What if you heat up a substance, what happens?
The particles in the substance move more quickly.
Total Energy of all the particles in an object
Thermal Energy
A substance that allows energy to pass through it easily
What is a conductor?
How did your thermos prevent heat loss through conduction?
Insulating materials! They slow down heat transfer through direct contact.
Heat flows from
warmer to cooler temperature
What if a substance is at absolute zero, what is the substance doing?
The substance is motionless.
Energy that is transferred from a warmer object to a cooler object
Heat
The average kinetic energy in the molecules of a substance.
What is a temperature?
If two objects are at the same temperature but have different masses, will they contain the same amount of thermal energy?
NO!!
The Three ways thermal energy is transferred are...
What is Radiation, Conduction, Convection
"I make this kind of thermal energy"
What is radiation?
This is used to measure temperature
Thermometer
The scale of temperature measurement that we use in science
What is the celcius scale?
You are supposed to get low toward the floor if you are ever caught in a building or house fire. The hotter air and smoke will rise and the cooler air will sink. What type of heat transfer does this represent?
What is Convection?
A material that conducts heat poorly is called a(n) __________________.
insulator
What if the kinetic energy of the particles in an object increases, the temperature will do what?
Increases
the process by which heat transfers from one particle to another when the particles collide
Conduction
True or False. Heat and thermal energy are the same thing.
False
Radiation is...
heat transfer through electromagnetic waves
A temperature scale that is based upon the idea that all molecular motion stops at absolute zero is this.
What is the Kelvin scale?
Describe how conductors and insulators differ. Include an example of each.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
A material that prevents the flow of energy is called an insulator. A material that permits the flow of energy is called a conductor.
An example of an insulator would be air, wool, plastic, etc.
An example of a conductor would be silver, aluminum, iron, metal
When energy transforms from one form to another, the total amount of energy in a system
is conserved.
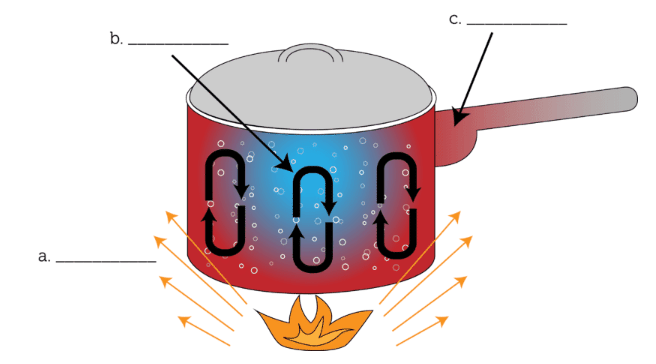
a) Radiation
b) Convection
c) Conduction
Explain how convection currents happen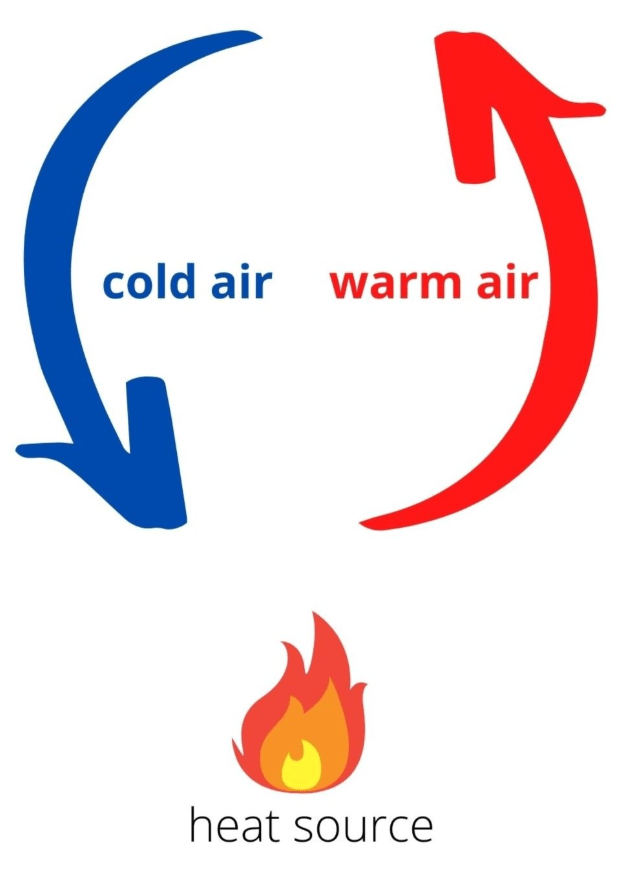
Air rises when heated because it becomes less dense. Cooler air sinks because it is more dense, creating a cycle.
This type of heat transfer can travel through empty space.
What is radiation?
