Are the breasts attached to bone?
What is NO?
What is the cardiac vein that is the final point in heart venous drainage?
What is coronary sinus?
What are the four structures with lines pointing to them(left (start with bottom) to right)?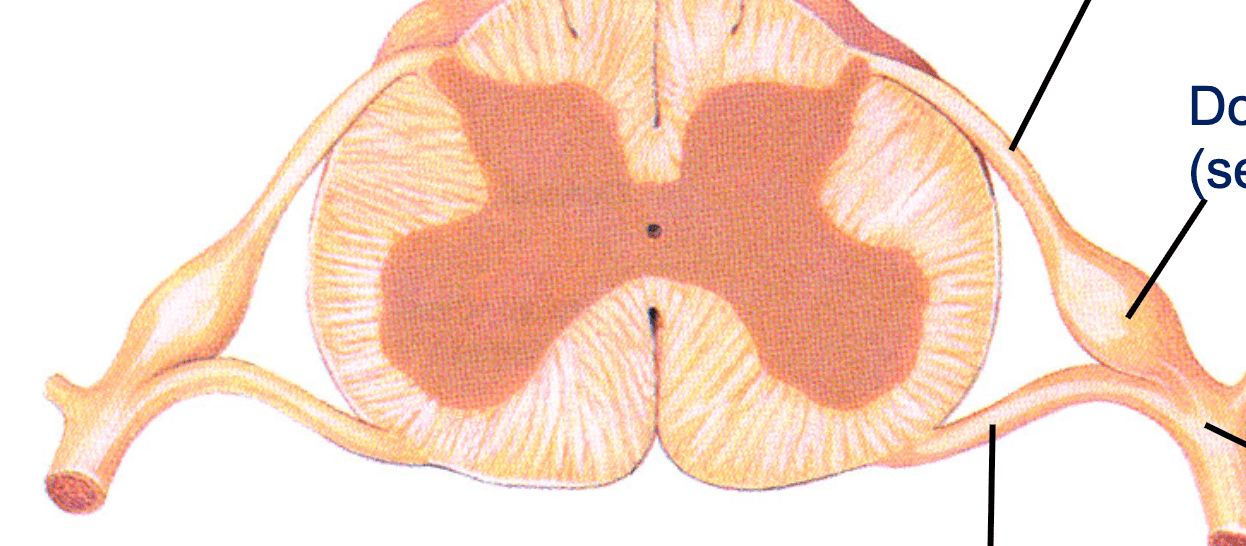
1. Ventral root (motor only)
2. Dorsal root (sensory only)
3. Dorsal root ganglion (sensory cell bodies)
4. Spinal nerve
Name the lobes and fissure(s) of each lung.
What is:
Right lung - 3 lobes (Superior, middle, inferior) with an oblique and horizontal fissures.
Left lung - 2 lobes (Superior and inferior) wiht an oblique fissure.
When do lung buds begin to develop in utero?
What is the fourth week of development?
What is the arterial supply for the posterior thoracic wall?
What is the aorta?
What nerve (and what cranial level is it at) innervates the diaphragm?
What is Phrenic nerve (C3,C4,C5)?
What are the three layers of the intercostal muscles?
What are the three levels of ribs (include numbers)?
What is
True ribs - 1-7False ribs 8-10
Floating ribs 11-12?
The apex of the heart is formed by what internal heart cavity?
What is the left ventricle?
What is the plane this image is in?
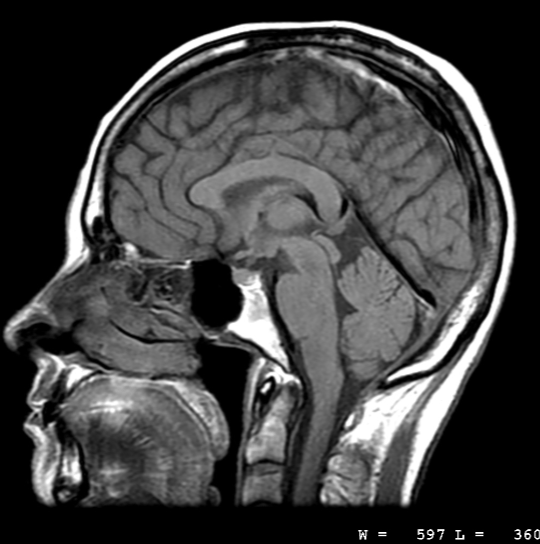
What is Sagittal plane?
What does pleural fluid allow for?
