The substance that is slowly dripped, in other words, titrated.
What is the titrant?
A piece of equipment used to slowly drip the titrate into another laboratory glassware at the bottom.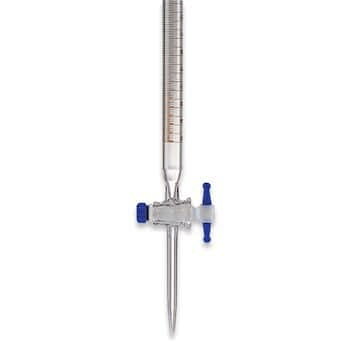
What is a burette?
The point at which the reaction is complete in a titration, can be indicated by the changing of color if an indicating substance is added.
What is endpoint?
A technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution using a solution of know concentration.
What is titration?
The type of titration commonly used by pharmaceutical and chemical companies to determine the pH, and in turn, the concentration of a substance.
What is an Acid-Base titration?
The formula for molarity.
What is moles of solute/liters of solution?
A piece of equipment used to hold the titrate dispensing structure.
What is a burette stand?
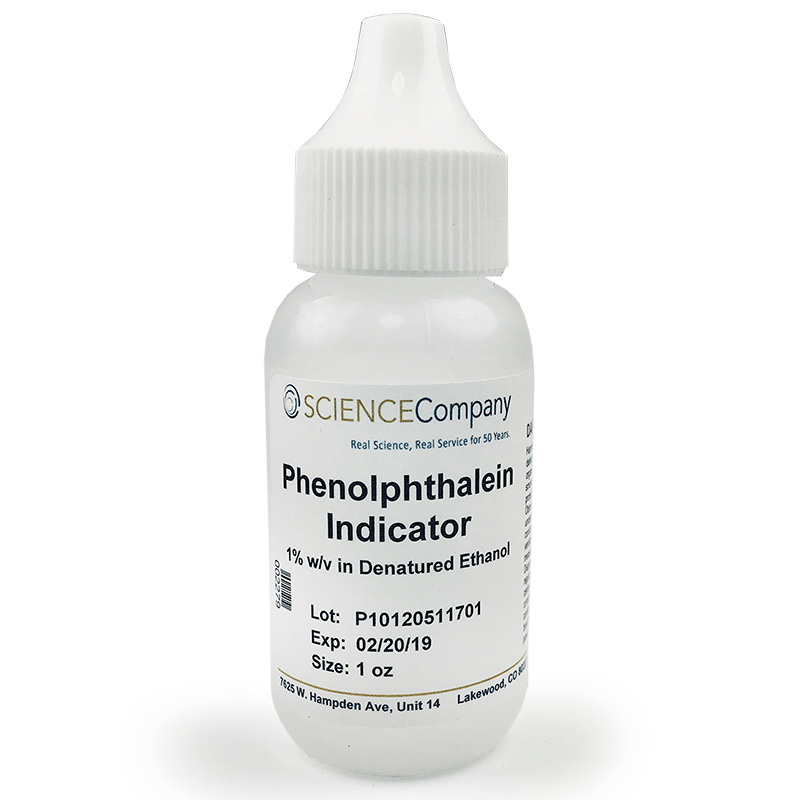 A chemical substance used to signal the chemical reaction has been completed.
A chemical substance used to signal the chemical reaction has been completed.
What is an indicator?
The technique and process of determining the exact concentration of a substance, most commonly calculated in molarity.
What is standardization?
In the medicine industry, acid-base titrations are used to ensure this safety quality of all produced medications.
What is analyzing the purity?
What is molarity (M)?
A piece of equipment that the titrate is slowly dispense into. Can depend on type of titration being performed, but this is the most commonly used.
