Order of medications given during RSI
What is pre- med, sedation, paralytic?
First, any pre-medications (Lidocaine, Atropine)
Second, induction agent (Versed, Etomidate, Propofol, Ketamine) for sedation.
Last, paralytic (Succinylcholine, Rocuronium, Vecuronium, Pancuronium) for jaw relaxation.
Location/Type of MI?
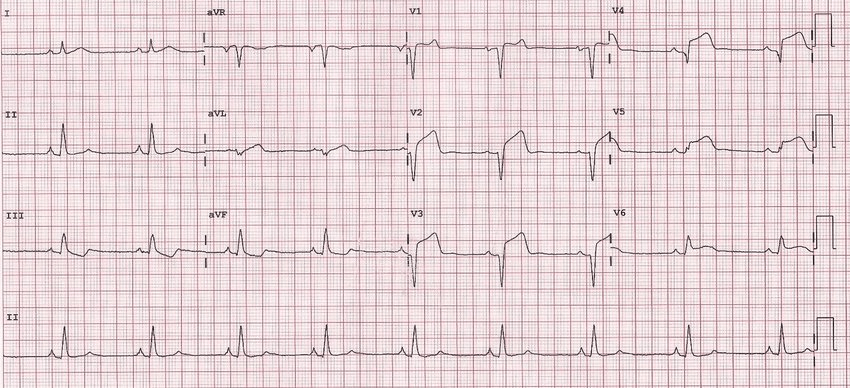
What is an Anterior STEMI?
Antiarrhythmic used for both atrial and ventricular arrhythmias
What is amiodarone?
Name 2 Signs and symptoms of tension pneumothorax
What are: SOB, chest pain, hypoxia, tachycardia, tachypnea, absent lung sounds, tracheal deviation
These 3 things make up stroke volume
What is preload, afterload and contractility?
List types of sedation on the sedation continuum
What is anxiolysis, moderate sedation, deep sedation, and general anesthesia?
Documentation to use in EPIC if giving One-Step Meds to Code STEMI
What is the STEMI Narrator
Positive inotrope used to lower both preload and afterload causing increased cardiac output
What is dobutamine?
The below patient has a transvenous pacer. How should you adjust it based on the below strip?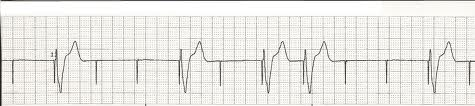
What is increase the energy or output?
The anatomical location where the arterial line transducer should be positioned.
What is the phlebostatic axis or right atrium?
This event occurs at the same time as the first dose of sedation
What is the time out?
Changes seen in Leads V1, V2, V3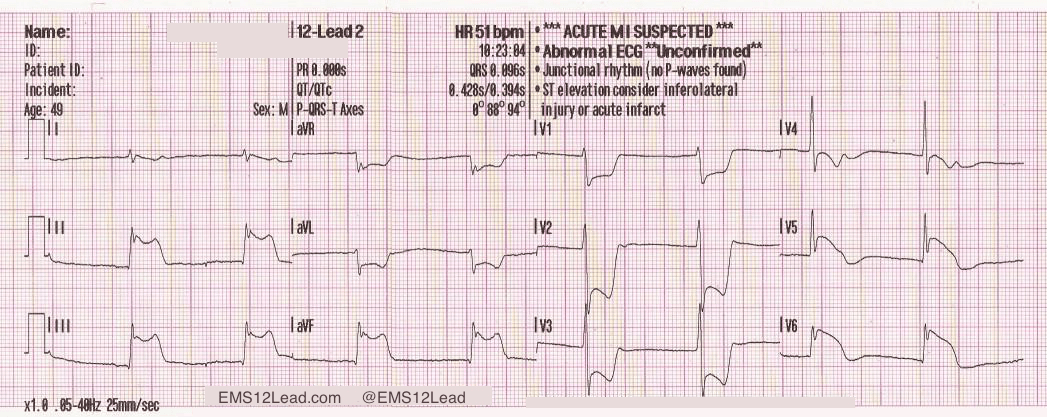
What are reciprocal changes?
Medication used for hypotension caused by low SVR
What is levophed?
The steps in the ACLS algorithm for the below rhythm
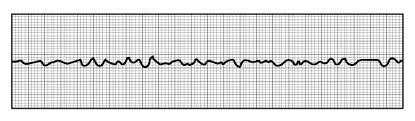
1. Check patient, call Code Blue, begin CPR
2. defibrillate ASAP
3. give 1 mg epinephrine IVP, continue CPR
4. give 300 mg amiodarone IVP.
One possible Indication for therapeutic hypothermia
What is ROSC after witnessed cardiac arrest?
Type of sedation where patient is no longer following directions and airway is compromised
What is deep sedation or general anesthesia?
Type of MI where hypotension and heart blocks can occur (NTG may be contraindicated)
What is an Inferior MI?
Medication used to increase cardiac output by increasing heart rate and diminishing parasympathetic tone
What is epinephrine?
Type of shock suspected in STEMI patient brought into the ED with the following symptoms.
- Rapid breathing
- Severe shortness of breath
- Sudden, rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Loss of consciousness
- Weak pulse
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Sweating
- Pale skin
- Cold hands or feet
- No urine output
What is cardiogenic shock?
What is increase BP by increasing SVR?
Capnography Phase DE below 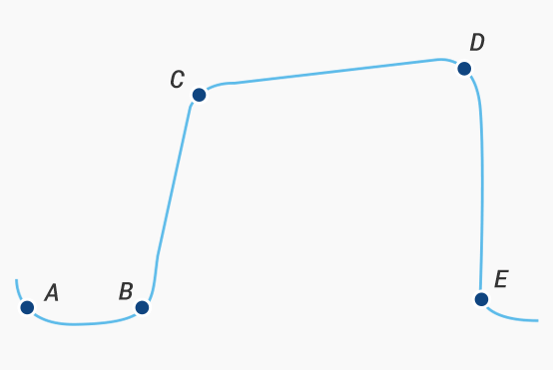
What is inspiration?
Leads V7, V8, V9
What is a posterior ECG or additional leads that confirm diagnosis of a posterior MI?
Relaxes smooth muscle thereby decreases PVR and SVR, also causes venous dilation and decreases preload
What is Nipride or Nitroglycerin?
Transvenous Pacer setting changes needed in the below patient
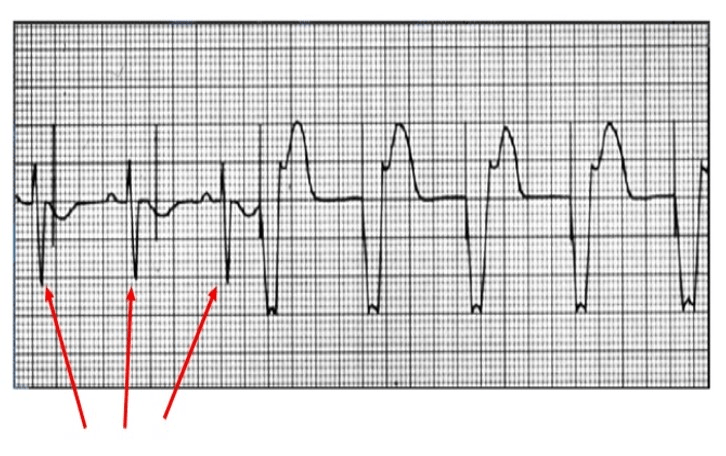
What is increase the sensitivity?
Signs and symptoms if patient has low cardiac output