The acronym is SIRS
What is Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome?
Normal minimum urine output for a healthy human

What is 0.5 – 1 mL/kg?
One of these is a false statement:
A. Hypovolemic shock is associated with low cardiac output
B. Septic shock is associated with cold, clammy skin
C. Cardiogenic shock is associated with arrhythmias, MI and myocarditis
D. Obstructive shock is associated with cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, and PE
What is Septic shock is associated with cold, clammy skin?
True or False: Prior to administering the first dose of antibiotics to a patient with septic shock, blood cultures must be obtained no matter how long it is taking.
What is True?
Obtain oxygen saturation

What is the first action a nurse should take when treating shock of unknown etiology?
The medication you expect your patient with an elevated NH3 to receive
What is Lactulose?
This results from the body's systemic over-response to infection
What is Sepsis?
These organisms are the most common cause of sepsis
What is Gram-positive bacteria?
It is the definition for MODS

What is the failure of two or more organ systems in an acutely ill patient such that homeostasis cannot be maintained without intervention?
These are five ongoing monitoring that should be done for a patient with a diagnosis of shock

What is Level of Consciousness, v/s, lactic, fluids, temperature, antibiotics?
The Cardiac rhythm represented below
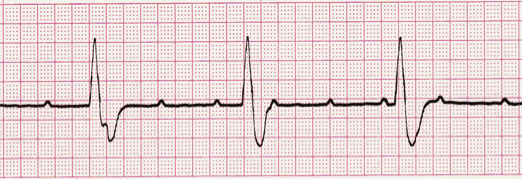
What is Third Degree AV Block?
The diagnosis you suspect when you auscultate hyperactive “tinny” bowel sounds on your patient
What is Bowel Obstruction?
The time frame during which the initial dose of antibiotics should be administered to a patient with pneumonia
What is Less than 3 hours?
It is the normal value for a venous lactate acid
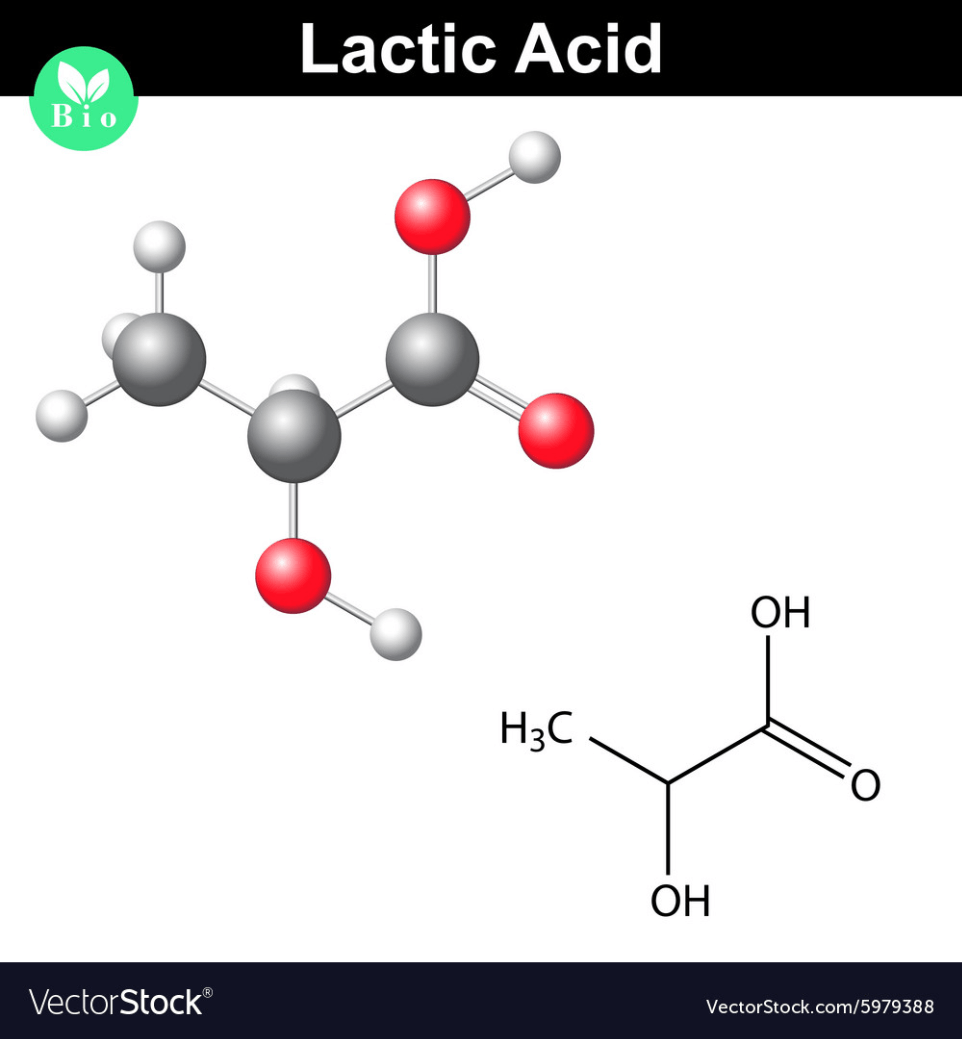
What is 0.5 – 2.2 mmol/L?
A patient is admitted into the hospital with acute agitation. Vital signs are BP 88/64, HR 120, RR Which stage of shock is the patient displaying?
What is Progressive shock?
The health care provider prescribes these actions for a patient who has possible septic shock with a B/P of 70/42 mmHg and oxygen saturation of 89%. The nurse implements these actions in this order

