What features on thyroid ultrasound are suspicious for malignancy.
Irregular borders, microcalcifications, gross extrathyroidal extension, taller-than-wide morphology, hypoechoic (especially if markedly hypoechoic)
What PTC characteristics help guide a decision to perform total thyroidectomy instead of lobectomy?
Tumor size greater than 4 cm, gross extrathyroidal extension, clinical nodal disease, distant metastases.
Vandetanib, cabozantinib, selpercatinib, and pralsetinib are four FDA-approved ___ for treatment of metastatic MTC.
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Selpercatinib and pralsetinibare RET-specific inhibitors with a lower side effect profile. Can be used as neoadjuvant therapy.
Describe this thyroid nodule's characteristics
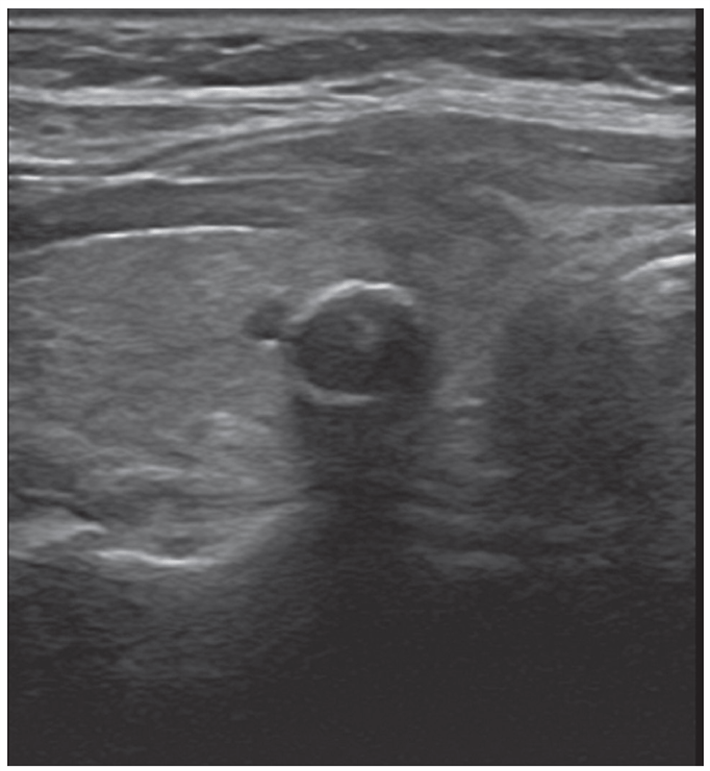
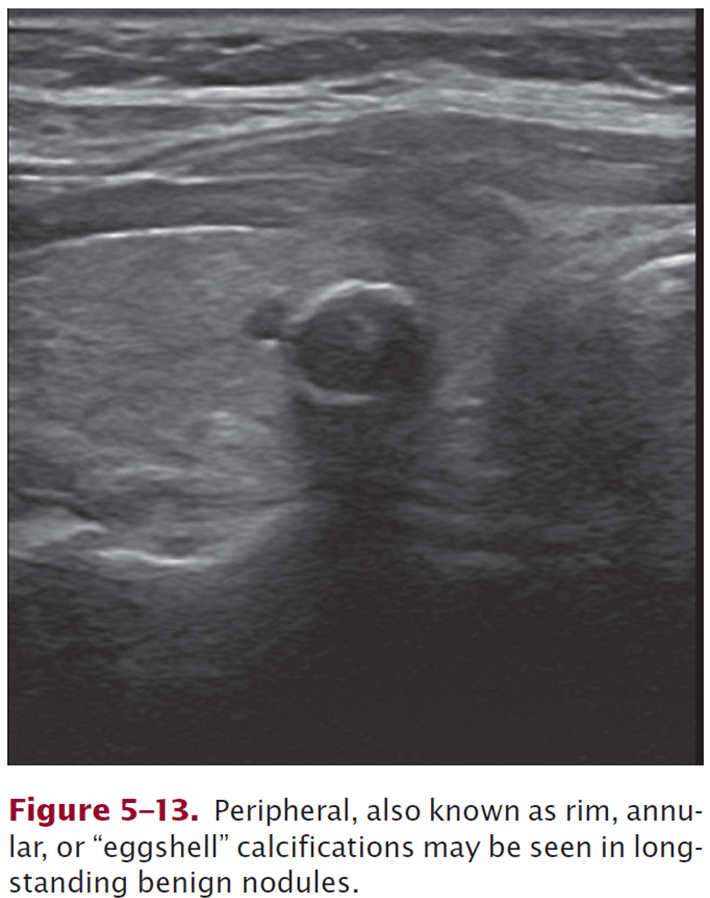
Peripheral (rim) annular (“eggshell”) calcifications may be seen in long-standing benign nodules.
The blood supply to the parathyroid glands is primarily from the _(1)_ , and should be protected during surgery by _(2)_ dissection technique.
(1) inferior thyroid artery
(2) dissection immediately on the surface of the thyroid gland medial or anterior to the parathyroids (Fig. 1)
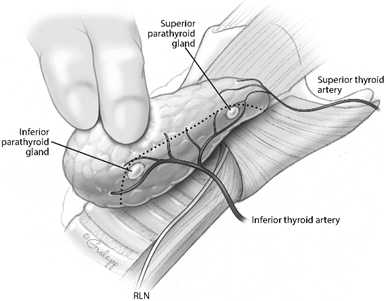
Plane of capsular dissection (dotted line) during thyroidectomy, dividing vasculature medial (distal) to the parathyroid glands in order to allow preservation of the parathyroid blood supply.
