Name the Biome:

Tropical Rainforest
Define Biome
A biome is a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions.
A community of organisms (biotic) that interact with the physical environment (abiotic) is what?
An Ecosystem
Define population
A group of the SAME species living in the SAME area, which are capable of inbreeding
Define Quadrant
squares (or circles) of a set size placed in an ecosystem that allow you to measure number or types of species in a specific area. They can be moved easily to randomize the area for data collection.
Name a specific example of a Temperate Grassland.
Answers will vary. Examples include: Great Plains USA; Russian Steppes; Pampas in Argentina
>Insolation (solar radiation reaching earth, measured in solar energy/cm2/min)
>Precipitation
>Temperature
Describe the difference between a fundamental niche and a realized niche.
´Fundamental Niche- full range of conditions and resources in which a species could survive and reproduce
´Realized Niche- describes the actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interactions
What are three factors that affect population growth?
natality (birth rate); mortality (death rate); and migration (immigration and emigration)
Why should you use a random number generator when doing a random quadrant procedure?
if you do not randomize which quadrants you choose of an area, you are more prone to bias.
Name two animals and two plants that you would find in a Temperate Deciduous Forest
Animals: wolves, foxes, rabbits, deer, bear, frogs, lizards, etc. (answers will vary)
Plants: Maple, beech, oak, hickory, etc (answers will vary)
What is zonation and how does it relate to biomes?
Zonation = changes in Biomes due to abiotic factors such as elevation or salt level rather than latitude.
Write the scientific name of a human properly.
Homo sapiens
Give three things that may limit population growth.
´Examples:Minerals and nutrients in soil or water, Oxygen in the water or nitrogen in the soil, Temperature, Population of prey
Which area has the greatest species richness and which the greatest species evenness?
Species richness = number of species in a defined area
> They are the same (have the same total number of species
Species evenness = how close in numbers each species is.
> Area A has the better evenness as there are more similar numbers of each species in the area.
Indicate difference in the P/E ratios between a Tundra and a Desert. Give one reason why this may be.
Desert: <1, E>P evaporation is greater than precipitation
Tundra: >1, P>E precipitation is greater than evaporation
reasoning may include: latitude, rain or precipitation, wind effects, Tricellular model
What does a P/E ratio of less than 1 mean in terms of Biome and relate to a specific Biome's characteristics.
Precipitation (rain or snow little) is less than evaporation (very high), which means water is more likely to be evaporated from the surface leaving behind salts so plants cannot grow.
Example: Desert (Sahara, Jordan, Navajo, etc)
Give one example of the following interactions:
Parasitism
Commensalism
Mutualism
Parasitism: tapeworm in dog; tick on deer; fleas on cat; Lice on humans; mistletoe on an oak tree
Commensalism: bird in a tree; orchids on tree branches; Sharks And Remora; Whales And Barnacles
Mutualism: Bees and flowers; clown fish and sea anemone; bacteria and humans; Aphids and ants
-Describe the differences.
Describe a scenario in which you would use a belt transect vs a random quadrant method
Belt transect: anything involving distance from something (road, trail, tree, river, etc)
Random: comparison of two areas from each other (forest vs prairie, south shore vs north shore, etc)
Compare (2) and contrast (3) a tropical rainforest with a temperate deciduous forest.
Comparison: Similar P>E, both are fertile soils, with a rich diversity of life in animals and plants
Differences: significantly higher amounts of rainfall in rainforest (2000-5000mm/ year) than deciduous (500-1500mm/ year), temperatures do not change significantly in rain forest (27C) vs deciduous (+30C to -30C), Latitude: Rainforest is around equator, deciduous is around 40-60N & S latitudes, Productivity is significantly high for both but higher in rainforest.Deciduous forest:
Explain how the Tricelluar Model explains rainfall variance across the earths surface.
1.Heat from the sun and collision of trade winds cause uplift in air… warm air rises (@0° latitude)
2.Air cools to the surrounding temperature causing instability and condensation… rain falls (@0°)
3.Air moves towards poles, cooling as it goes, beginning to sink Descending air creates compression and cloudless rainless sky (@30°N and S) Cold air sinks creating high pressure.
4.Air moves toward equator and toward poles warming as it travels along the earth
5.@ the poles cold air sinks creating high pressure and dry conditions
6.@60°N and S the cold air from the poles and the warm air moving along the earth collide. Forcing the warm air to rise again creating rain @ 60°N and S
For the following species make a dichotomous key.
