how can you test for centralization/peripheralization
repeated movements
sustained postures
traction (manual or mechanical)
widening/bulging of the abdominal aorta
risk factors: >60 years old, men > women, history of cardiovascular disease, history of smoking
signs and symptoms: LBP, abdominal pain, pulsatile mass near umbilicus (ie belly button pulse)
death may occur quickly with rupture
what is spondylosis
spinal degeneration of vertebrae and disks, often involving arthritis
how do you know when leg pain is more likely radicular?
when accompanied by signs of conduction loss (myotomal weakness, dermatomal sensation change, hyporeflexia) and stretch intolerance (+SLR, +slump, +Elys) AND
radicular symptoms are below the knee (95% SENS)
what is this special test used for and what is a positive test
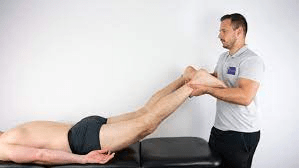
used for lumbar spine instability
positive test would be pain or 'heaviness' in the low back (symptoms should reside when legs are set back down)
84% SENS, 90% SPEC
why do we perform muscle endurance testing of the trunk
LBP may be more common in individuals with low lumbar endurance
strong correlation between trunk muscle endurance and back "health"
what would be typical in a pt with severe acute LBP
high level of pain (>7/10), irritability, and disability
may have no directional preference (ie movement in all directions is painful)
may have hypomobility but too irritable to manip/mob to increase movement (you can still do it for pain modulation tho)
may have hypermobility, but too irritable for intense exercise
what type of mattress should someone with LBP use
medium-firm mattress promotes comfort, sleep quality, and spinal alignment
BUT
depends on the pt, recommend trial in putting board under mattress to firm it up or trying softer bed/couch and seeing how that fares
what are the exercises you can use for someone who centralizes with extension
prone: props or press ups
standing: back bends
quadruped: camel or forward rocking into press up
additionally, you can do manual therapy to increase the extension or the pt can use a strap/pillowcase/fingers to create a fulcrum on their back
what is stability
controlled stiffness/rigidity
it is also a result of coordinated, properly sequenced muscle activity that controls vertebral movement while maintaining adequate spine stiffness
what is symptom onset like for LBP typically
onset is idiopathic with most LBP
there are likely contributory lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior
what is cauda equina syndrome
due to compression of multiple lumbosacral nerve roots below conus medularis
sources of compression can include large central disc herniation, tumor, and spondylolisthesis
pts not treated in 48 hours of symptom onset have significantly poorer outcomes, including chronic incontinence
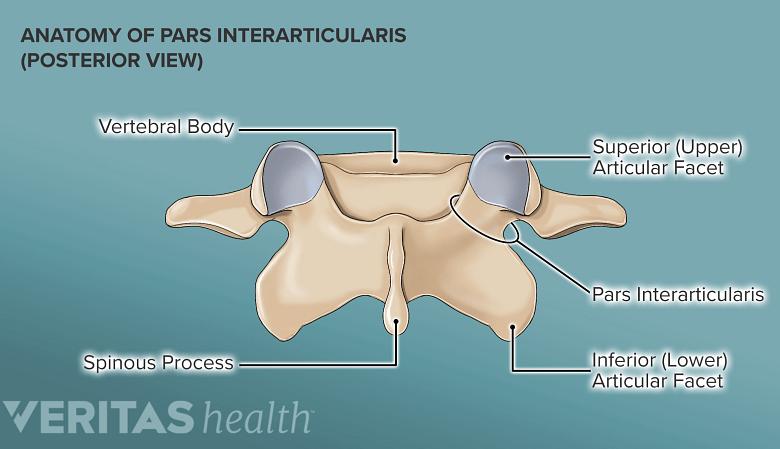
what is the pars interarticularis
bone bridge between inferior and superior articular surfaces of a single vertebra
what is the purpose of the SLR test
used to ID L-spine disc pathology or nerve root irritation
tenses lumbosacral nerve roots (primarily L4-S2), sciatic nerve, and branches
