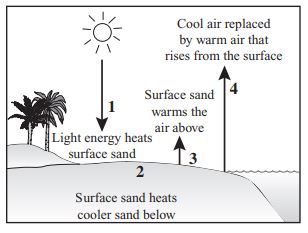
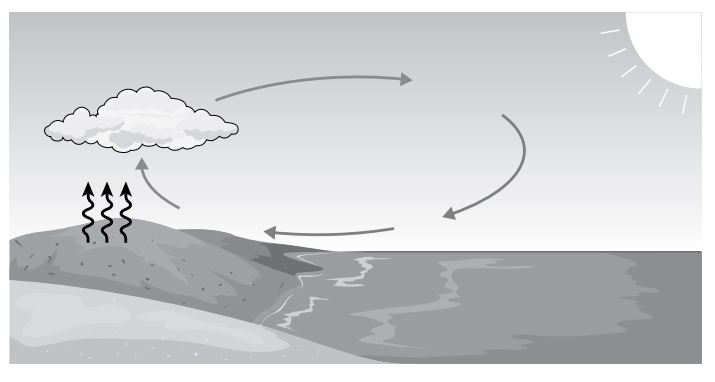
The arrows in the picture below show several ways heat is transferred from the Sun as it strikes sand on the surface of a beach.
Which arrow shows convection?
What is 4? Cool air replaced by warm air that rised from the surface.
Earth's atmosphere is important to the living organisms of the biosphere. Which of the following describes how the atmosphere best protects living organisms?
Responses
- A- by providing enough carbon dioxide in the ocean to support sea animals
- B- by changing oxygen into nitrogen, which can be used as a nutrient for animals
- C- by refracting visible light, allowing certain animals to see and capture their prey
- D- by trapping electromagnetic radiation, keeping temperatures within a range best suited for animal life
What is D? By trapping electromagnetic radiation, keeping temperatures within a range best suited for animal life.
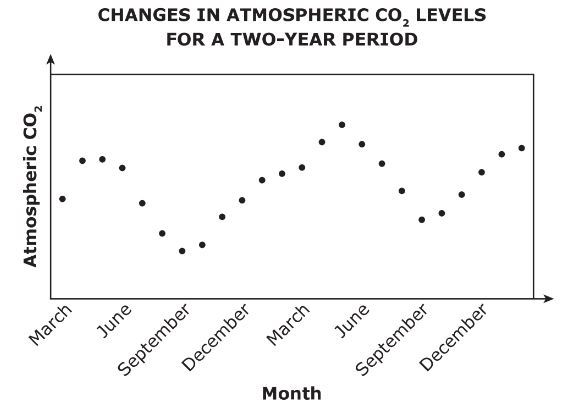
Many interactions occur between the biosphere and the atmosphere. One of these interactions results in changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. The graph below shows these changes over a two-year period.
Which of the following statements is supported by the data in the graph?
Responses
- A- Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is constant and does not vary seasonally.
- B- There is more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in the spring than in the fall.
- C- There is more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in the winter than in the summer.
- D- Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have only been measured over the last 100 years.
What is B? There is more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in the spring than in the fall.
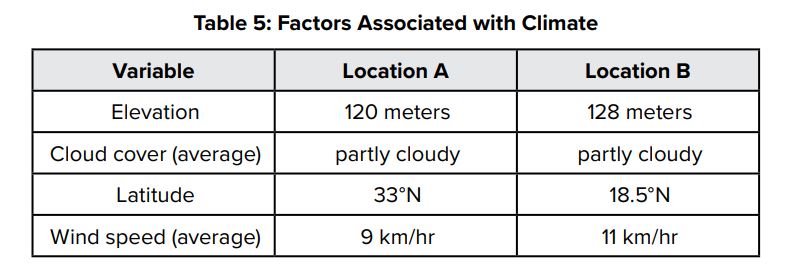
Raphael is comparing various factors at two locations in the Northern Hemisphere. Both locations are in the interior of a continent. The table shows the location and weather data that he has collected in his research.