What is lubrication in respiration?
When does the zygote become a morula (in terms of cell number)? Is this bigger than it was originally?
What is 16 cells and no?
What forms an anastomosis (specifically in the thorax)?
What is the intercostal arteries?
Name the makeup of a spinal nerve and what it exits through: Include the original makeup and whats sensory and motor.
What is:
Dorsal - Sensory (afferent) - dorsal root ganglion
Ventral - Motor (efferent)
Exits through the intervertebral foramen
What is the difference between the pulmonary valve and the conus arteriosus?
What is he conus arteriosus is the smooth, muscular, outflow tract of the right ventricle, which leads to the pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary valve, also known as the pulmonic valve, is located just above the conus arteriosus?
Look at the darker portion of the first rib on the interior side. What is the vein and artery that comes through those grooves?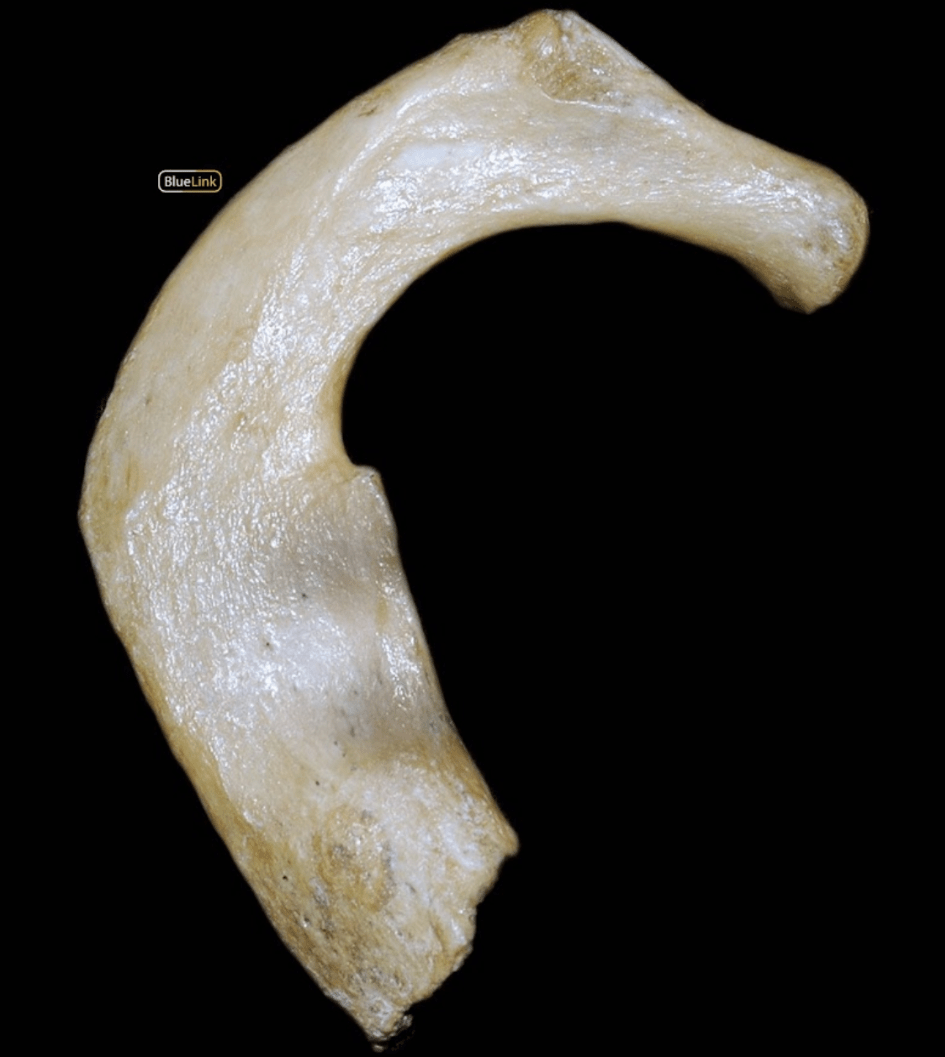
What is subclavian?
What are the three layers of the pericardium from superficial to deep (the heart itself)?
What is the fibrous pericardium, serous parietal pericardium, and serous visceral pericardium (epicardium)?
Which side of the diagram shows the muscles support expiration and which side shows the muscles supporting inspiration?