what is this special test used for and how do you perform it
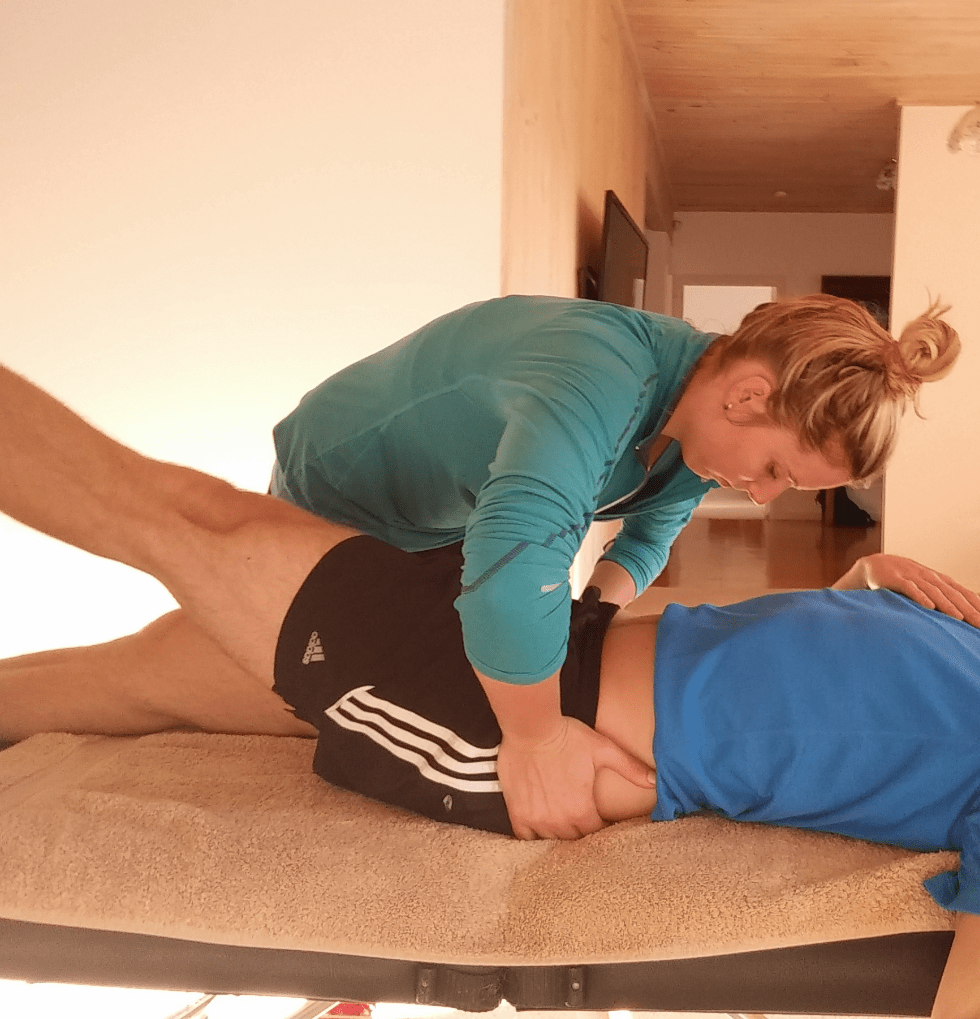

this is used for SIJ instability
pt supine, performs 6 inch SLR; if painful, stabilize pelvis and have pt repeat SLRpositive test = decreased pain with stabilization
87% SENS; 94% SPEC
what do you do with pts who do not improve at all despite treatment for 2-4 weeks
additional examination!:
is there something important you overlooked
is there a disconnect between pts goals the PT's POC
is the pt continuing to micro-traumatize injured tissue
is there an underlying systemic pathology
what treatments should you prioritize in pts with chronic LBP
exercise including: trunk muscle strengthening and endurance, multimodal exercise interventions, specific trunk muscle activation exercise, aerobic exercise, aquatic exercise, general exercise
manual therapy: joint mobs and manips, soft tissue mobs, dry needling maybe, neural mobilization
pain neuroscience education
psychosocial intervention
how is LBP like the common cold
both are ubiquitous - part of the human experience
there are steps a person can take to reduce their risk, but some individuals are more susceptible than others
both tend to resolve over time (regardless of treatment)
there are multiple symptom remedies available
some individuals over react
what exercises can you do for someone who centralizes with flexion
supine knees to chest
posterior pelvic tilt
quadruped rocking (childs pose)
sidelying knee to chest
sitting flexion
(also adding lumbar rotation may improve symptoms further by increasing IV foramen diameter)
what are the spine stabilizing components
passive: vertebrae, IVDs, ligaments
active: neuromuscular control
what is stenosis and what are the clinical findings associated with it
narrowing that can occur in the central neural canal (central stenosis) or lateral foramen (lateral foraminal stenosis)
clinical findings:
>48 years old
bilateral symptoms
leg pain>back pain
pain with walking/standing
pain relief with sitting
history of LBP (94% SENS)
rapid onset of symptoms within 24 hours (90% SENS)
urinary retention (90% SENS)
sacral sensation loss aka saddle anesthesia (85% SENS)
loss of sphincter tone (80% SENS)
fecal incontinence
gait disturbance
what is spondylolysis
unilateral or bilateral fracture in the pars interarticularis
90% occur at L5
can be caused by:
overuse/traumatic: occurs in younger individuals, common with forceful flexion/extension, rotation to immature skeleton OR
degeneration: occurs in older individuals as a progression from spondylosis
at what degree range will concordant radiating symptoms likely occur when doing a SLR test
when hip is flexed between 30 and 70 degrees (with knee extended)
SENS 91%: thus negative SLR strongly rules out a L-spine disc herniation
what are the special tests used for SI joint pain/instability
pelvic instability test (aka active SLR test)
thigh thrust test (used to distinguish between pelvic girdle pain and LBP)
Gaenslen's test
SIJ compression test
SIJ distraction test
(maybe sacral thrust and maybe FABER)
when classifying someone into chronic LBP without generalized pain, what is the treatment approach generally
moderate to high intensity exercise
