Define the three types of biodviersity
Numbers - total number of species present
Habitat- range and diversity of biomes/ ecosystems present
Genetic - variations within the DNA of a population
What is natural selection?
Those individuals with genetic variation better adapted to the environment/ pressure are able to survive and reproduce allowing for future generations to obtain the same traits.
What factors lead to a loss of biodiversity?
•Natural Disasters (volcanoes, drought, ice age, meteor impact, flood, etc)
•Habitat degradation, fragmentation, and loss (logging, farming, etc)
•Agricultural practices (monoculture – using only one crop, pesticides, uses of genetically modified species)
•Introduction and/or escape of non-native species (invasive species)
•Pollution
Hunting, collecting, and harvesting (poaching)
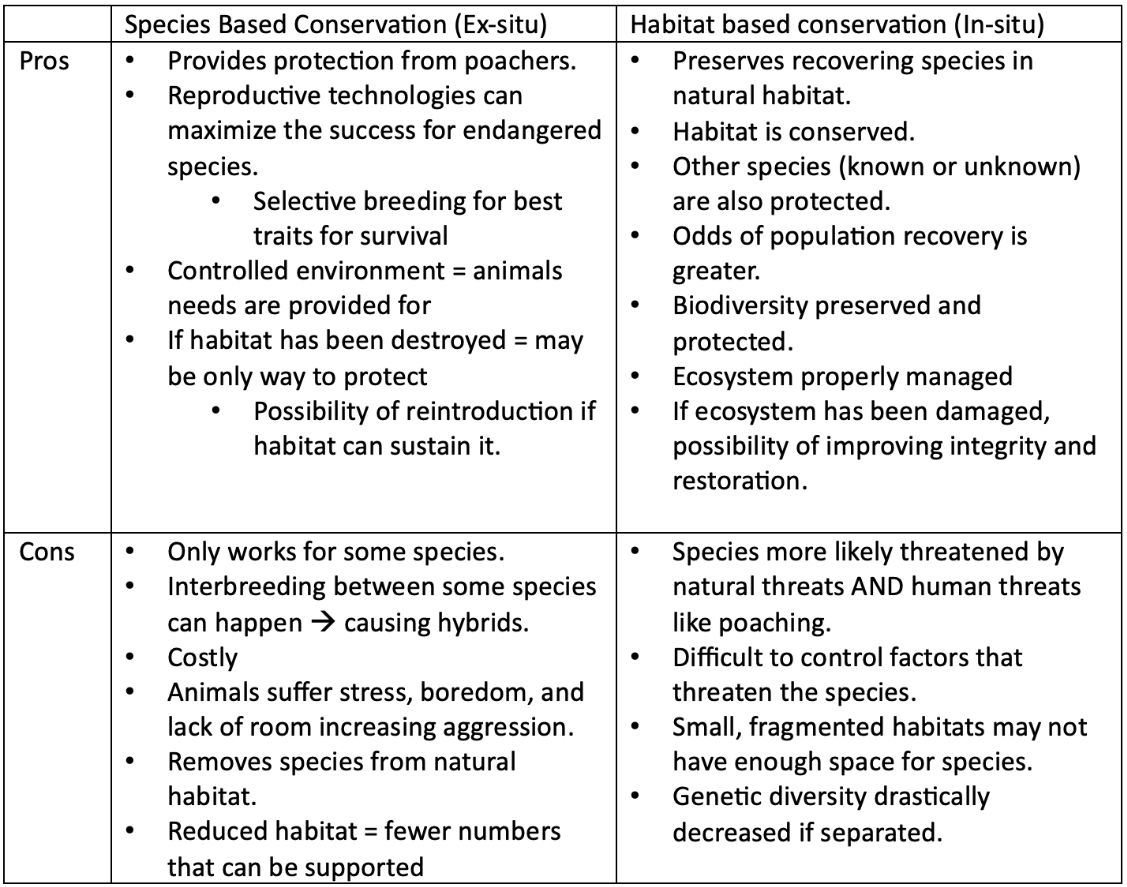
Ex-situ = species based conservation, removing the organism from it's natural habitat to help preserve it.
In-situ = habitat based conservation, protecting the entire habitat of an endangered species to help preserve all aspects.
What is the difference between sustainability and sustainable development?
Sustainability = the ability to maintain the resources so that they can be used but not run out for the next generation.
Sustainable development = improving the long term economic and social development of communities without compromising future generations.
Species diversity is a measurement of what two variables?
the number of species (richness) and their relative proportions (evenness)
How is speciation related to natural selection?
As a population changes due to natural selection, given enough time, the same consistent pressure, and reproductive isolation from the original population, this population will develop unique enough characteristics to be considered separate species from the original population
How do volcanos lead to mass extinction?
Large volcanos produce tons of rock and dust pushing it into the atmosphere. If the eruption is large enough this can block out the sun for a large period of time over large parts of the globe leading to drastically changing climates. As the sun is blocked this creates changes in plant life and ultimately food webs as well as mass die off of species.
Describe at least 3 reasons for why we should conserve biodiversity.
Answers may vary, but can contain any of the following (or other reasonable answers)
•Food sources
•Natural products
•Environmental services
•Scientific and educational value
•Biological control agents
•Gene pools
•Future potential
•Human health
•Human rights
•Recreational
•Ecotourism
•Ethical/ Intrinsic Value
What is the value of the CITES international agreement?