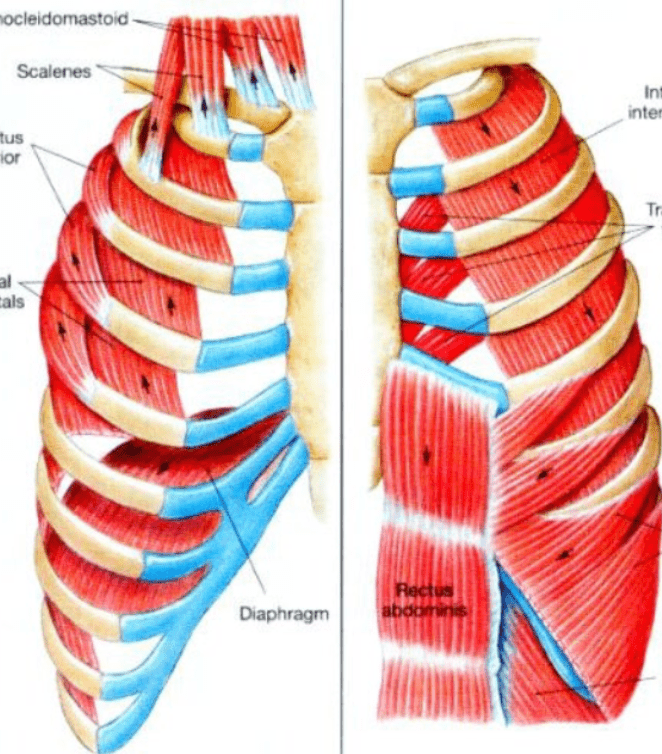
What is Inspiration (Left) and Expiration (right)?
Name the three structures that the arrows are pointing to and their function:
What is
Carina - ridge in trachea where bifurcation occurs into the right and left main bronchus?
Which of the following is NOT a primary derivative of mesoderm? heart, kidneys, lungs, ribs?
What is lungs?
What is the structure that can be easily used when doing a coronary bypass (Hint: Not on heart)?
What is one or both of the internal thoracic arteries?
The phrenic nerve originates from which spinal nerve(s)?
What is C3-C5?
What is the layer germ layer (be specific) that is the primary body segmentation?
What is Paraxial mesoderm?
What structures does the manubrium articulate with?
What is articulates with clavicle and first and second costal cartilages?
Which of the following structures is an internal feature of the right ventricle? - pectinate muscles, fossa ovalis, crista terminalis, trabeculae carneae, valve of coronary sinus
What is trabeculae carneae?
What is this germ layer and what are the individual sections and what do they develop?
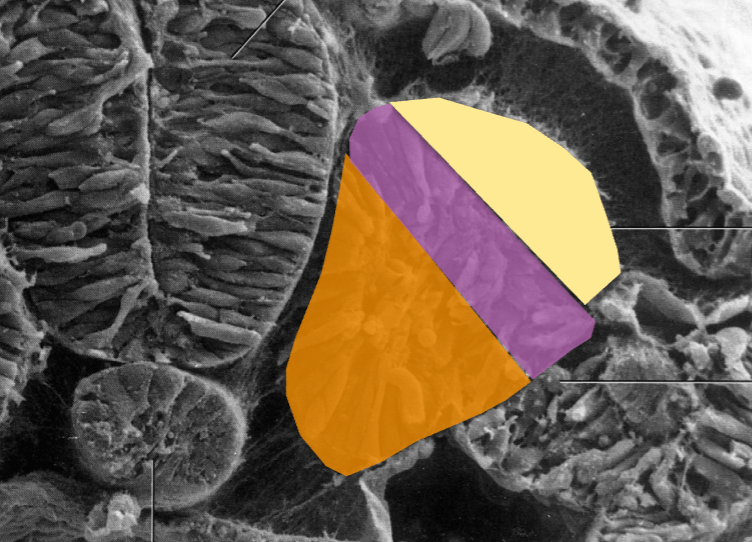
What is: Mesoderm
Orange - Sclerotome - Axial skeleton
Purple - Myotome - muscles
Yellow - Dermatome - dermal strucutures
If an object is inhaled into the trachea and continues to the lung, it is most likely to follow the path of the ______________ bronchus because _____________
What is right because it takes a more vertical path toward the lung relative to the left bronchus?
What is the function of the foramen ovale?
What is The foramen ovale is a fetal shunt allowing oxygenated blood to flow directly from the right atrium to the left atrium thus bypassing the lungs.
What is
Vein
Artery
Nerve?
What is the longest cranial nerve and how does it exit the thorax? what type of innervation is it?