when should you do neural mobilization techniques and what are the two techniques often used
when radiating symptoms are non-irritable
you can do nerve sliding and nerve tensioning
what type of training is just 1 set of exercises normally good enough for
strength training for chronic LBP
what to do if someone has a lateral shift
address this before doing flexion/extension for centralization
can either do manual or have pt lean against the wall
when doing manual, pressure on, then release pressure by about 50%
go slowly and be patient
what are the mechanisms by which spinal stability is achieved
muscular compression/constraint
intra-abdominal pressure: decrease abdominal cavity volume leads to increased abdominal pressure; this can increase trunk stiffness by about 40%
what are some important SRMs for LBP
Oswestry Disability Index (ODI)
Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ)
STarT Back Screening Tool (SBST)
what is myelopathy
spinal cord compression that is due to degenerative stenosis , degenerative or traumatic spondylolisthesis, posterior IVD herniation, tumor
symptoms tend to be more neurologic over pain and include sticky gait, balance difficulties, non-dermatomal sensory loss, urinary dysfunction, UMN signs (hyperreflexia, primitive reflexes like Babinski and clonus; LE weakness)
usually occurs after age 50
not very common in the lumbar spine
what is spondylolisthesis
forward slippage of superior vertebra on inferior vertebra
occurs only with bilateral spondylolysis
what strongly rules in a L-spine disc herniation
positive crossed SLR
practitioner must focus on the history, location of pain, and SIJ provocative maneuvers
if pt exhibits > or equal to 3 provocative maneuvers, then the SIJ may be considered as a possible source of pain
when classifying someone into chronic LBP with generalized pain, what is the treatment approach generally
progressive, low-intensity, submaximal fitness and endurance activities along with pain management and health promotion strategies
what is the purpose of treatment with subacute back pain
shift from "making the pt better" to preventing chronicity and recurrence
address strength/endurance/flexibility impairments
address functional limitations
what is one concern about the McKenzie method
it might increase risk of kinesiophobia
pts may become over fearful of flexing or extending
what is centralization strongly associated with in terms of pathoanatomical findings
centralization is strongly associated with discogenic pain and predictive of intact annulus
centralization is also predictive of high non-operative success
what is abdominal hollowing
pull abs in towards your spine as you exhale
has been shown to be ineffective for stabilizing spine after sudden perturbation
when might a leg length difference be relevant to a pts LBP
if:
LBP increases while weightbearing AND
LBP decreases while non-weightbearing
colon cancer what do you know about it
3rd most common cancer
usually occurs after age 50
red flags include blood in stool, pain unchanged by position or movement, pain >1 month, unexplained rapid weight loss, history of colon cancer in immediate family, smoker (?)