Reference: Orloff et al. American Thyroid Association Statement on Postoperative Hypoparathyroidism: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Management in Adults. Thyroid. Jul 2018.830-841.
4D CT is based on ___ of iodinated contrast by parathyroid adenomas compared to thyroid nodules or lymph nodes.
Rapid uptake and washout of iodinated contrast
- Initial noncontrast scan
- Arterial phase scan at 30 s – both thyroid and parathyroid tissue enhance
- Venous phase – thyroid tissue will continue to enhance, but parathyroid adenoma will “washout” with loss of enhancement
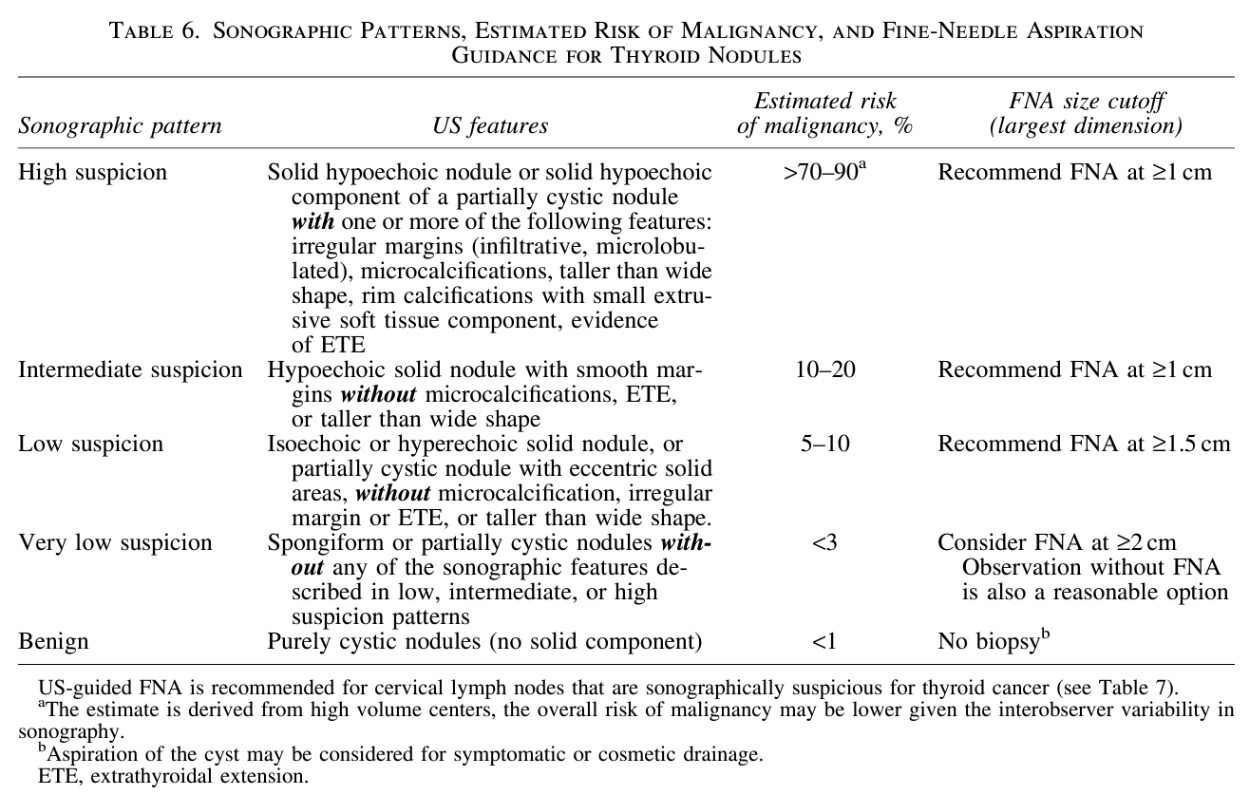
Which thyroid nodules should undergo FNA?
>1 cm and intermediate or high suspicion for malignancy
Lymph node metastases are ___ in PTC and ___ in FTC.
Lymph node metastases are relatively common in PTC and very rare in FTC.
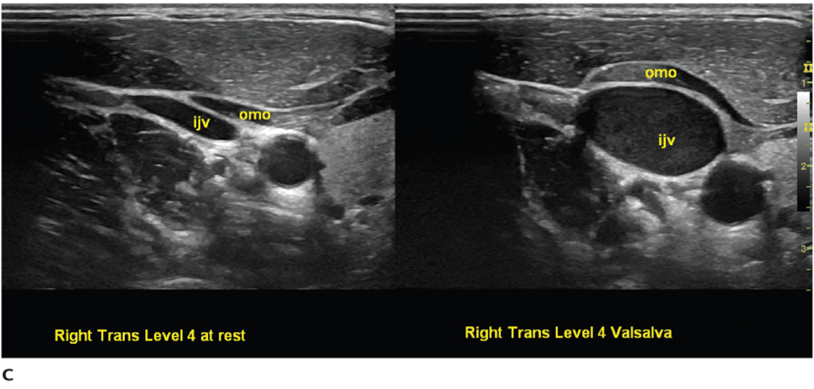
Describe the ultrasound video and what the patient is doing:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/8715/4767/2350/video4-2.mp4
Left trans carotid sheath. The IJ is compressible and increases diameter with maneuvers such as Valsalva.