What is Vagus nerve, exits through the esophageal hiatus, and it is parasympathetic?
What does the posterior interventricular artery anastomoses with?
What is the anterior interventricular branch?
What is the landmark for the difference between manubrium and body of sternum?
What is the Sternal angle?
What is the complete flow of blood from start to finish if it comes in deoxygenated including all valves if it is going out to the limbs?
What are the three main muscles we see at this level?
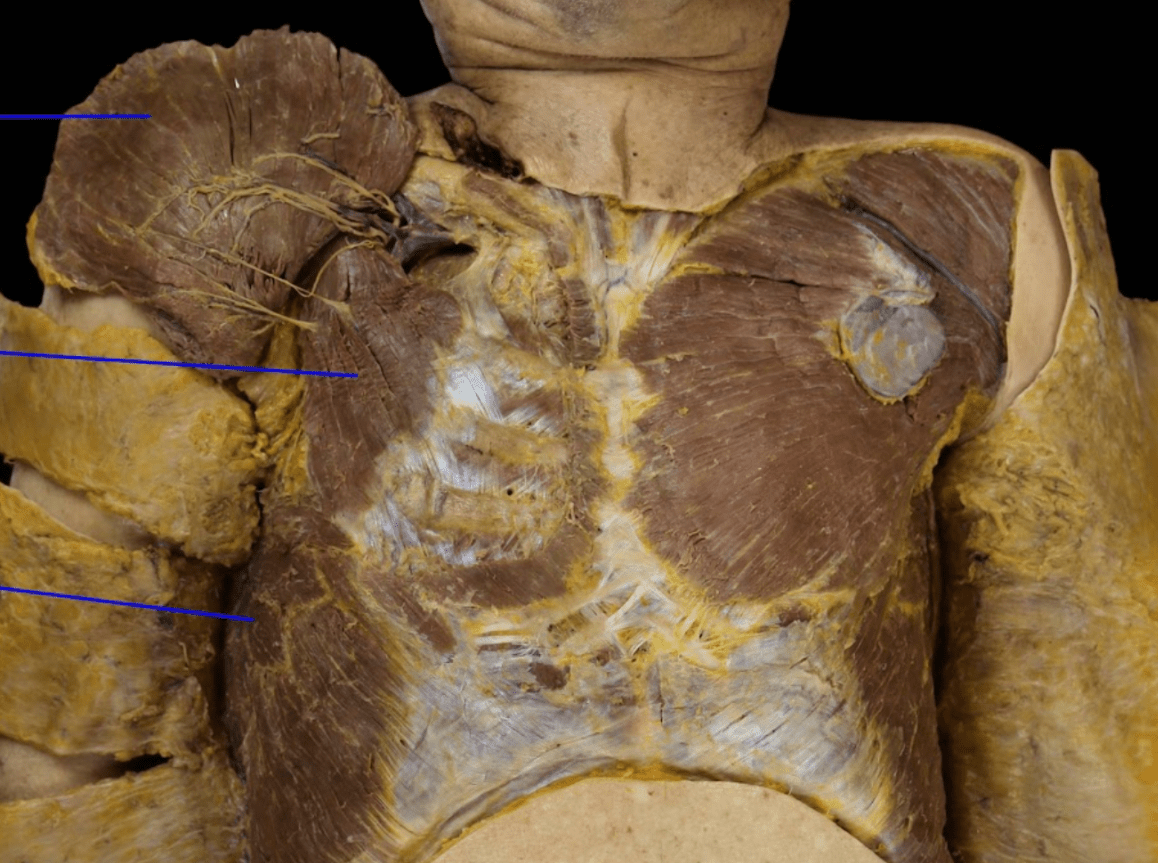
What is pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, and serratus anterior?
What is included in a bronchopulmonary segment and what does it allow in terms of "collateral" in the human body?
What is
Each bronchopulmonary segment includes a bronchus, artery, and vein. It allows if there is an issue with one that surgical intervention can occur but function can remain the same.
Name the three germ layers from superficial to deep and what the three of them make up? What week of development is this formed in?
Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm
trilaminar embryonic disc
By end of the 3rd week
The superior epigastric artery branches from which artery?
What is internal thoracic?
The right recurrent laryngeal nerve loops around what structure? right subclavian artery, ligamentum arteriosum, arch of the aorta, axillary artery, brachiocephalic trunk
Right subclavian artery
What features prevents the valves in the heart from having backflow?
What is Chordae tendinae?
