endothermic
True or false: the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be created and destroyed.
False
How many moles of oxygen will produce -2200 kJ of energy.
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O ∆H = -2200 kJ
5 moles O2
The symbol for heat energy
q
If you flip a reaction what must you do to the enthalpy of the reaction?
Change its sign
Rate of reaction relates these two things
Change in concentration vs. time
The SI unit for heat energy
Joule
H2O(g) --> H2O(s)
exothermic
What is the SI base unit for energy?
What is a more common/recognizable unit for energy?
Joule(J)
calorie(cal)
Calculate the enthalpy change if 5.00 mol N2 reacts with O2 to make NO:
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) ΔH = +181.8 kJ
909 kJ
If two metals of equal mass with different heat capacities are subjected to the same amount of heat. Which one will undergo the smallest temperature change?
The metal with the higher heat capacity.
Calculate ΔH for
C2H2(g) + 2H2(g) --> C2H6(g)
given
C2H6(g) + 7/2O2(g) --> 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ΔH = -1560 kJ
2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) --> 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ΔH = -2599 kJ
H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) -->H2O(l) ΔH = -286 kJ
-312 kJ
As temperature increases, reaction rate will _______
Increase
The amount of energy that must be overcome in order for a reaction to proceed
Activation energy
Mg(s) + Cl2(g) --> MgCl2(s) ΔH= -641kJ
exothermic
In an ____thermic reaction more energy is ________ from the bonds of reactants broken than energy is __________ from the bonds of products formed.
endo, absorbed, released
When 3.00g of carbon burns in the reaction below, what would be the enthalpy change?
C(s) + O2(g) --> CO2(g) ΔH = -393.5 kJ
-98.3 kJ
How much heat must be added to increase the temperature of 500.g of water from 22.5 C to 39.1 C? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g*C
34,700 J
Calculate ΔH for
Cu(s) + Cl2(g) --> CuCl2(s)
given
2Cu(s) + Cl2(g) --> 2CuCl(s) ΔH = -274.4kJ
2CuCl(s) + Cl2(g) --> 2CuCl2(s) ΔH = -165.8 kJ
-220.1 kJ
Increasing surface area increases the rate of reaction by ___________
Providing a greater area for collisions to occur
Particles must collide with the correct energy and at the right orientation
Collision Theory
If you mix two solutions that are each originally at the same temperature, and the temperature of the overall resulting solution increases, what is the likely explanation?
The solutions react and release heat (exothermic)
A cup of water is put into a refrigerator to cool.
1. What is the system in the scenario?
2. What happens to the temperature of the water before it begins to freeze?
3. Is this process endothermic or exothermic?
1. the water
2. the temperature will decrease
3. exothermic
The heat of combustion for propane (ΔH) is -2219 kJ/mol. What mass of propane (C3H8) must be burned to release 4650 kJ of heat?
92.41 g
On a hot summer day you and your friends decide to drive to the lake to cool off. You each hop in your own cars and your leather seat burns your skin but your friend's cloth seat does not burn them. If both seats are the same size and have been in the sun for the same amount of time, why would the leather seats be hotter.
The specific heat capacity of the cloth is higher than that of the leather.
Calculate ΔH for
Zn(s) + 1/2O2(g) --> ZnO(s)
given
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) --> ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) ΔH = -152.4 kJ
ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq) --> ZnCl2(aq) + H2O(l) ΔH = -90.2 kJ
2H2(g) + O2(g) --> 2H2O(l) ΔH = -571.6 kJ
-348.0 kJ
Which phase would allow for the slowest reaction rate?
Solid
Which would be a formation equation:
C(s) + CO2(g) --> 2CO(g)
N2(l) + 2H2(g) --> N2H4(l)
2Fe(s) + 3/2O2(g) --> Fe2O3(s)
2Fe(s) + 3/2O2(g) --> Fe2O3(s)
Classify each process as exothermic or endothermic:
a) ice melts
b) gasoline burns
c) steam condenses
d) reactants --> products ΔH= -50kJ
a) endothermic
b) exothermic
c) exothermic
d) exothermic
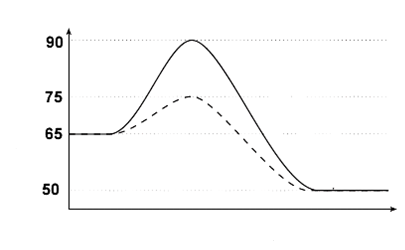 1. What is the ΔH of the forward and reverse reactions?
1. What is the ΔH of the forward and reverse reactions?
2. What is the forward and reverse activation energy?
3. Is the forward reaction endo or exothermic?
4. What does the dashed line indicate has been done to the reaction?
1. -15; +15
2. 25; 40
3. Exothermic
4. A catalyst has been added
Another reaction used to propel rockets is:
N2O4(l) + 2N2H4(l) --> 3N2(g) + 4H2O(g) = -1140 kJ
The advantage of this reaction is that no toxic fumes are produced. If 10.0g of N2 are produced, how much energy was released?
(-)136 kJ
Calculate the heat required, in kJ, to heat 250 grams of ice at -32.0 C to water at 46.7 C.
cice = 2.05 J/gC
cwater = 4.184 J/gC
ΔHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol
148.6 kJ
Calculate ΔH for
Mg(s) + 1/2O2(g) --> MgO(s)
given
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) --> MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) ΔH = -462 kJ
MgO(s) + 2HCl(aq) --> MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) ΔH = -146 kJ
2H2(g) + O2(g) --> 2H2O(l) ΔH = -571.6 kJ
-602 kJ
Lowers the activation energy of a reaction
Catalyst
A 122.6 g sample of a metal is heated to 95.2 C and placed into a calorimeter containing 100 g of water at 21.6 C. The final temperature of the metal and water is 24.5 C. What metal was used?
Al (.89 J/gC)
Fe (.45 J/gC)
Cu (.20 J/gC)
Pb (.14 J/gC)
Lead, Pb