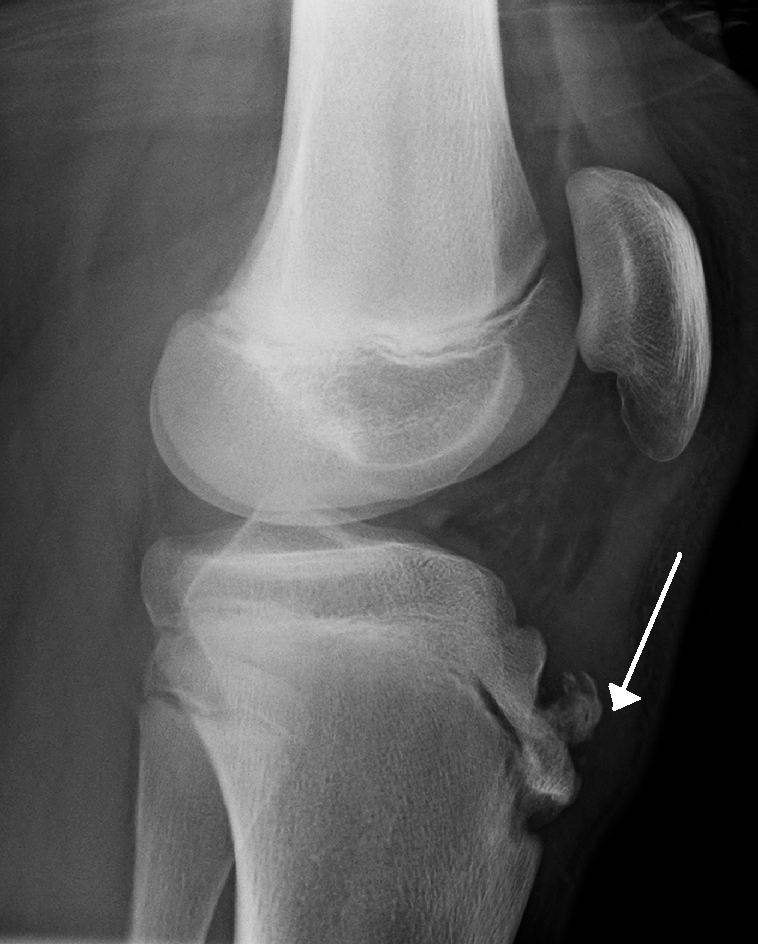
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
What enzyme does St John’s wort induce, and what is the clinical consequence for women taking the combined oral contraceptive pill?
Induces CYP3A4 → lowers hormone levels → risk of breakthrough bleeding, ovulation, and pregnancy.
Through which foramen does the mandibular nerve (V3) exit the skull?
Foramen Ovale
When performing arthrocentesis on the knee, list the layers a needle penetrates (anterolateral approach).
Skin → subcutaneous tissue (fat/adipose) → quadriceps tendon or retinaculum → joint capsule → synovial membrane → joint space for synovial fluid collection
What movement would be weak in a common peroneal/fibular nerve injury?
Foot dorsiflexion (foot drop)
How do you differentiate between a normal growth plate (physis) and a fracture line on a child's xray?
Growth plate is smooth, regular, symmetric, with sclerotic margins;
Fracture lines are irregular, lucent, may extend into metaphysis/epiphysis and often asymmetrical.
If a product has an AUST L number but no “(A)” after it, what does that specifically mean about how it was assessed by the TGA?
Assessed for quality and safety, but not efficacy.
Which cervical vertebra has the most prominent spinous process and where is it usually palpable
C7 - usually palpable at the base of the neck
What are 3 functions of synovial fluid?
Shock absorption
Nourishment of cartilage
Immune surveillance / removal of debris
What does weakness in all four limbs with brisk reflexes and extensor plantar responses suggest and why?
Cervical cord or bilateral pyramidal lesions
All limbs = spinal cord --> cervical cord
Reflexes are from local circuits and do not require input from the brain
Even if the upper motor neurone pathway (corticospinal tract) is damaged, the reflex arc at the spinal level is intact
Identify the marked feature and describe its location

What proportion of Australians report using at least one complementary medicine in the past year, and which demographic is the highest user group?
~70% of Australians; younger to middle-aged women with higher income and education.
In portal hypertension, bleeding esophageal varices arise from communication between which two veins?
Left gastric vein (portal) and azygos vein (systemic).
Why does the synovium play a central role in inflammatory arthritis (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis)?
It is highly vascular, contains immune cells, and can proliferate (pannus formation) → releases cytokines/enzymes → cartilage and bone destruction.
What does a positive Babinski sign look like, and what does it mean?
Plantar Reflex --> Big toe extends upwards; indicates an UMN lesion.
What are the classic features of osteoarthritis seen at synovial joints
Joint space narrowing,
subchondral sclerosis,
osteophyte formation,
subchondral cysts
At what daily dose of vitamin E do adverse outcomes like haemorrhagic stroke and increased mortality become more likely?
≥400 IU/day.