•All living things are composed of cells (or cell products)
•The cell is the smallest unit of life
•Cells only arise from pre-existing cells
What is the cell theory?
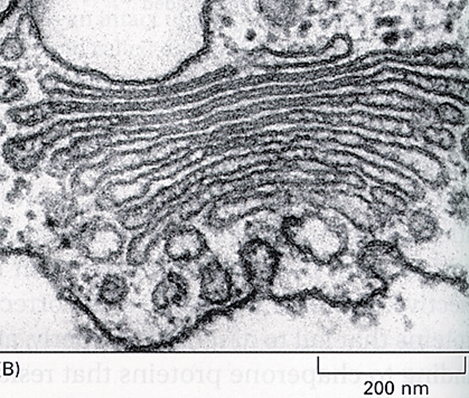
Golgi apparatus; processes proteins that are brought in by vesicles form the rER.
Why do phospholipids form bi-layers in water?
amphipathic properties (part is hydrophobic and part is hydrophilic). The hydrophobic tails are attracted to each other (not water) and the hydrophilic phosphate heads are attracted to water.
Function of vesicles
move materials within cells. (around, into or out of)
Origin of eukaryotic cells can be explained by this theory
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
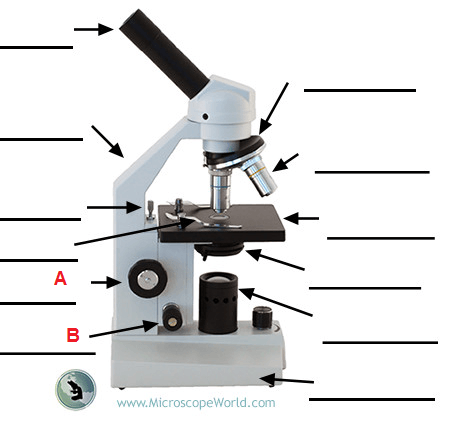
A- Course Focus B- Fine focus; A: Course Focus
These types of cells divide by binary fission and have a simple cell structure.
What are prokaryotes?
What are components of the fluid mosaic model of the membrane structure?
phospholipids, integral proteins, peripheral proteins, cholesterol
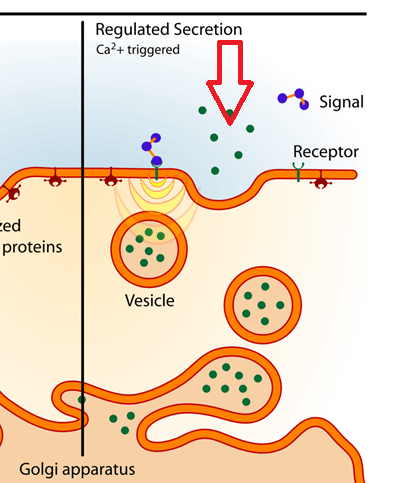 What is shown?
What is shown?
Endocytosis
Name one feature that suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria evolved from independent prokaryotes.
-they have their own genes
- they have their own 70s ribosomes (similar to prok)
-they transcribe DNA and use the mRNA to make some of their own proteins
- only can be produced by division of pre-existing cells.
The seven functions of life
MR H GREN: Metabolism, response, homeostasis, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition
measured length/actual size =
magnification
What is the function of ONE of the components of the cell membrane?
phospholipid- separates the cell from its environment
proteins- hormone binding sites, cell adhesion, cell to cell communication, channels for active and passive transport, immobilized enzymes with active site on outside
cholesterol-controls membrane fluidity and permeability to some solutes
Differentiate between facilitated and simple diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion require specific channels to travel in and out of the cell. In simple diffusion particles move through the membrane.
Spontaneous generation of cells and organisms does not now occur on Earth. Pasteur's experiment supported this. Summarize his experiment.
Broth in swan necked flasks. One boiled and one not. Fungi and other organisms appeared in unboiled not in boiled, even after long periods of time. Both were exposed to air.
How do specialized tissues develop?
Cell differentiation
What is III pointing to?
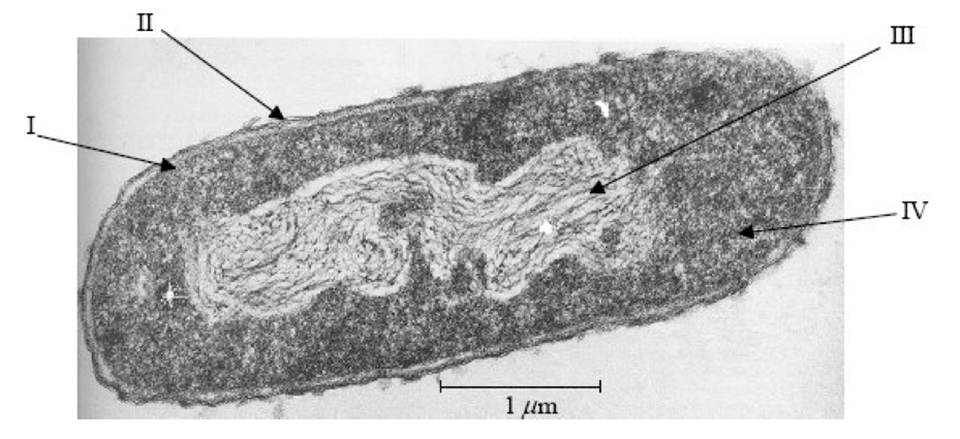
Nucleoid region
Draw a cell membrane
...
Particles move _______ the concentration gradient in simple and facilitated diffusion and move ______ the concentration gradient in active transport.
down; against
What are cilia and flagella used for?
Locomotion; cilia can be used to create a current in the fluid next to the cell
What are the two properties of stem cells that make them useful?
1. Stem cells can divide repeatedly to make new cells (growth of tissues or replacement of lost or damaged cells)
2. Stem cells are not fully differentiated- they can differentiate in different ways to produce different cell types
Exocrine gland cells of the pancreas secrete digestive ENZYMES into the small intestine. What organelles would you expect to see in one of these cells? (Think about what enzymes are).
Plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondrion, rough ER, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, lysosomes
Who gave our current model of the cell membrane its name?
Singer and Nicolson
Tissue bathed in an isotonic solution has the ____ osmolarity.
A hypertonic solution has a _______ osmolarity than the tissue.
A hypotonic solution has a ________ osmolarity than the tissue.
same; higher; lower
Prokaryotes divide by binary fission. Eukaryotes divide by _______.
mitosis