What is the study of living things?
Biology
(Bio = life)
These three scientists, Theodor Schwann, Mathias Schleiden, and Rudolph Virchow, are known for proposing this basic principle of biology in the 19th century.
Cell Theory
This term describes the process in which a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells.
What is cell division?
Living things are classified as autotrophs or heterotrophs depending on the source of fuel molecules and energy.
Which one describes a type of organism that synthesises fuel molecules for respiration using non-living materials in the environment?
Autotroph
This thin boundary separates the cell from its extracellular environment and controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell
What is the cell membrane (or plasma membrane)?
Which property of the cell membrane allows only certain materials to be transported between the cell and the extracellular space?
A. Selective permeability
B. Fluidity
C. Rigidity
D. Impermeability
A. Selective permeability
These unicellular prokaryotes inhabit most environments on Earth and have characteristic shapes including spheres, rods, and spirals.
What are bacteria?
"Living things carry out life processes including movement, metabolism, respiration, growth, responding to stimuli, and excretion"
What other process is missing from this definition?
Reproduction
Topic: Prokaryotic Cells
These tail-like structures are responsible for movement and the response to external stimuli in a rod-shaped bacterium.
A. Flagella
B. Capsule
C. Cytoplasm
D. Plasmid
A. Flagella
In the parent cell, this process occurs before cell division to ensure both daughter cells contain a complete copy of the DNA.
A. Transcription
B. DNA replication
C. Translation
D. Cytokinesis
B. DNA replication
The Giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) is classified as which type of organism based on its method of obtaining fuel molecules for respiration?
A. Autotroph
B. Heterotroph
C. Chemotroph
D. Phototroph
B. Heterotroph
Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. When exposed to water, how do phospholipids arrange themselves in the cell membrane?
A. Hydrophilic heads facing the interior, hydrophobic tails facing the water
B. Hydrophobic heads facing the water, hydrophilic tails facing the interior
C. Hydrophilic heads and tails both facing the water
D. Hydrophilic heads facing the water, hydrophobic tails facing the interior
D. Hydrophilic heads facing the water, hydrophobic tails facing the interior
Simple diffusion involves the net movement of particles down a concentration gradient. Which of the following statements best describes simple diffusion?
A. Particles move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration until the concentration gradient is zero.
B. Particles move passively from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration gradient is zero.
C. Particles move actively from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy.
D. Particles move actively from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration using energy.
B. Particles move passively from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration gradient is zero
Which fungus is responsible for the production of the antibiotic penicillin?
A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
B. Penicillium chrysogenum
C. Aspergillus niger
D. Candida albicans
B. Penicillium chrysogenum
Movement is a life process observed in many living organisms. Which of the following is NOT a reason why living things use movement?
A. To hunt
B. To acquire nutrients
C. To avoid predation
D. To reproduce
D. To reproduce
Topic: Eukaryotic Cells
This organelle stores the DNA and coordinates the cell’s activities including growth and metabolism.
A. Chloroplast
B. Mitochondria
C. Nucleus
D. Golgi apparatus
C. Nucleus
What is the process called in which a single circular DNA molecule in prokaryotes is replicated and the cell is divided into two genetically identical daughter cells?
A. Mitosis
B. Meiosis
C. Binary fission
D. Cytokinesis
C. Binary fission
Which of the following is the correct word equation for the process of photosynthesis?
A. Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
B. Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
C. Oxygen + Glucose → Water + Carbon dioxide
D. Water + Carbon dioxide → Oxygen + Glucose
B. Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
Which of the following sterols is found in the cell membranes of animal cells and helps regulate membrane fluidity?
A. Ergosterol
B. Cholesterol
C. Sitosterol
D. Glycolipid
B. Cholesterol
Osmosis involves the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Water diffuses passively from:
A. A region of higher solute concentration to a region of lower solute concentration.
B. A region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration.
C. A region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
D. A region of lower water concentration to a region of higher water concentration.
A region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration.
Which protozoan is responsible for causing roughly 50% of all malaria cases and is transmitted to humans through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito?
A. Euglena acus
B. Paramecium caudatum
C. Amoeba proteus
D. Plasmodium falciparum
D. Plasmodium falciparum
Metabolism refers to the life-sustaining chemical reactions that occur in the cells of living things. Which of the following processes is NOT part of metabolism?
A. Chemical breakdown of molecules to release energy
B. Synthesis of molecules for growth and maintenance
C. Physical movement of muscles
D. Digestion of food to release nutrients
C. Physical movement of muscles
These small molecules are used in the synthesis of proteins in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What are amino acids
In eukaryotic cells, what is the term for the protein complex that joins two sister chromatids together after DNA replication?
A. Histone
B. Chromatin
C. Centriole
D. Centromere
D. Centromere
This process releases energy by breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water.
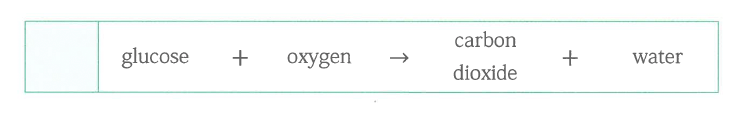
Which type of membrane protein spans the entire membrane and can facilitate the rapid diffusion of materials between the cell and the extracellular space?
A. Peripheral proteins
B. Enzymes
C. Channel proteins
D. Receptor proteins
C. Channel proteins
When a red blood cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, what is the most likely outcome?
A. The cell will decrease in volume due to water diffusing out.
B. The cell will remain the same volume due to equal solute concentrations inside and outside the cell.
C. The cell will burst (lysis) due to water diffusing into the cell.
D. The cell will undergo crenation due to water diffusing out.
C. The cell will burst (lysis) due to water diffusing into the cell.
In ideal conditions, the population of Streptococcus pneumoniae doubles in size every 20-30 minutes. What is the term for this type of growth?
A. Linear growth
B. Exponential growth
C. Logarithmic growth
D. Arithmetic growth
B. Exponential growth
Identify the life process described in the following example:
Phytoplankton are microorganisms that synthesise glucose and other large molecules from carbon dioxide and water
Metabolism
Prokaryotic cells do not have these structures, whereas eukaryotic cells do.
What are Organelles?
Which of the following lists the stages of mitosis in the correct order?
A. Metaphase, Prophase, Anaphase, Telophase
B. Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
C. Prophase, Anaphase, Metaphase, Telophase
D. Telophase, Metaphase, Prophase, Anaphase
B. Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
This waste product of anaerobic respiration in humans is produced when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
(Hint: there is a build up of this when you exercise)
What is lactic acid?
These proteins, embedded in the membrane, catalyze specific reactions at the surface of the cell membrane and become activated only when energy is supplied in the form of ATP.
What are enzymes?
This ratio decreases as a cell grows, reducing the efficiency of transporting raw materials for metabolism and waste removal, ultimately causing the cell to divide once a certain size is reached.
What is the surface area to volume ratio?
This food preservation technique involves heating food products to high temperatures to inhibit the growth of microorganisms by reducing their metabolism and other life processes.
What is pasteurisation?