Cells that cover _____ or _______ surfaces form epithelial tissue
Internal, external
Connective tissue is sometimes exposed to the outside environment. True or False?
False, it is never exposed
What is muscle tissue made up of?
Protein filaments
Covers body surfaces, line body cavities, form protective sheets around organs
Which tissue has continuous regeneration of damaged cells?
Epithelial tissue
What are the types of epithelial tissue?
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
Which one is not a function of connective tissue?
A. Support and protect other tissues
B. Defend against microorganisms
C. Send messages to brain
C. Send messages to brain
What tissue(s) is(are) striated?
What are striations?
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/skeletal-muscle/0kdrKFzTosiUmeSgQIFJjQ_Skeletal_muscle_01.png)
Cardiac and skeletal
repeating groups of muscle filaments
The diminished ability to activate vitamin D leads to
Reduced skeletal health
What is the function of nervous tissues?
Where are they mostly found?
Transmission of electrical impulses
Brain and spinal cord
If epithelial cells have multiple layers what is it called?
What stratified tissues is found in areas with high mechanical stress?
stratified
stratified squamous
_________ connective tissue contains collagen fibers and fibroblasts that stabilize connections between body structures.
Dense Regular, Fluid, or Loose?
Dense Regular
Which type of muscle tissue contains 1 nucleus?

Cardiac
What is the ABCDE rule for detection?
What is the rule detecting?
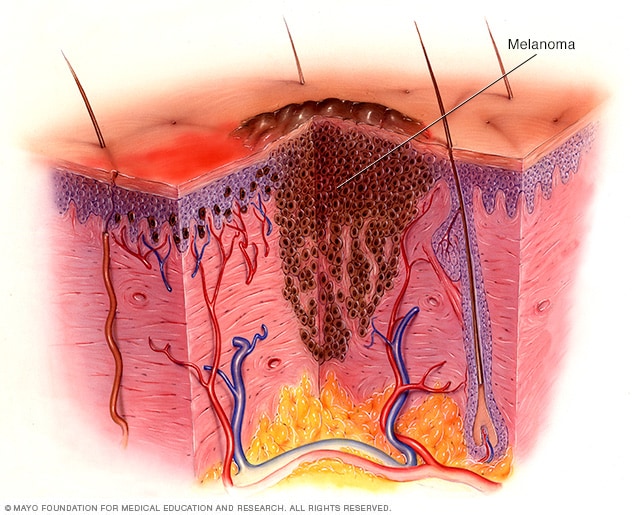
Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolution
Malignant Melanoma
How many types of nervous tissues are there
What are they?

2
Neurons and neuroglia
What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
Give an example of an exocrine gland

Exocrine discharge secretions to the outside, Endocrine secrete directly into tissue fluid or blood
Sweat glands
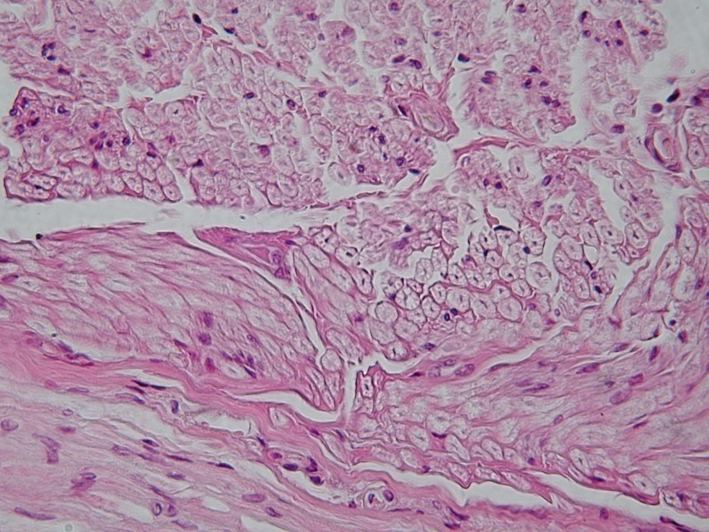
What are the only two types of fluid connective tissue?
What is one of their functions?
Blood and Lymph
Transport oxygen/carbon dioxide/nutrients/wastes
Which type of muscle tissue is found in various hollow organs?
What is the function?

Smooth
Contraction of hollow organs
List the layers of the epidermis from deepest to most superficial
Label 5 parts the skin diagram

Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, hair shaft, pore, dermal papillae, adipose tissue, hair follicle receptor
What the main functions of hair
Where will you NOT find hair?

Temp regulation
palms, soles, lips, nipples
What epithelium tissue is a mixture of columnar and cubodial cells that appears layered, but all cells touch the basement?
Where is the PCC located? Trachea or Bladder?
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar
Trachea
What is the Extracellular Matrix?
What are the parts in the Extracellular Matrix?
Non-living material that surrounds living cells
Fibroblast, macrophages, mast cells, collagen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers
What is the main purpose of muscle tissue?
Name 2 things that will happen without our muscle tissue
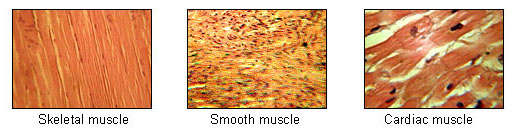
To produce movement
Muscle atrophy and death
List the layers of the epidermis from deepest to most superficial
Name which layer has cells undergoing mitosis

Stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
Stratum basale
What are the 4 types of epidermal cells?
Name the function of 2 of the cells
Keratinocytes, melanocytes, langerhans cells, merkel cells
produces keratin, produce the pigment melanin, produce immune response against pathogens, detect/touch sensations