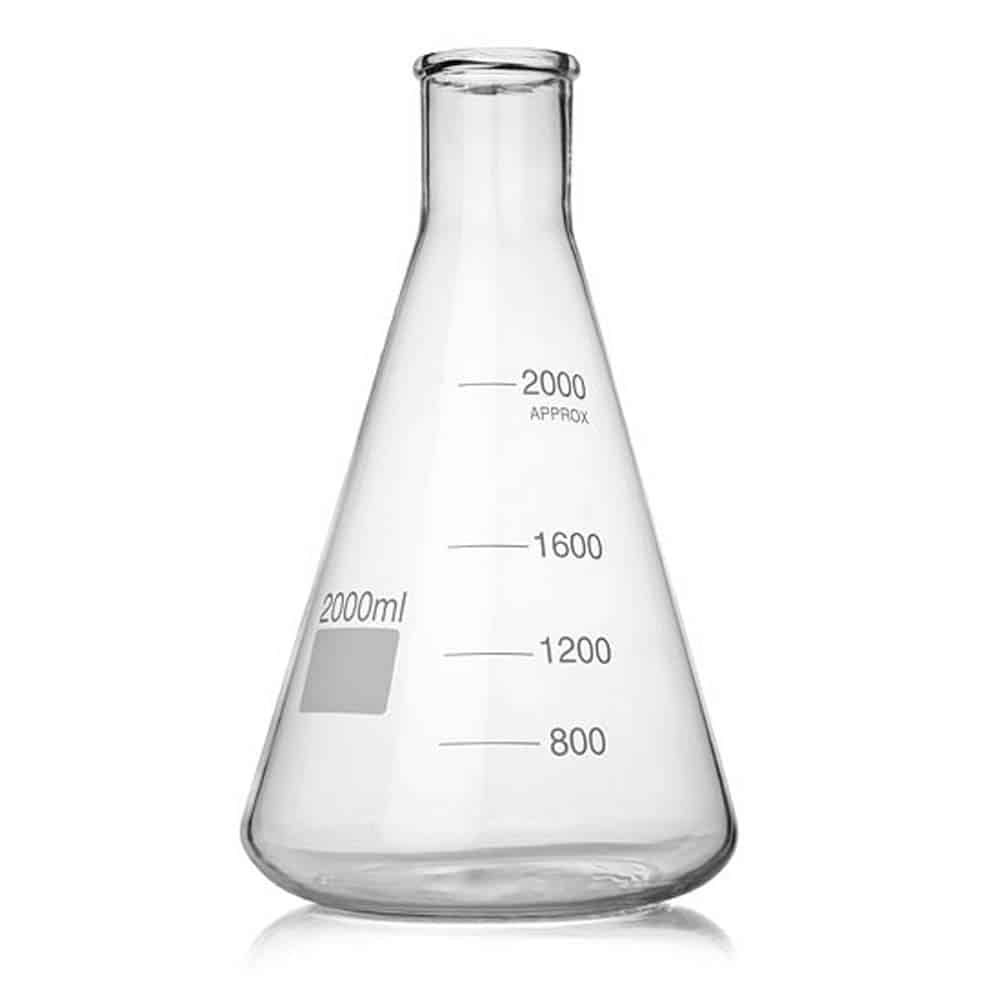

What is an Erlenmeyer flask?
The structure at the bottom of the burette used turned to dispense titrant.
What is the stopcock?
Most of the time, this process needs to be performed to perform a titration correctly.
What is a standardization.
Since titrations are used to as a quantitative analysis tool determining the numerical value of certain substances, this name is used by many to refer to titrations.
What is volumetric analysis?
The known substance of a known amount that the titrant is titrated into.
What is the titrate/analyte?
A piece of equipment used to constantly keep the solutions mixing.
What is a stir plate?
The stopcock turned in this orientation allows titrant to flow out. The stopcock turned in this orientation does not allow titrant to flow out.
What is vertical? What is horizontal?
This process and equation is sometimes used to complete standardizations.
What is a dilution?
Titration techniques are used by food manufacturers to determine this in a sample of product.
What is the quantity of a rectant.