signs and symptoms of degenerative spondylolisthesis
tend to have focal LBP
pain may improve with lying down since this stabilizes the spine
walking may intensity pain due to lumbar spine movement
(slippage of vertebrae can cause spinal nerve root, nerve root compression (radiculopathy) or central cord compression (myelopathy)
where do disc herniations most commonly occur
at L4-L5 and L5-S1
what special test can be used to test for piriformis syndrome and how is it performed
FAIR test
pt sidelying with involved LE on top; position pts hip in 90 flexion, adduction, and IR
stabilize pelvis and press down on lateral knee to increase IR and adduction
positive = concordant pain in middle of piriformis or pain shooting down posterior thigh and leg (Frieburg sign)
88% SENS, 83% SPEC
what is recommended in the treatment of pts with acute LBP
reassure them
advise to return to normal activities (find out what exercises/movements they are most likely to do)
discourage bed rest
use NSAIDs and weak opioids for short periods
consider manipulation
maybe try lumbosacral corset transiently
try superficial heat for pain relief, improving muscular strength and flexibility
try TENS
refer to specialist if no improvement within 4 weeks
no mention of exercise
what patients are most appropriate for manipulation
mechanical LBP
mobility limitations
EROM pain
agreeable to manipulation
no/low fear avoidance beliefs
no/low irritability
no radicular or myelopathic symptoms
no contraindications
is sitting back for your back
it has been shown that sitting for 1-7 hours per day for 5 days is associated with immediate increases in LBP in people with and without a history of LBP
prolonged sitting time and prolonged driving time are significant risk factors of LBP among adults BUT
important for clinicians not to perpetuate worry that sitting down for more than 30 minutes in one position is dangerous or should always be avoided
for pts that centralize with flexion, how can you help increase walking tolerance
stretch hip flexors to increase hip extension