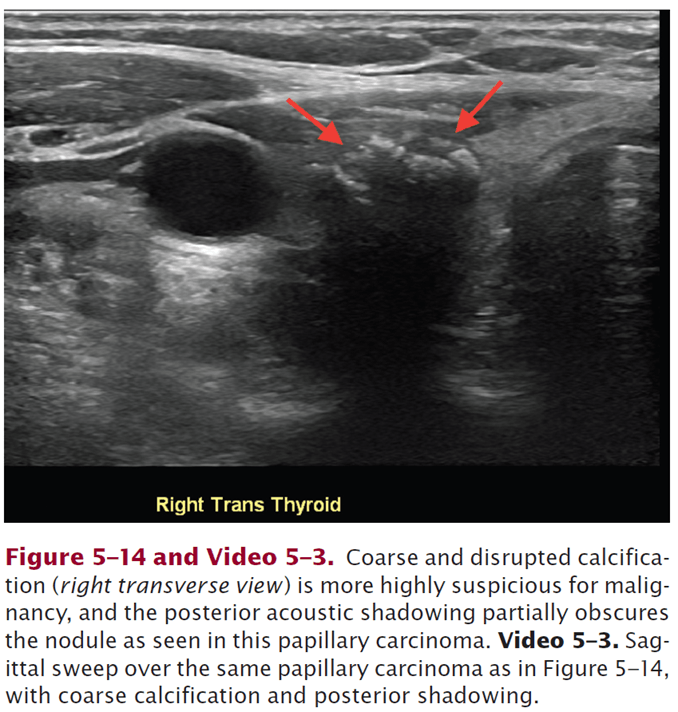
Describe this thyroid nodule: https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/7715/4767/2372/video5-3.mp4
Sagittal sweep showing coarse (shadowing posterior) and disrupted calcification in PTC.
Name five types of hyperparathyroidism.
Bonus: describe mechanism of each cause.
Primary, secondary, tertiary, parathyroid carcinoma, FHH
- Primary: autonomous hypersecretion of PTH by one or more parathyroid glands.
- - Single adenoma in 89% of cases; hyperplasia or multiple adenomas in remainder.
- - Double adenomas in 4-16%
- Secondary – chronic hypocalcemia, most commonly from CKD but also chronic vitamin D deficiency. Low calcium intake, GI disorder
- Tertiary – chronically hyperplastic parathyroid glands autonomously secrete PTH, usually after successful renal transplantation
- Parathyroid carcinoma – extremely high calcium, usually > 13 mg / dL
- Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia – mutation in intracellular part of CaSR, resulting in lack of PTH suppression in setting of hypercalcemia.
What are indications for parathyroidectomy in patients with primary HPT? (2013 guidelines)
Symptomatic or complications.
Asymptomatic with any of the following:
- Serum Ca > 1.0 above upper limit of normal
- T-score < 2.5 (lumbar spine, otal hip, femoral neck, or distal 1/3 radius)
- Fragility fracture
- eGFR < 60 mL / min
- 24-h urine calcium > 400 mg AND increased stone risk by biochemical stone risk analysis
- Nephrolithiasis or nephrocalcinosis
- Age < 50
Surgery should be considered for even healthy elderly asymptomatic patients with reasonable life expectancy, as bone density, HLD, and QOL have been shown to improve quickly after surgery.
What genetic syndromes are associated with the development of PTC?
- Cowden syndrome – mutation in PTEN. Cerebellar tumors, facial trichilemmomas, acral keratoses, and papillomatous papules
- Gardner syndrome – intestinal polyps, osteomas, cribriform-morular variant of PTC (also called FAP – Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Majority of medullary thyroid cancer occurs sporadically via a somatic tumor mutation, most commonly ___ .
RET
Describe the ultrasound exam:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/8115/4767/2352/video4-7.mp4
Transverse view of cervical esophagus at rest and during swallow.