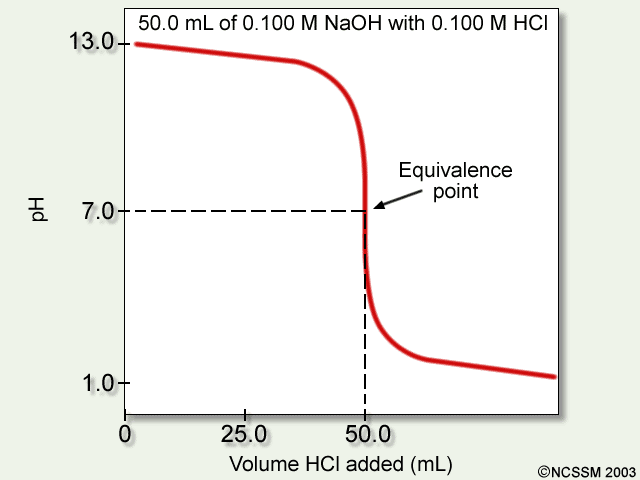
The exact point in a titration in which the moles of the substance being titrated is equal to the number of moles of titrant.
What is the equivalence point?
A piece of equipment used in some titrations to determine the pH of the titrand, used to determine the equivalence point.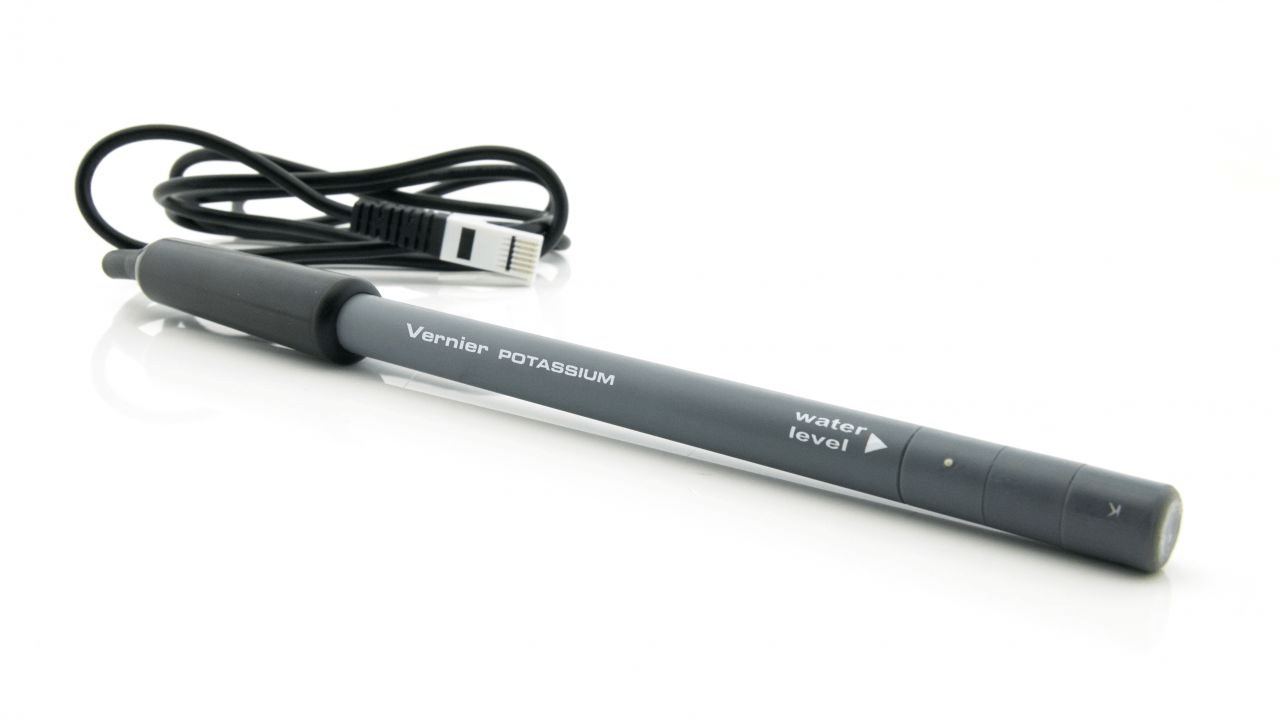 
What is a pH probe?
What is at the bottom of the meniscus?
The four types of titrations are...
What are Acid-Base titrations, Redox titrations, Precipitation titration, Complexometric titration?
On a titration curve, the point at which the pH of the titrate should be neutral 7.0.
What is the equivalence point?