use overhead unloading system/alterG/pool
what is abdominal bracing
tense your entire trunk, without drawing in or pushing out
has been shown to provide greater stability than hollowing with minimal increases in spine compression
actively stabilizes the trunk and decreases L-spine displacement after perturbation
what is piriformis syndrome and what are the signs and symptoms
pain from inflamed or irritated piriformis muscle; may compress sciatic nerve and cause radiating pain
usually due to trauma, overuse, or anatomic anomalies
S&S: deep gluteal pain and TTP that may radiate down posterior thigh; + FAIR test
signs and symptoms of ureter infection, blockage, or injury
posterior pain typically located near costovertebral angle
may radiate into lower abdomen, upper thigh, groin, and genital region
can be excruciating
may have fever, malaise, etc with infection
what is retrolisthesis
backward slippage of superior vertebra on inferior vertebra
occurs after bilateral spondylolysis
usually at L5-S1 or L4-L5
less common
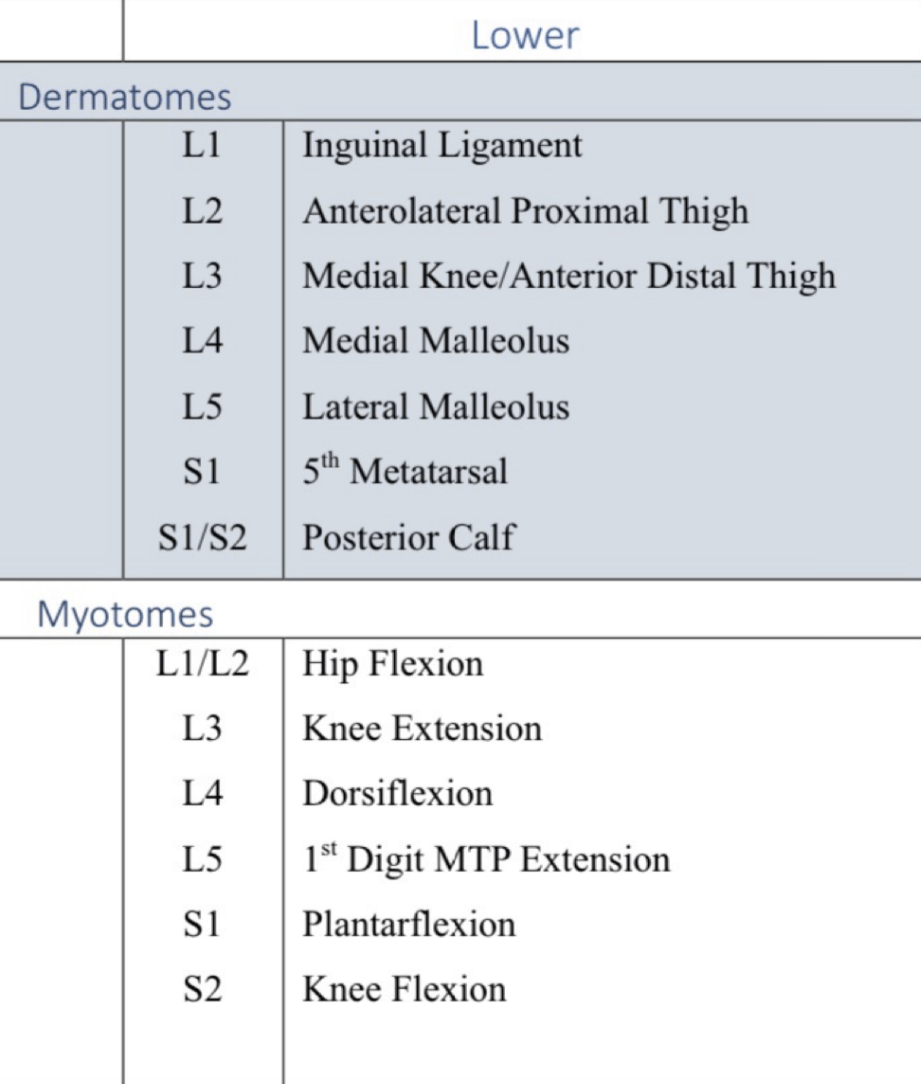
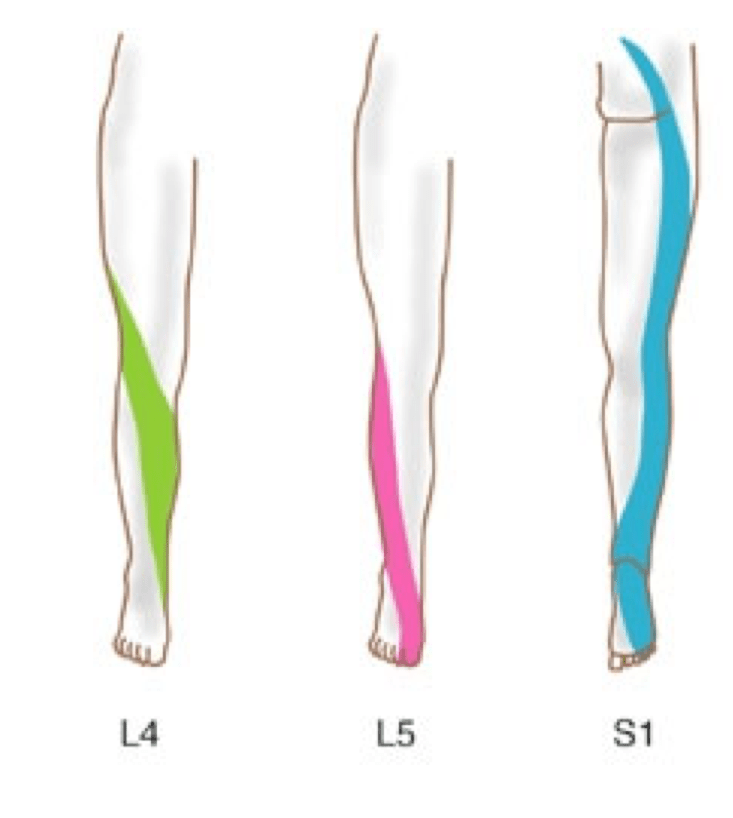
what are the lower leg dermatomes and myotomes
what does radicular pain that does not centralize suggest
poor prognosis with non-surgical treatment
consider lumbar traction, and if they don't respond to this, consider PCP referral
what are the 2 typical pt profiles for those with radiating symptoms that centralize
pts who centralize with extension or lateral flexion tend to be 30-50 years old and often have sxs of IVD pathology
pts who centralize with flexion tend to be >50 years old and often have degenerative or stenotic spinal conditions
for exercises for chronic LBP, what are the positive outcomes likely from
should you do traction for pts with radicular symptoms?
research has shown that traction has little or no impact on pain intensity, functional status, global improvement, and return to work among people with LBP but you should base your reasoning on current evidence
what does manipulation do
