Then neurotransmitter found at the neuromuscular junction.
Acetylcholine
This type of muscle opposes an agonist (prime mover).
Antagonist
Primary action of erector spinae (when contracting bilaterally).
Trunk extension
The primary action of the triceps brachii.
Elbow extension
The primary function of the lateral compartment of the lower leg.
Ankle eversion
The type of muscle contraction (eccentric/concentric/isometric):
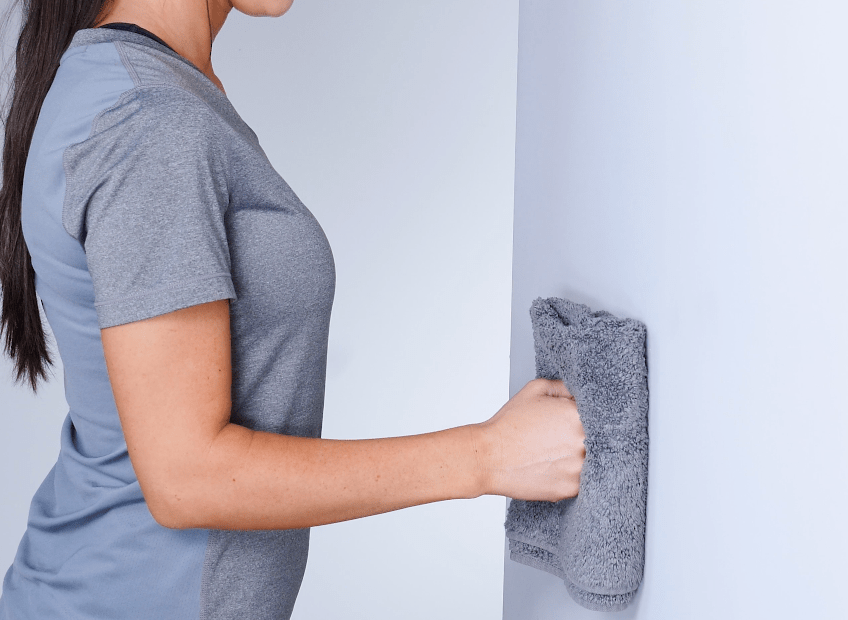

Isometric
In a sarcomere, this protein (myofilament) appears dark in colour.
Myosin
This muscle, found between the ribs, acts as a synergist for inspiration.
External intercostals
Muscle used during a sit up.
Rectus abdominis
3 muscles that act on the scapula.
Levator scapulae (elevation)
Upper fibres of trapezius (elevation)
Middle fibres of trapezius (retraction)
Lower fibres of trapezius (depression)
Rhomboids (retraction)
Gluteus medius
The primary agonist muscle:
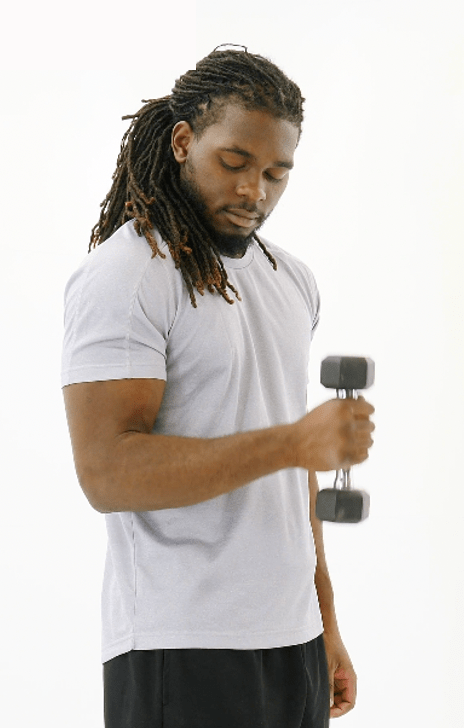

Brachioradialis
A fascicle is composed of bundles of these.
Muscle fibers
The agonist muscle as you go from sitting to standing.
Quadriceps group
3 main layers of the abdominal wall that form the rectus sheath (from superficial to deep).
External oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis
3 muscles that produce shoulder flexion.
Anterior deltoids
Long head biceps brachii
Coracobrachialis
3 muscles that produce hip flexion.
1. Iliopsoas
2. Sartorius
3. Rectus femoris
The action and primary muscle being used (concentrically):

Hip extension, gluteus maximus
The organelle that acts as a storage site for calcium.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
The antagonist muscle in the lower body as you move from sitting to standing.
Hamstrings group
__________ produces ipsilateral trunk rotation, while __________ produces contralateral trunk rotation.
Internal obliques
External obliques
Pronator teres, supinator
With respect to the medial hamstrings, the ____________ is found superficial to _____________. The lateral hamstring is called the _____________. All hamstrings produce the actions of hip ______ and knee _____.
semitendinosus, semimembranosus
biceps femoris
hip extension, knee flexion
The muscle being stretched:

Gastrocnemius
_____ ions attach to ______ promoting a change in position of _________.
Calcium, troponin, tropomyosin
On your tiptoes, the:
Agonist is __________
Antagonist is _________
Synergist is __________
Antagonist - tibialis anterior
Synergist - soleus
The most lateral of the erector spinae is the ___________ muscle that attaches to the _______.
Iliocostalis, ribs
Function of each rotator cuff muscle (*there are 4).
Supraspinatus - shoulder ABD
Infraspinatus - shoulder ER
Teres minor - shoulder ER
Subscapularis - shoulder IR
The 4 quadriceps muscles, working together to produce knee _______.
1. Rectus femoris
2. Vastus medialis
3. Vastus lateralis
4. Vastus intermedius
knee extension
The movement being shown and the 2 muscles being used (concentrically):
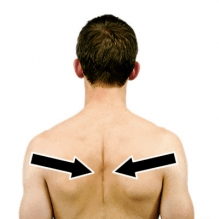
Scapular retraction
Muscles: levator scapulae, rhomboids