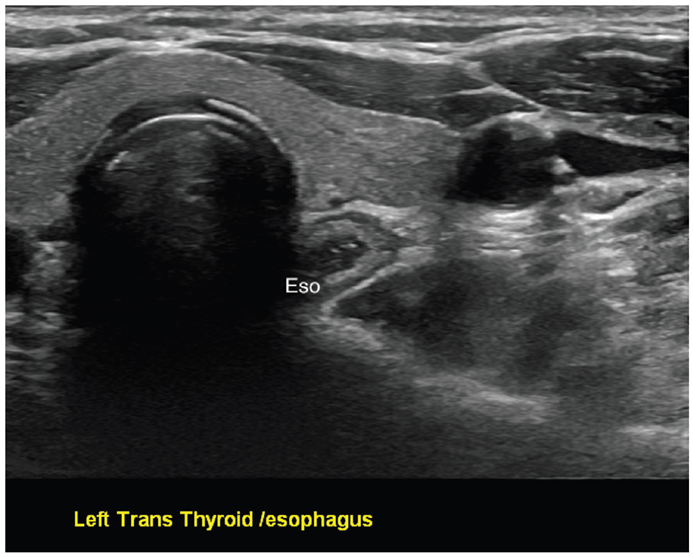
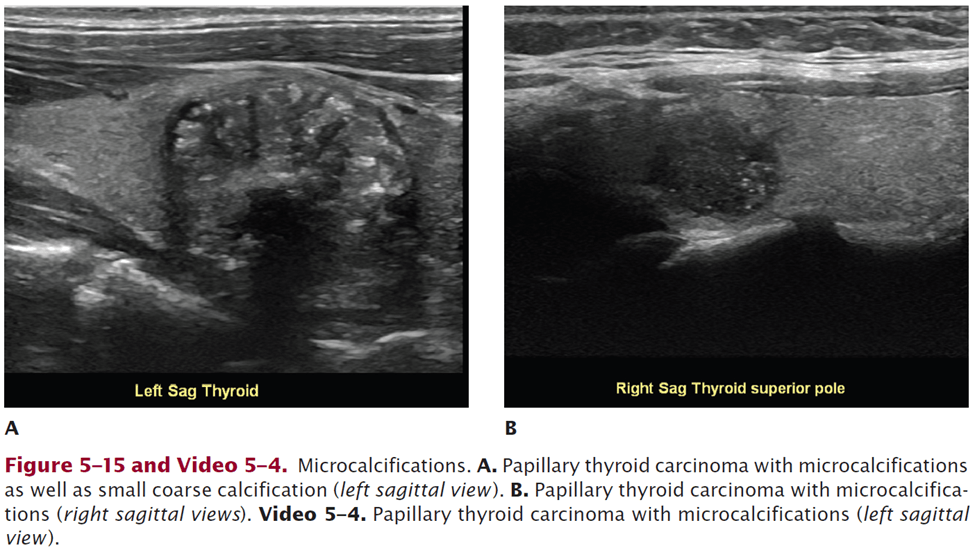
Describe this thyroid nodule:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/2515/4767/2371/video5-4.mp4
Microcalcifications – PTC nodule, left sagittal view
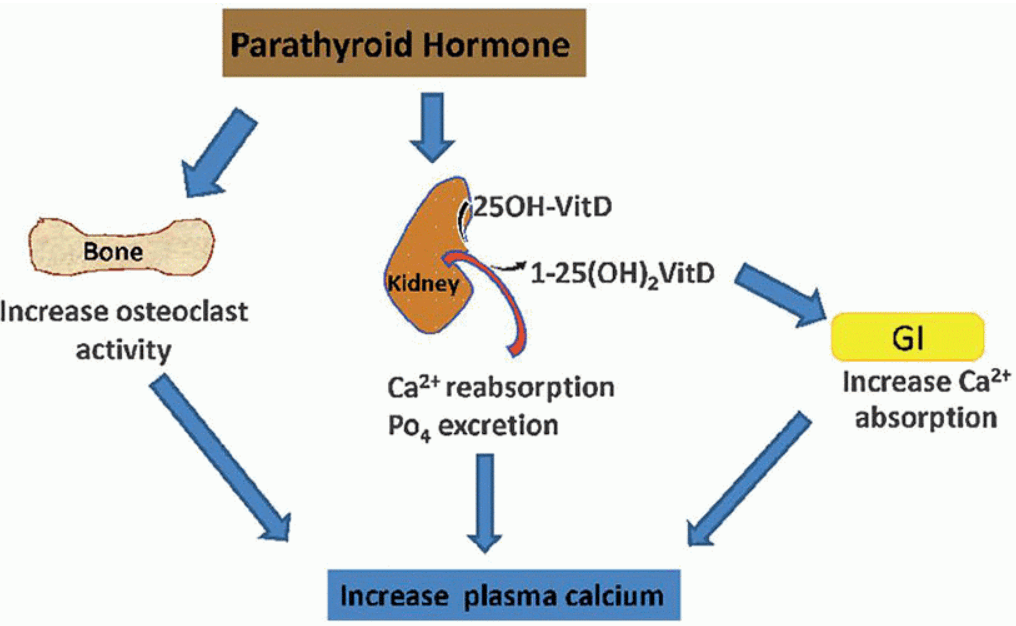
Name three actions of parathyroid hormone for maintaining serum calcium homeostasis.
- Increase osteoclast activity
- Increase kidney reabsorption of Ca and excretion of PO4
- Increase kidney conversion of 25OH-VitD to 1-25(OH)2-VitD, which increases GI Ca absorption
In bilateral ("four-gland") exploration, if a superior parathyroid gland is missing, the ___ areas should be explored. If an inferior gland is missing, exploration should first be directed to ___ . If the gland is not found in these locations, the ___ should be explored. The last location to consider is ___ .
- (1) Paraesophageal and retroesophageal areas
- (2) Thymus and superior mediastinum
- (3) Carotid sheath
- (4) Intrathyroid (intraoperative thyroid ultrasound with a small probe vs ipsilateral hemithyroidectomy?) -> Possibly, but even more likely would have performed ultrasound prior to incision and identified any thyroid nodules, which could undergo FNA/aspiration for PTH, even in the OR.
Why are well-differentiated thyroid cancers like PTC susceptible to treatment in the form of radioactive iodine?
They retain the ability to concentrate iodine, produce thyroglobulin, and maintain TSH receptors on their cell surface.
Levels of __ should be measured and help for biochemical surveillance of residual or recurrent MTC.
calcitonin and CEA
- Doubling time can serve as indicators of disease progression and predictors of survival
- *Polymerized calcitonin can form amyloid deposits
21F with sore throat and neck for 7 days. Describe her US exam:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/5315/4767/2358/video4-13.mp4
Transverse view of acute lymphadenitis, level 5 lymph node, with central radiating vascularity (hilar blood flow) on Doppler.