neurophysiologic mechanisms: decrease pain via "gate control", reflexive alteration of muscle activity; serotonin release
somewhat treatment expectations and placebo
what is important to remember about exercises for specific muscles for LBP
no one muscle is though to contribute more than 30% to lumbar spine stability, any muscle that increases spinal stiffness contributes to spine stability THUS
we should focus on training motor patterns that involve the contribution of many lumbar spine stabilizers because focusing on a single muscle, or only a few, appears to be a misdirected clinical effort if the goal is to ensure a stable spine
what value of newtons puts the spine at risk of spine injury
>3300 N increases risk of spine injury
what exercises have the highest EMG for glute med and glute max
glute med: sidelying hip abduction
glute max: single limb squat and single limb deadlift
what are good exercises for glute max (which has been proven to be weak and fatigable with chronic LBP)
single leg squat
single leg deadlift
supine leg supine bridging
single leg extension in quadruped
what two trunk flexor exercises provide high levels of oblique activity while producing low levels of spine compression
abdominal curls with torso rotation
hanging SLR to 90 degrees hip flexion
compare muscle activation and shear forces in sit ups with knees bent vs knees straight
psoas activity higher during hip-flexed sit up vs extended position
rectus abdominis torque same in both positions
compression and shear higher during hip flexed sit up
what is the cost of exercise
compressive and shear stress
overall, what do you do for someone with LBP
base POC on exam findings and current best available evidence
be encouraging, optimistic, and positive
educaterefrain from stoking fear
strike a careful balance between providing palliative interventions and promoting physical activity
carefully guide recovery with an emphasis on preventing recurrence and chronicity
benefits of exercise for LBP
decreased pain
increased self-efficacy
increased function
improved quality of life
reduced likelihood of long term disability