Ionic bonds form when electrons are ____________.
transferred from one atom to another.
Covalent bonds form between___________ and ___________.
non-metal and a non-metal
Valence electrons that spread throughout a sea of metal atoms.
Delocalized electrons.
This is what VSEPR stand for.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
NaCl
What is ionic?
This is an instantaneous attraction that occurs because of the constant motion of electrons.
What are London Dispersion forces?
Refers to the uneven distribution of molecular charge.
What is polarity?
Metals losing an electron form a ________, while non-metals gaining an electron form a __________.
What is a cation & an anion?
A covalent bond produced by sharing three pairs of electrons.
What is a triple bond?
The ability of a substance to be drawn, pulled, or extruded through a small opening to produce a wire.
Ductility
How many electron domains surround the central atom in H2S?
4
MgS
What is ionic?
The strongest order of intermolecular forces in terms of weakest to strongest.
What are London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding?
This determines whether a bond between two atoms is polar or non-polar.
What is the difference in electronegativities?
What does coordination number refer to?
expresses the number of ions that surround any one given ion in the lattice.
Draw Lewis structure for the following molecule. Show resonance structures, if they exist.
N2

The metals copper & zinc are melded together to make this section of the band....

What is brass?
Draw the shape of H3O+ and write its electron geometry, molecular geometry and corresponding bond angle.
What is tetrahedral electron geometry, trigonal-pyramidal with a bond angle of 107 degrees?
NaSO4
Both
All these types of molecules are ones found with hydrogen bonding.
Molecules that follow the H-FON rule.
Draw the lewis structure of CH4 and identify if it is polar or non-polar.
: non-polar
A group of covalently bonded atoms with a charge.
What are polyatomic ions?
Draw the Lewis structure of CO and include the dative bond.
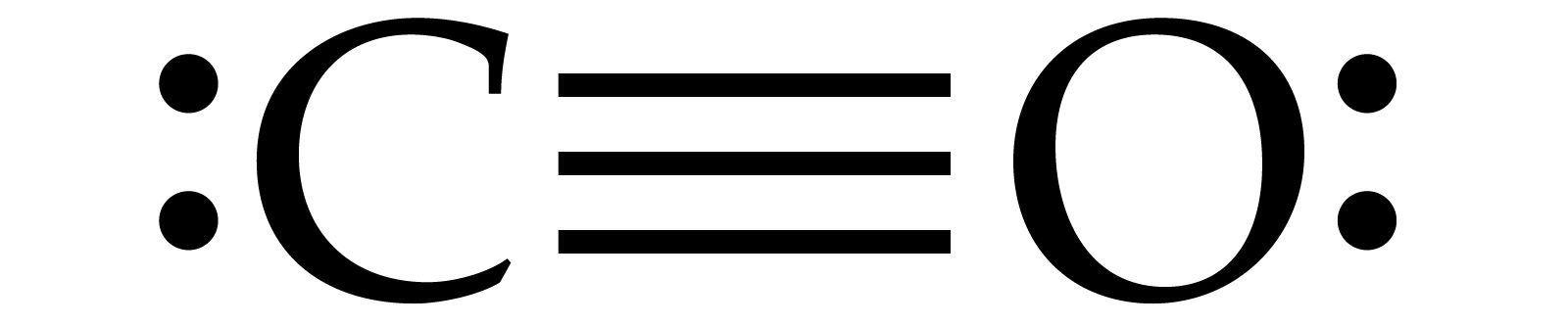
These properties of metals determine their metallic bond strength.
Charge & Radius of cation
The number of delocalized electrons
Why do molecules with boron take on a trigonal planar shape?
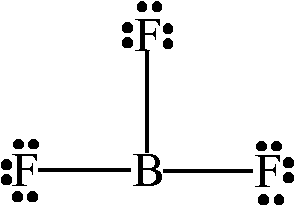
Boron has three valence electrons and is satisfied with 6 electrons total.
Water
What is covalent?
Why is the boiling point of CH4 much lower than that of C2H2 when they both only have london dispersion forces.
C2H2 is more massive so it takes more energy to boil.
Draw the lewis structure of CHCl3 and identify if it is polar or non-polar.
Polar
Explain why molecules that are ionically bonded have high melting points.
Due to electrostatic attraction being extremely strong, therefore requiring a lot of energy in the form of heat to break
Explain the difference between polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond and how that affects the electrons.
Non-polar EN difference = 0.0 - 0.3
Polar EN difference = 0.4 - 1.8
Non-polar bonds are ones where electrons are evenly distributed
Polar bonds are ones where there is unequal sharing of electrons.
Explain why Magnesium has a stronger metallic bond then Calcium?
Magnesium has a smaller radius which keeps the outermost electrons closer to the positive nucleus.
Draw Lewis structure for CO32- ? Give the name of the shape, bond angle and show resonance structures, if they exist.
Trigonal Planar; 120 degree bond angle.
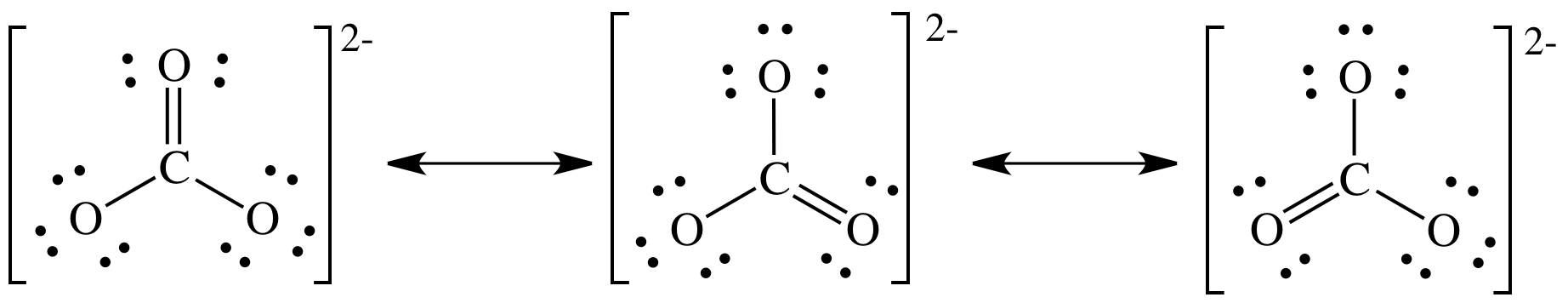
This refers to the bonding in molecules or ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single Lewis structure.
What is resonance?
Explain in terms of intermolecular forces, why water has a higher boiling point than sulfur dioxide.
Water has: London dispersion forces, permanent dipole, and hydrogen bonding.
Sulfur dioxide only has London dispersion forces and permanent dipole.
Draw the lewis structure of CH2F2 and identify if it is polar or non-polar.
Polar