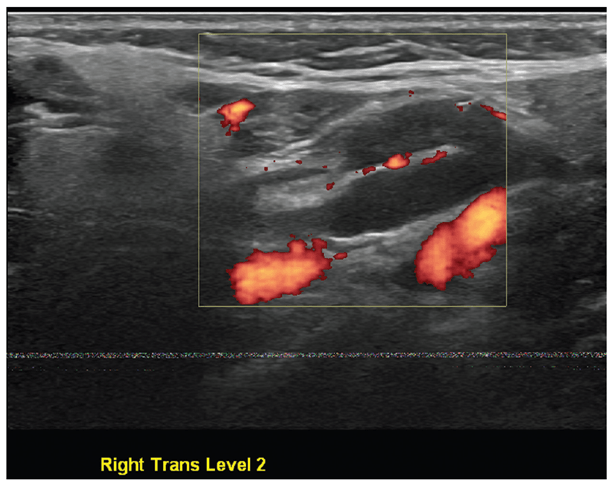
Benign right level 2 lymph node with visible hilum. A. B-mode, transverse view. B. Power Doppler showing flow within hilum, transverse view.
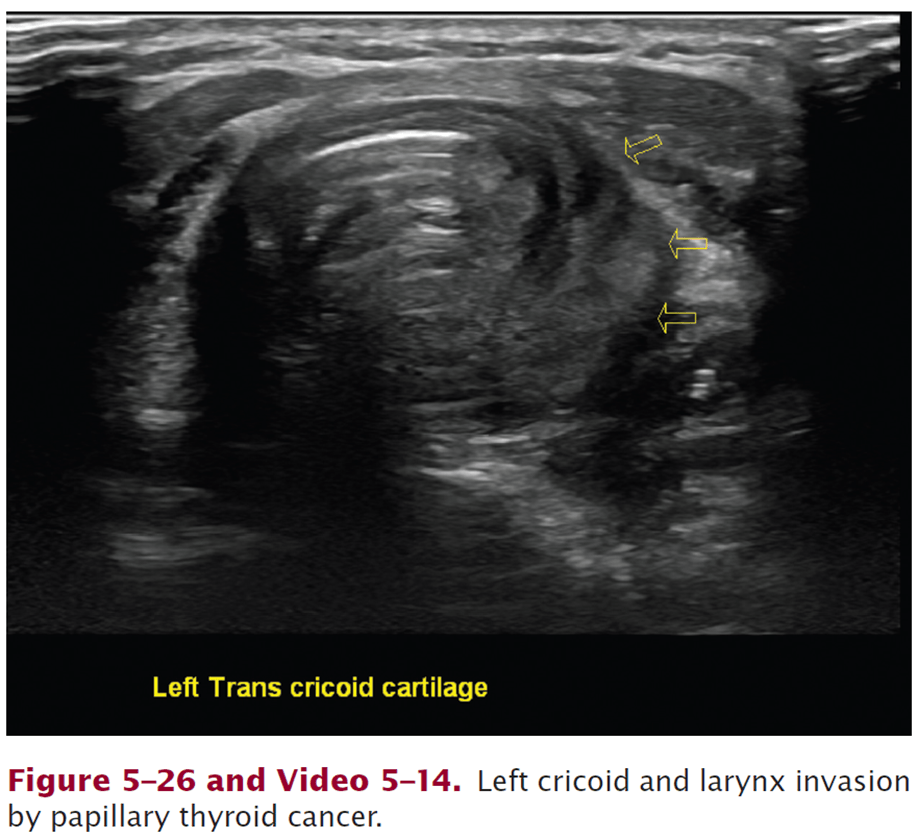
Describe this US exam of the larynx:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/5715/4767/2385/video5-14.mp4
Left cricoid and larynx invasion by PTC
During history for hypercalcemia, medications that can cause hypercalcemia should be elicited, specifically ___ (name 4).
- Thiazide diuretics, lithium, dietary supplemental calcium, and vitamin D
- Also ask about family history of hypercalcemia to assess for FHH or familial hyperparathyroidism
What extent of parathyroidectomy should be performed for secondary or tertiary HT?
- Controversial.
- Consider subtotal for younger patients, postkidney transplants, or candidates for kidney transplants. *Preserving part/half of the most normal-appearing gland, preferably an inferior (more superficial) gland.
- Consider total with autotransplantation for patients expected to undergo long-term dialysis or who are not candidates for kidney transplantation (even so, subtotal reasonable to avoid prolonged period of hypocalcemia)
BRAF mutations are ___ in PTC and ___ in FTC.
BRAF mutations are common in PTC and do not occur in FTC. (Ras mutation in FTC)
What is the surgical management of MTC?
Total thyroidectomy, bilateral central neck dissections. Lateral neck dissections if clinical lateral neck disease.
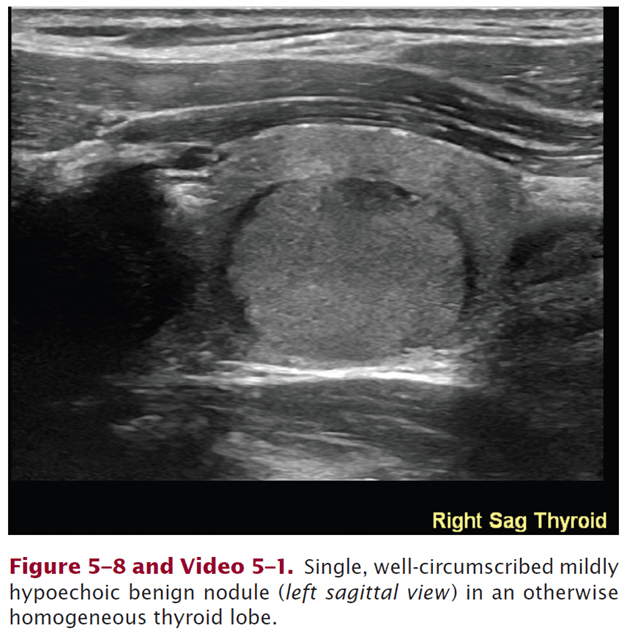
30F with palpable right thyroid lobe. Describe her US exam:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/6215/4767/2370/video5-1.mp4
Single, well circumscribed mildly hypoechoic (essentially isoechoic) benign-appearing nodule (left sagittal view) in an otherwise homogenous thyroid lobe.