If there are no other factors affecting the climates of the two locations, which conclusion is best supported by the information in the table?
Responses- A- Location A likely has a warmer climate than Location B because it has a lower elevation.
- B- Location A likely has a warmer climate than Location B because it receives more sunlight during the year.
- C- Location A and Location B likely have similar climates because they have similar levels of cloud cover.
- D-Location A and Location B likely have similar climates because they are at similar latitudes and have similar wind patterns.
What is B? Location A likely has a warmer climate than Location B because it receives more sunlight during the year.
How do the three methods of heat transfer—radiation, conduction, and convection—affect the Earth's atmosphere?
Responses
- A- Radiation from the Sun heats the Earth’s surface, conduction transfers that heat to the air, and convection moves warm air upward.
- B- Conduction warms the Earth’s surface, while radiation cools the air and convection has no effect.
- C- Radiation cools the Earth, conduction heats the oceans, and convection does not occur in the atmosphere.
- D- Convection is the only method that affects the Earth’s atmosphere.
What is A? Radiation from the Sun heats the Earth’s surface, conduction transfers that heat to the air, and convection moves warm air upward.
Which of the following is NOT an efficient greenhouse gas that traps heat in Earth's atmosphere?
Responses
- A- helium
- B- methane
- C- carbon dioxide
- D- water vapor
What is A? Helium
Which of the following best explains why routine weather observations are considered a scientific investigation, but not a true experiment?
Responses
- A- Weather observations do not use scientific instruments, so they are less reliable than experiments.
- B- An experiment requires manipulating and controlling variables to test a hypothesis, while weather observations involve systematically collecting data about a naturally occurring system without controlling it.
- C- Weather observations are only useful for immediate forecasting, whereas experiments are designed to establish timeless scientific laws.
- D- Experiments are conducted by professional scientists in a laboratory, while weather observations can be made by anyone and are therefore not scientifically valid.
What is B? An experiment requires manipulating and controlling variables to test a hypothesis, while weather observations involve systematically collecting data about a naturally occurring system without controlling it.
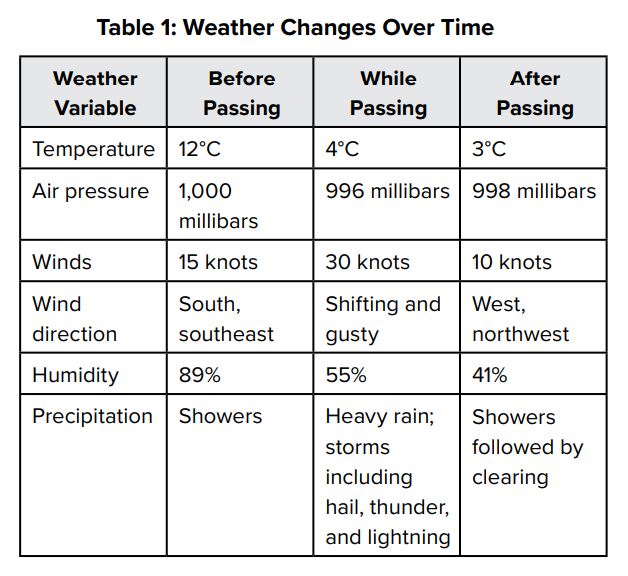
The table indicates the changes that occur during the passing of a cold front at a fixed location over time.
Which statement describes a change that takes place during a cold front?
Responses
- A- Winds shift as the front passes.
- B- Humidity rises as the front passes.
- C- Air pressure increases, then decreases.
- D- Temperatures increase after the front passes.
What is A? Winds shift as the front passes.
Which description best represents heat transfer through radiation?
Responses
- A- Warm air moves upward, and cold air moves downward.
- B- Energy from the Sun heats the Earth's surface.
- C- Warm air transfers heat to the land as it blows across the Earth's surface.
- D- A stream of hot air from the mouth of a volcano heats the air that touches the stream.
What is B? Energy from the Sun heats the Earth's surface.