What is the structures in blue?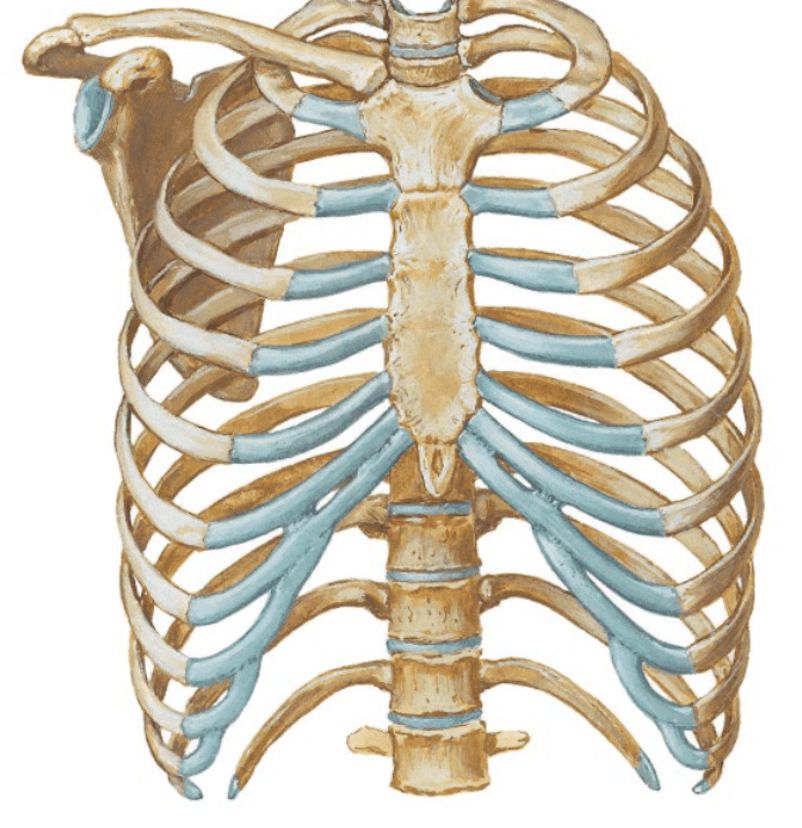
What is Costal cartilage?
In the typical heart (most common anatomy), the left coronary artery gives rise to
What is the anterior interventricular branch?
What is the structures identified by the black line and the upper right line? What chamber are we in?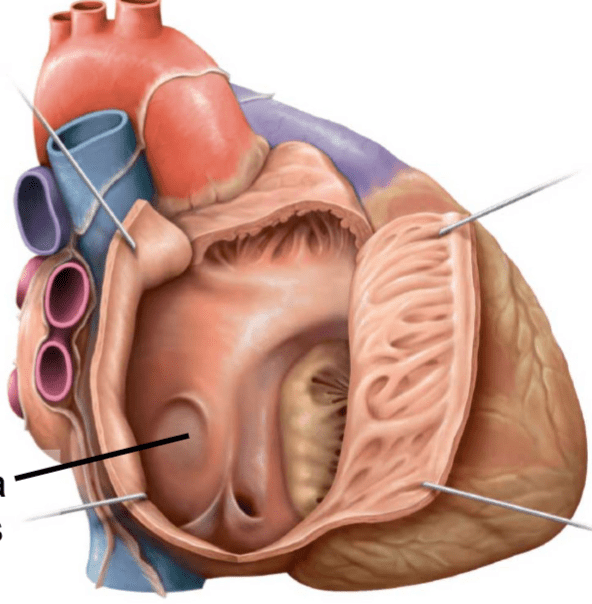
What is:
black line - Fossa ovalis
white line: pectinate muscles
right atrium?
What is the differences and functions of pulmonary arteries and veins?
Pulmonary veins take oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
Pulmonary arteries beings deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs to be oxygenated.
In neurulation, what prompts the overlying ectoderm to thicken and fold and what is the progression of structures that will eventually be the central nervous system?
What is the function of the embryonic structure, ductus arteriosus, and what is it present as in adults?
What is shunts right ventricular blood from the
pulmonary trunk to the aorta, bypassing
the nonfunctional lungs and ligamentum arteriosum?
Outflow from the central nervous system into the sympathetic trunk can be found at which spinal levels?
What is T1-L2?
What is the bilateral structure on either side of the vertebral column that provides innervation to the posterior thoracic wall?
What is the sympathetic trunk/chain?