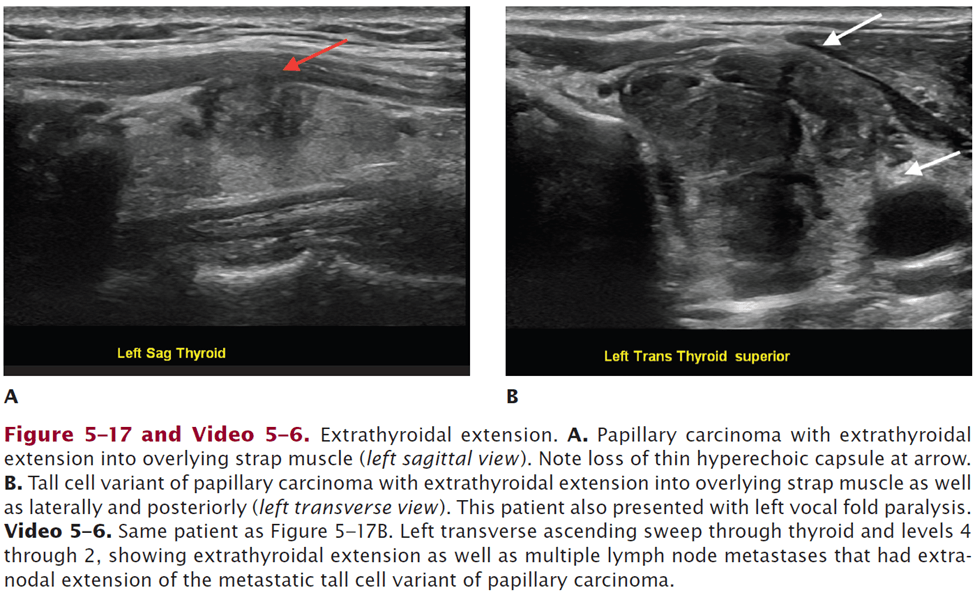
Describe US exam (ascending transverse sweep) for this patient with left thyroid mass:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/2615/4767/2373/video5-6.mp4
Left transverse ascending sweep through thyroid and levels 4-2, showing extrathyroidal extension and multiple lymph node metastases with ENE of metastatic tall cell variant of PTC. (0:05)
50F walks into clinic with bone and joint pain, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, kidney stones, polyuria, peptic ulcers, constipation, and depression for 2 years. A diagnostic workup including ___ tests should be ordered, and if showing ___ would confirm a suspected diagnosis of ___ .
(1) Plasma calcium level and intact PTH (on same day). (Can also obtain serum phosphate, 24-hour urine calcium, and vitamin D.)
(2) Elevated plasma calcium and high intact PTH level
- “Inappropriate” midrange to upper limits of normal PTH level (normohormonal variant) also diagnostic.
- Serum phosphate should be low. 24-hour urine calcium is normal or elevated.
(3) Primary hyperparathyroidism
50F with bone and joint pain, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, kidney stones, polyuria, peptic ulcers, constipation, and depression for 2 years. Describe her ultrasound exam:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/9715/4767/2351/video4-3.mp4
Transverse sweep inferiorly reveals hypoechoic right descended superior parathyroid adenoma detected inferior to the right thyroid lobe in level 6 (and found deep to RLN at surgery).