CITES = Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
It helps to create a world wide network of governments that work together to protect specific species.
What is a biological hotspot? Including a named example.
Areas on the planet that contain a large amount (>1500) of endemic plant species and are under threat by human habitation/ development, with <30% of it's original natural vegetation.
Examples include: Madagascar, Brazil, New Zealand, Sundaland (SE Asia), Horn of Africa, Caribbean, Tropical Andes, Japan, Mesoamerica, etc...
Name three ways in which reproductive isolation can be achieved.
Geographic isolation
Temporal isolation
Behavioral isolation
Name three reasons why the tiger is critically endangered and prone to extinction.
> poaching/ illegal trade
> small number = low genetic diversity
> Significant habitat fragmentation
> Decrease in food sources
Accept other reasonable answers
Explain the pros and cons of conserving flagship species compared to keystone species.
Flagship species often raise a lot of money. That money is often used to protect a large number of other species, however, a large number of them are primarily other flagship species. They can also be used as umbrella species to help save many species. Some Keystone species are flagship species like beavers and otters. However, conserving only flagship species detracts from help needs for extremely important species like ants, sea starts, and others. If we only save the flagship species, and we fail, we risk the extinction of that species.
What are two reasons the current mass extinction is different from the previous mass extinctions?
rate of change is faster/happening over a shorter time frame; caused by another species changing the environment/not caused by natural phenomena as in the past/caused by humans; humans can prevent current extinction.
Name 3 reasons why it is important to preserve biodiversity.
Accept any reasonable answer. Answers could include:
•Ensures and increases food security
•Helps fight diseases
•Supports livelihoods of various communities around the world
•Controls/ supports ecosystems to prevent disasters like flooding, erosion, soil depletion.
•Improves economic benefits.
•Can protects & help mitigate effects of climate change
How do land bridges and continental drift create opportunities for speciation?
Land bridges - allow populations to move away from enough and/ or create situations for reintroduction of two isolated populations to interact
Continental drift- separates populations by the splitting of land forms or the creation of new geographical formations to further separate populations
Explain two of the biggest threats to rainforests.
Agriculture- as human development increases so does the need for food. Often this results in a cutting down of the forests to make space to plant crops.
Deforestation/ logging - value is often seen only for its land and natural capital (trees) to build a profit. Often cut down for the income and money needed.
Describe three aspects that need to be considered when designing a nature reserve.
Edge effect - limiting the amount of edge available as this can disrupt the number of species present.
wildlife corridors to help reduce population isolation and edge effect
Size and shape of the reserve matter in trying to save as many animals as possible.
CARE (connected, adequate, representative, and efficient)
What is the edge effect?
The edge effect occurs when habitat fragmentation decreases the size of various ecosystems, creating space for more of the species the thrive on the edges of forests (such as deer) and reducing the space or eliminating all together the space needed for larger or more space dependent animals (such as bears and some species of owls)
What are the advantages of functional redundancy to environmental health?
Functional Redundancy indicates a repetitiveness of similar niches in the environment. Increasing diversity does not always indicate an increase in functional redundancy (only add 1 new niche for every 10 species). Identifying vulnerabilities to the functional redundancy and underrepresented niches may be even more important than the number of species themselves in terms of ecosystem health.
How do converging plates due to plate techtonics aid in speciation?
Converging continental plates create subduction zones, which usually result in mountains, volcanos, and islands forming (if in the ocean). Mountain ranges isolate populations from each other as well as create distinct climates allow for natural selection and speciation.
Discuss one way in which the rainforest can be managed sustainably.
Sustainable logging - by cutting down only a small number of trees at a time and managing when and where those are cut so as to aid the rainforest in simulating normal growth and decay of trees can increase the biodiversity an improve the forest overall. (example: borneo)
Sustainable development for indigenous people: Two examples- 1) teaching framing techniques to indigenous people that do not create the need for slash and burn and help to maintain the rainforest. (chuckra integral) 2) creating ways to help indigenous people use the resources at the disposal to produce desirable products for consumption. One example is the making of latex from natural rubber.
Evaluate whether species based conservation vs habitat conservation is more beneficial as overall to conservation?
Answers will vary.
Describe two advantages and two disadvantage of ecotourism as a method of conservation.
Advantages:
increased revenues to invest back into conservation;
raises awareness leading to greater support/public engagement with wildlife conservation;
consideration of wildlife as an asset that needs to be looked after;
if local population have jobs in the tourism industry they are less likely to engage in unsustainable farming/fishing activities.
Disadvantages:
growth in tourist sites/hotels could cause loss of habitats/forests;
creation of roads that fragment habitats;
noise from tourism that disrupt wildlife/mating / disturbances caused by tourists can alter animal behaviour;
litter that can degrade environment / harm wildlife;
increased tourism puts greater demand on limited freshwater that is unsustainable / increase demand for limited water resources that competes with wildlife;
greater access to wildlife areas that could lead to increased poaching/illegal fishing/increase capture for illegal pet trade;
increase in tourism could increase demand of goods/services that cause deforestation/use unsustainable resources (e.g. fossil fuels);
animals/wildlife used as a tourist attraction maybe inappropriately/unethically treated / focus on popular tourist sites may leave less visited sites with fewer conservation resources/funds.