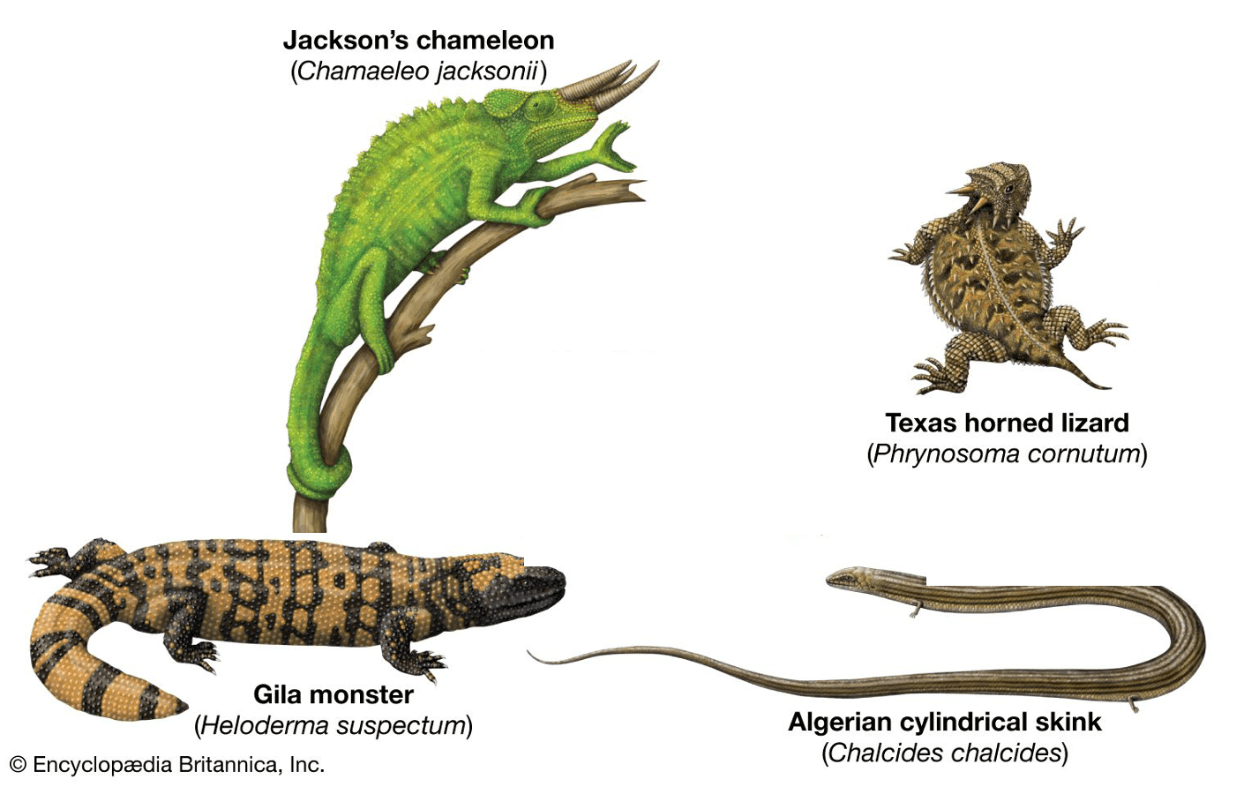
Answers will vary, but need to be in dichotomous style (two separations) with numbers, using characteristics to delineate them, and scientific names written properly when pulled out. Example:
1a. If it has long think body .... Chalcides chalcides
b. If it has a thick body ..... go to 2
2a. If it has horns ....go to 3
b. If it does not have horns.... Heloderma suspectum
3a. If it's tail and fingers can grip around a tree branch.... Chamaeleo jacksonii
b. If it has long fingers but not a long tail ....Phrynosoma cornutum
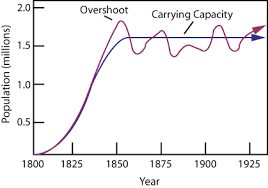
Draw a graph that represents how a population actually works with carrying capacity. label carrying capacity and overshoot and dieback
Name a scenario in which you would use the Lincoln AND one where you would use the Simpson's Diversity Index
Lincoln Index: when you wanted to count how many frogs are in the pond (anything with species number)
Simpson's Diversity index: To determine species richness of an area. How many types of birds are in the area?