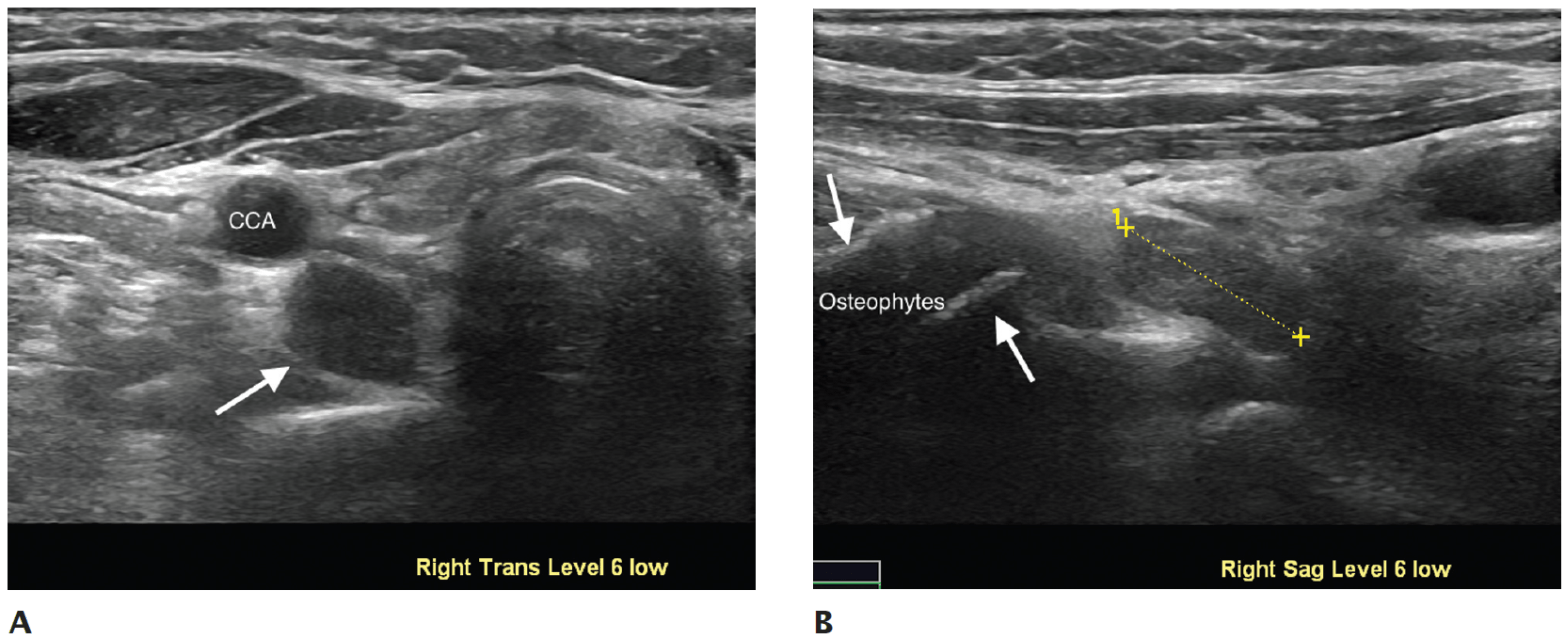
Hypoechoic right inferior parathyroid adenoma detected inferior to the right thyroid lobe in level 6. A. Transverse view. B. Sagittal view.
What distinguishes stage I and stage II differentiated thyroid cancers for patients younger than 55 years old (AJCC 8th edition)?
Distant metastases

By what age should children with the following inherited MEN2 mutations undergo prophylactic total thyroidectomy?
- MEN2B children with the highest risk: ___
- MEN2A patients with high risk: ___
- MEN2A with moderate risk: ___
- <1 year
- <5 years
- when calcitonin levels become elevated or when parents no longer wish to continue evaluation
Describe this transverse US image of the left thyroid
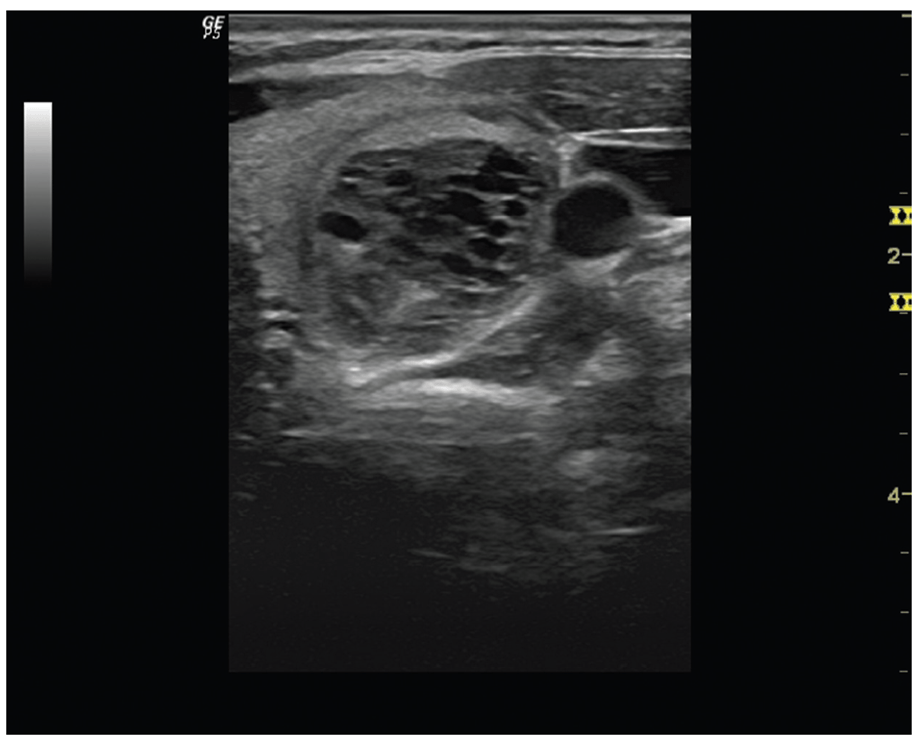
Spongiform nodule with internal microcystic appearance, involving more than 50% of lesion.

[Hard] Describe this lateral neck US exam for patient with diagnosis of PTC:
https://www.pluralpublishing.com/application/files/3015/4767/2379/video5-10.mp4
Primary PTC in right thyroid lobe with lymph node metastases in levels 2-4. Note abnormal nodes indenting IJ and extending superior to carotid bifurcation.
Cervical node mets can have same characteristics of malignant thyroid nodule, including microcalcifications, cystic degeneration, peripheral or diffuse vascularity, enlargement, rounded shape, loss of hilar strip, and irregular borders with extracapsular extension.