Which of the following statements would best describe an affect that losing the atmosphere would have on Earth?
- A- Severe storms would occur around the world.
- B- There would be flooding along rivers and coasts.
- C- The planet would increase in temperature.
- D- Ultraviolet (UV) waves would reach the surface unfiltered.
What is D? Ultraviolet (UV) waves would reach the surface unfiltered.
How does energy from the sun cause wind to blow?
Responses
- A- The sun's magnetic field directly pushes the air in Earth's atmosphere, creating global wind patterns.
- B- Sunlight heats the oceans, causing water to evaporate and form clouds, which are then pushed by the Earth's rotation to create wind.
- C- The sun unevenly heats the Earth's surface, causing some air to become warmer and less dense and other air to be cooler and denser. Less dense air rises and more dense air moves into to replace it.
- D- Solar radiation charges particles in the atmosphere, causing them to repel each other and generate air movement.
What is C? The sun unevenly heats the Earth's surface, causing some air to become warmer and less dense and other air to be cooler and denser. Less dense air rises and more dense air moves into to replace it.
Which statement is NOT a major factor involved in how energy from the Sun influences weather and climate?
Responses
- A- Thermal energy differences between locations create wind.
- B- Thermal energy is released in the atmosphere, forming clouds.
- C- Thermal energy received by a location depends largely on altitude.
- D- Thermal energy is absorbed by the hydrosphere, driving evaporation.
What is C? Thermal energy received by a location depends largely on altitude.
The Sun heats Earth mainly through _________.
A- Conduction
B- Convection
C- Radiation
D- Temperature Inversion
What is C? Radiation
An increase in the levels of greenhouse gases is causing climate change due to global warming. What is most likely to occur if the amount of greenhouse gases were reduced to zero?
Responses
- A-Earth’s climate would return to what it was before global warming.
- B-Earth would be cooler overall because more heat would radiate into space.
- C-Global warming would continue because it cannot be reversed after it has started.
- D-The climate would show no change because the greenhouse effect would not exist.
What is B? Earth would be cooler overall because more heat would radiate into space.
This diagram shows how energy moves during the daytime near the shore of a large lake. The arrows from the ground show a transfer of energy from land to the atmosphere. The arrows in the sky show the motion of air above the land and the water.
What type of energy flow is represented by the upward arrows and by the arrows in the sky?
Responses
- A- The upward arrows represent radiation, and the arrows in the sky represent conduction.
- B- The upward arrows represent radiation, and the arrows in the sky represent convection.
- C- The upward arrows represent convection, and the arrows in the sky represents conduction.
- D- The upward arrows represent convection, and the arrows in the sky represent radiation.
What is B? The upward arrows represent radiation, and the arrows in the sky represent convection.
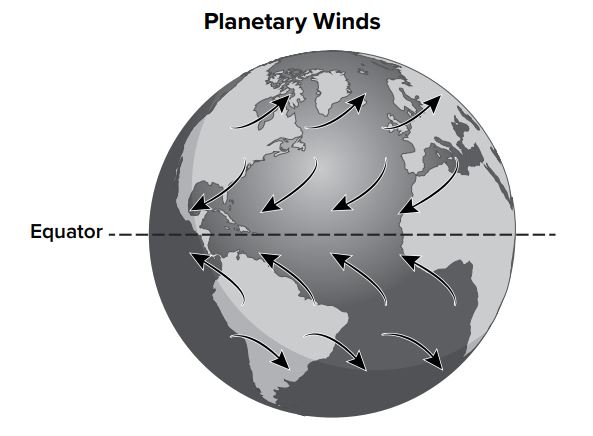
Jamaica is an island in the Caribbean Sea. It has a latitude of 18.1096° N.
The map shows global wind patterns.
What type of wind does Jamaica experience most of the time?
Responses
- A- trade winds coming from the northeast
- B- trade winds coming from the southeast
- C- westerlies from the northwest
- D- westerlies from the southwest
What is A? Trade winds coming from the Northeast.