What is the Big Bang Theory
The universe formed during a single event in which all matter and energy suddenly expanded from an extremely small point.
Name 2 pieces of evidence supporting the Big Bang.
Any 2 of the following:
Measurable expansion of the universe (Red shift of galaxies)
Cosmic microwave background radiation
Relative abundance of hydrogen and helium
What powers a star?
Nuclear fusion
List the 9 celestial bodies that make up our solar system
Sun, mercury, venus, earth, mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
What galaxy is our solar system located in?
The Milky Way Galaxy
What is this a picture of?
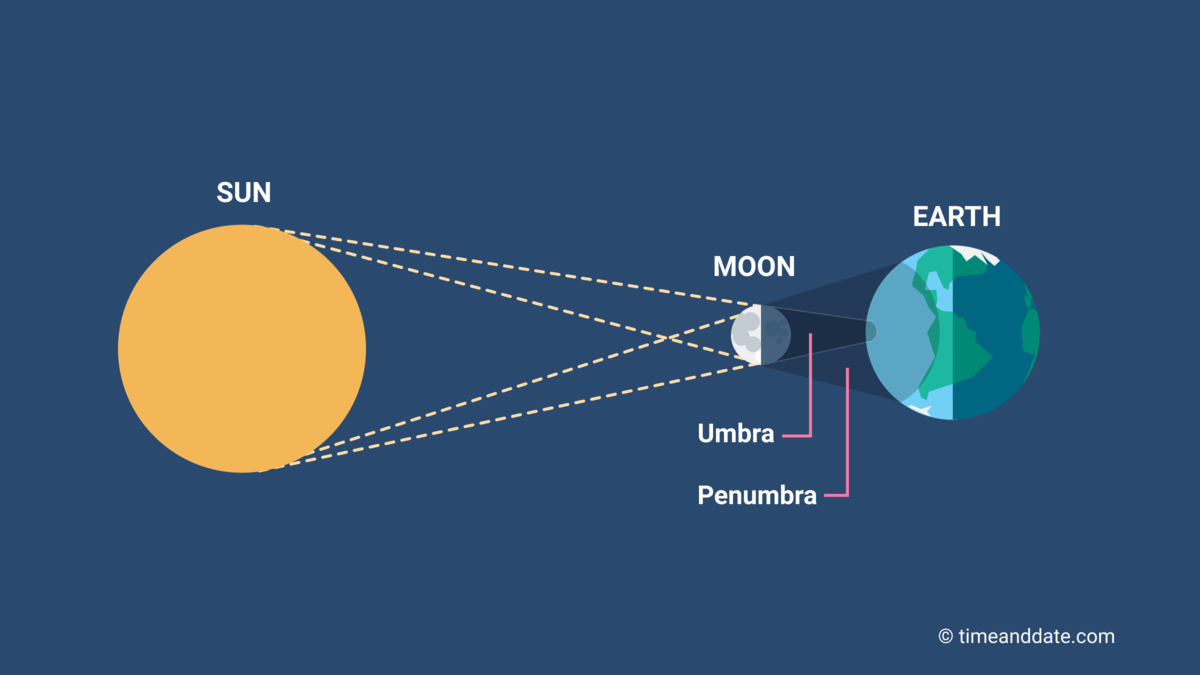
What is a solar eclipse?
About how long ago did the Big Bang occur?
about 13.8 billion years ago
Do the majority of stars and galaxies exhibit red shift or blue shift? Why?
What stars are the brightest and the hottest?
What are Blue Giants?
What is the latitude and longitude for teal/aquamarine location?

What is 105 degrees East and 60 degrees North?
Name the three main types of galaxies
Spiral, elliptical, irregular
What moon phase will create a solar eclipse?
What is new moon?
What were the first two elements to form after the Big Bang?
Hydrogen and Helium
Explain why the relative abundance of hydrogen and helium in the universe is consistent with the Big Bang theory
According to the Big Bang Theory, they were the first to form, and so they are the most abundant in the universe.
What property of a star determines whether it ends as a white dwarf, a neutron star or a black hole?
Its mass
Explain what a light-year is
The distance that light travels in a year.
What type (shape) of galaxy is the Milky Way?
Spiral
What is this image of?
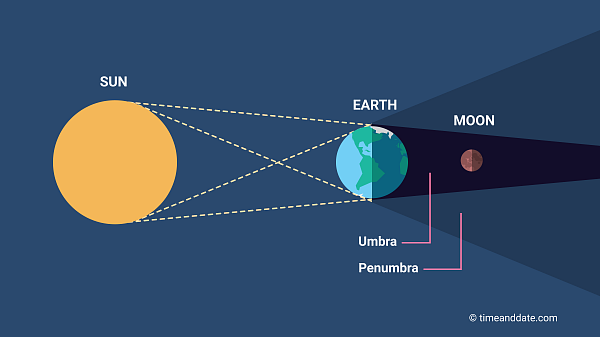
What is a lunar eclispe?
Why do scientists study distant galaxies to gain a better understanding of the beginnings of the universe.
Light from distant galaxies must travel for millions or billions of years before we are able to detect it. So, when we look at images of galaxies far away, we are actually seeing what these galaxies looked like long ago.
Explain why cosmic microwave background radiation is consistent with the Big Bang Theory
In any explosion, energy is released. Cosmic background radiation is "leftover energy" from the big bang
Name a group of stars that is located off from the main sequence
red giants, supergiants, red dwarfs, white dwarfs
True or false: all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed.
True; they travel at the speed of light
Name two main features of a spiral galaxy
A central bulge and spiral arms.
What moon phases produce spring tides?
What are new moons and full moons?
List both pieces of evidence for the big bang
1. Most galaxies appear to be redshifted
2. cosmic background radiation
When our sun dies, what will its next phase be?
What is a white dwarf?
Explain the process that resulted in the formation of our sun
The dust and elements that made up a planetary nebula (space dust left over from exploded stars) began forming into clusters under their own gravity. As these clusters became larger and larger due to their gravitational attractions, they eventually gained enough energy to undergo nuclear fusion.
What moon phases cause neap tides?
What are 1st and 3rd Quarter moons?
roughly how many stars are in the milky way galaxy?
100-200 billion
What is the moon phase?
What is waxing crescent?
