Label the picture provided
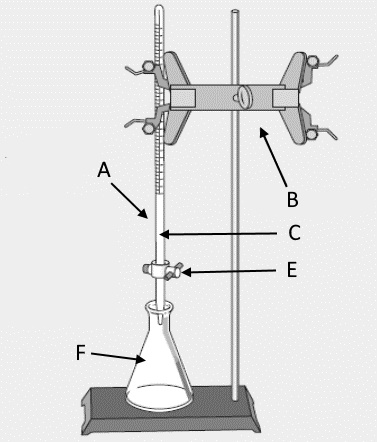
A: burette B: clamp C: titrant D:stand E: Stopcock F: Erlenmeyer flask
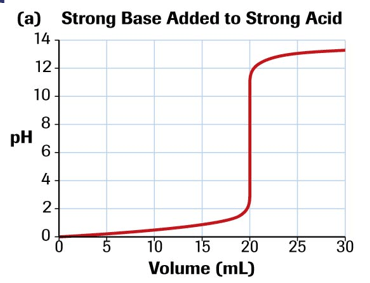
Describe the shape of a curve of a strong acid titrated with a strong base
Which is a precipitate reaction?
(A) SO3 + H2O --> H2SO4
(B) 2AgNO3 + Na2S --> Ag2S + 2NaNO3
(C) CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O
What is RXN B?
(2AgNO3 + Na2S --> Ag2S + 2NaNO3)
Cu + AgNO3 --> Ag + CuNO3 If 9.21 g of copper forms Silver and you also use 17.9 g of silver (I) nitrate, which is your limiting reagent?
What is Silver (I) nitrate.
Describe the shape of a curve of a strong base titrated with a strong acid and the equivalence point value.
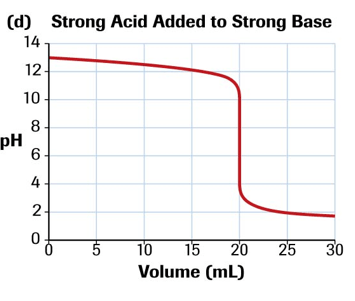
equivalence point=pH=7
Which indicator would be most useful in identifying the equivalence point of a titration for a solution that has an [H3O+] of 0.02 mol/L at the equivalence point?
What is cresol red (pH range for color change is 0.0-1.0)

Al2(SO3)3 + 6 NaOH ----> 3 Na2SO3 + 2 Al(OH)3 Determine the number of grams of excess reagent left over in the reaction.
What is 1.84 grams NaOH.
Describe the shape of a curve of a di-protic acid titrated with a strong base


A 50.6 g sample of Mg(OH)2 is reacted with 45.0 g of HCl according to the reaction: Mg(OH)2 + 2 HCl --> MgCl2 + 2 H2O What is the theoretical mass of MgCl2?
What is 58.6g of MgCl2
Describe the shape of a curve of a di-protic base titrated with a strong acid
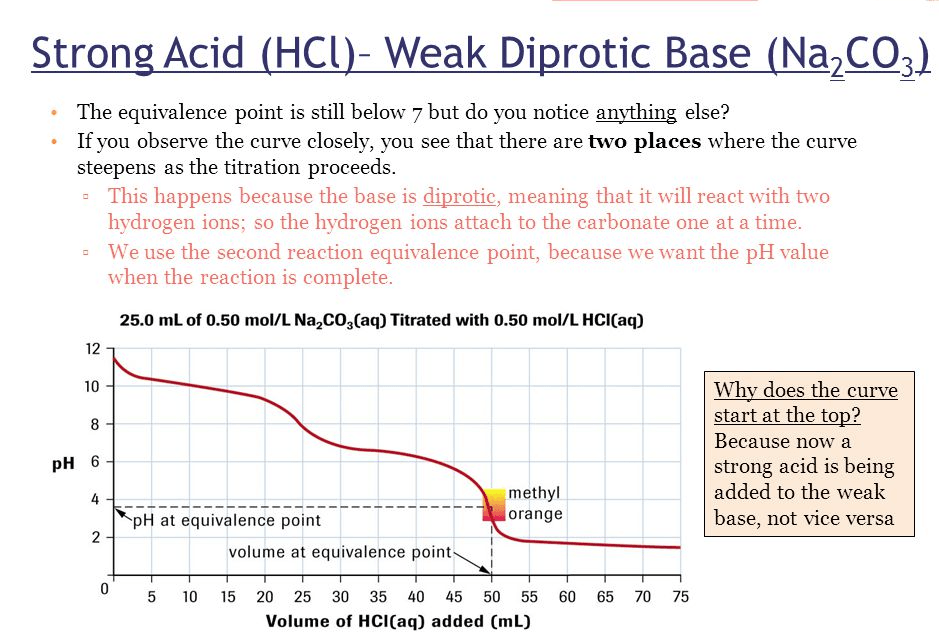
Name of solution in the burette during a titration.
What is the titrant?
During the titration of HCl with NaOH, a very rapid change in pH occurs at the equivalence point which is:
a. when the first addition of known solution is made.
b. when roughly equivalent amounts of H3O+ ions and OH- ions become presen
c. at several point
d. at no point.
What is b?