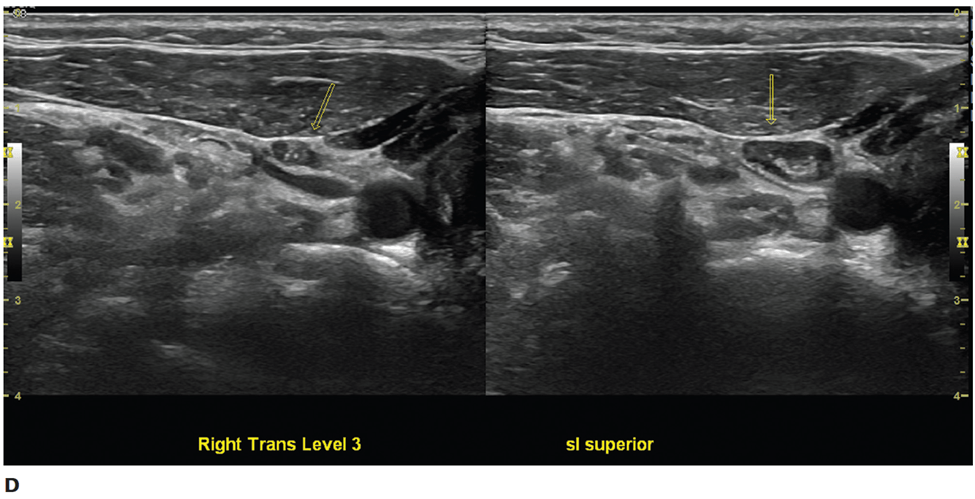
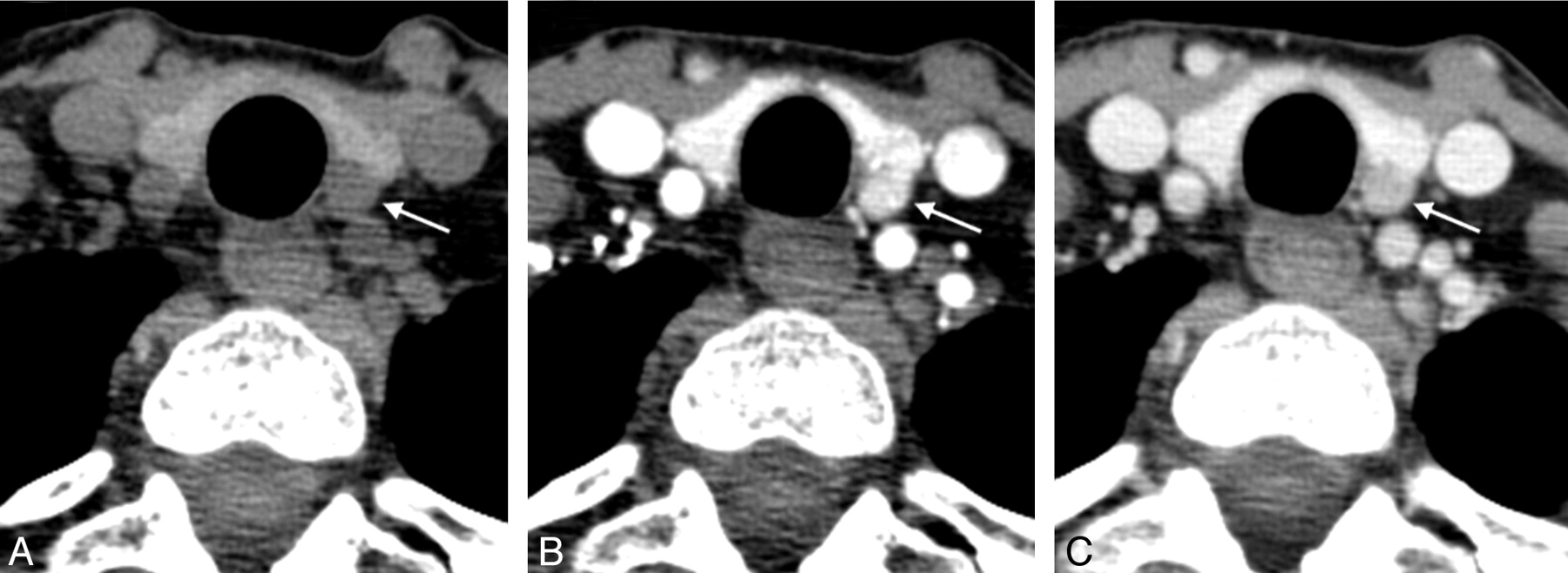
Small but multiple lymph node metastases from papillary carcinoma, showing microcalcifications despite oval shape and visible hilum (right transverse view ).
50F walks into clinic with bone and joint pain, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, kidney stones, polyuria, peptic ulcers, constipation, and depression for 2 years. Plasma Ca 11.5, intact PTH 75 pg/mL, 24-hour urine Ca 50 mg. A diagnostic workup of ___ tests should be ordered to evaluate for ___ .
(1) 24-hour urine calcium, plasma calcium, and urine and serum creatinine levels to calculate calcium-creatinine clearance ratio, to help differentiate primary HPT from FHH.
- Ratio greater than 0.01 is consistent with primary HPT
- Ratio less than 0.01 is suggestive of FHH
- Family history of hypercalcemia should also prompt consideration of FHH.
50F has a rapidly enlarging 2.1 cm nodule in the left inferior thyroid pole. FNA demonstrates significant dedifferentiation with no recognizable normal thyroid histopathology, consistent with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Ultrasound reveals no suspicious lymph nodes. PET-CT shows no distant metastases. What is the overall clinical stage?
All ATC are stage IV by the 8th edition of AJCC