What is
A. obtain blood and urine cultures
B. give vancomycin (vancomycin) 1 g IV
C. infuse norepinephrine to increase B/P
D. administer normal saline 1000 ml over 30 min
E. titrate oxygen administration to keep O2 saturation > 95%
Serum Na of < 120meq/L may be indicative of DI or SIADH
What is SIADH?
At least 2 of these are national Patient Safety Goals

A. Improve the accuracy of patient identification.
B. Improve the effectiveness of communication among caregivers.
C. Improve the safety of using medications
D. Reduce the risk of health care-associated infections.
E. Accurately and completely reconcile medications across the continuum of care
F. Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting from falls
G. Reduce the risk of influenza and pneumococcal disease in institutionalized older adults
H. Encourage patients’ active involvement in their own care as a patient safety strategy.
I. Prevent health care-associated pressure ulcers
The shock classification that anaphylactic shock belongs to

What is Distributive Shock?
This intervention is the INITIAL treatment for Distributive shock?

What is IV Fluid Bolus?
Soon after the recognition of septic shock, sepsis goals ideally require administration of an antibiotic within these number of minutes
What is within 60 minutes?
A. Gram positive wounds, pneumonia
B. Surgery
C. Diabetes
D. Burns
E. New central placement
What are factors that predispose patients to sepsis?
The type of diet you expect a patient with hepatic failure to be on

What is a Low Protein Diet?
These are the 4 hospital core values

Care
Competence
Respect
Joy
The shock classification that cardiac tamponade represent

What is Obstructive Shock?
•Stop heparin
•No LMWH
•No HEPARIN
•No platelet transfusion
•Plasmapheresis or protamine to counteract circulation heparin
•Give Thrombin inhibitor (argatroban)
What is treatment of HIT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia)?
This lab helps to identify hypoperfusion in a patient with septic shock

What is Lactate Level?
These are some preventative measures in the nurse’s plan of care that best prevents the development of SIRS, shock, and multiorgan dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
What is
Private Room,
Strict hand hygiene, and
No missed doses of medications?
The ABG for this condition is:
pH 7.45
pCO2 23
HCO3 16
What is Compensated Respiratory Alkalosis?
•Fibrin Split Products (FSP) or FDP↑
•Fibrinogen level ↓
•Platelet count ↓
•PTT & PT ↑
•INR ↑
•Thrombin time ↑
•D-dimer ↑
What are lab results of a patient with DIC?