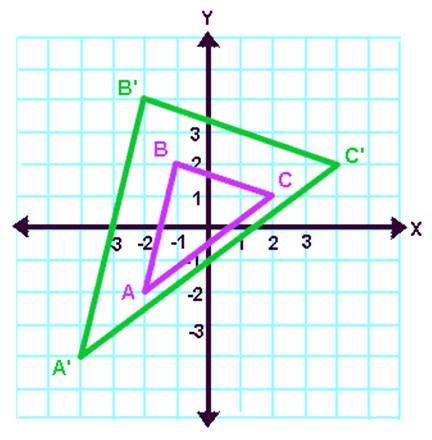
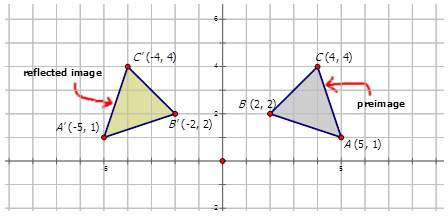
Define Transformation.....
A change in position, shape, or size of a figure. Four types of transformations are translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations
Example:
Triangle A'B'C' is a reflection of Triangle ABC. Triangle ABC was reflected across the y-axis
Define Line of Reflection.....
The Line of Reflection is a line across which a figure is reflected
Example: The Line of Reflection for the image below is the x-axis
Define Scale Factor.....
The Scale Factor is the ratio of a length in the image to the corresponding length in the original figure
Example: The Scale Factor is 2. P'R'/ PR = 4/2 = 2
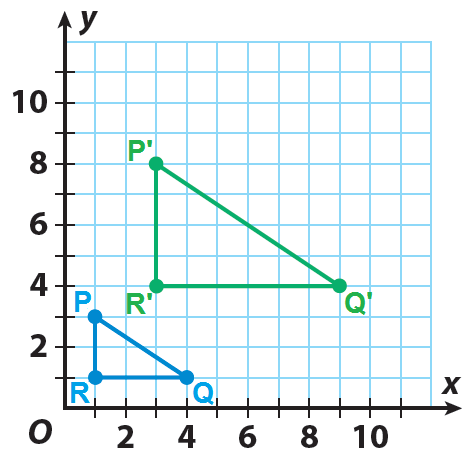
Define Transversal.....
A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines at different points on the line. Sometimes there may be more than one transversal.
Example: Line N is the transversal

Define Exterior angle of a triangle.....
An angle formed by a side and an extension of an adjacent angle
Example: Angle D is the Exterior Angle of a Triangle
Define Image.....
The Image is the result of a transformation of a point, line, or figure
Example:
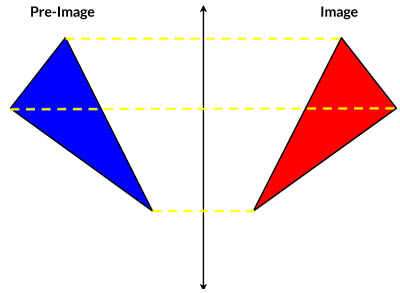
The red triangle is the image of the blue triangle
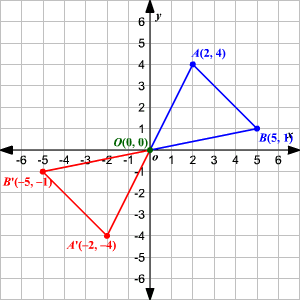
Define Angle of Rotation.....
The Angle of Rotation is the number of degrees a figure is rotated
Example: Triangle ABC was rotated 180 degrees about the origin
Define Enlargement.....
A dilation with a scale factor greater than 1. After an enlargement, the image is bigger than the original figure.
Example: Scale factor of 2

Define Corresponding Angles.....
Angles that lie on the same side of a transversal and in corresponding positions
Example: (1,5), (3,7), (2,6), and (4,8) are corresponding angles
Define Alternate Interior Angles.....
Angles that lie within a pair of lines and on opposite sides of a transversal.
Example: Angle (A and D) and Angle (B and C) are Alternate Interior Angles 
Define Reflection.....
Also considered a flip, a reflection is a transformation that flips a figure across a line of reflection
Example:
The blue triangle was reflected across the y-axis
Define Center of Rotation.....
The Center of Rotation is a fixed point which a figure is rotated
Example: The Center of Rotation is the origin or (0,0)
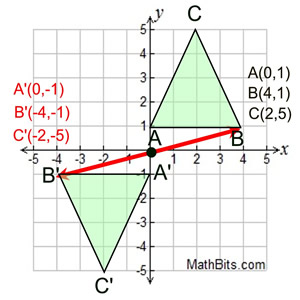
Define Congruent.....
Two two-dimensional figures are congruent if the second can be mapped from the first by a sequence of rotations, translations, and reflections.
Example: A'B'C' can be mapped onto ABC with a reflection across the y-axis
Define Reduction.....
A dilation with a scale factor less than 1. After a reduction, the image is smaller than the original figure.
Example: Triangle ABC can be mapped onto Triangle A'B'C' with a dilation with a scale factor of 1/3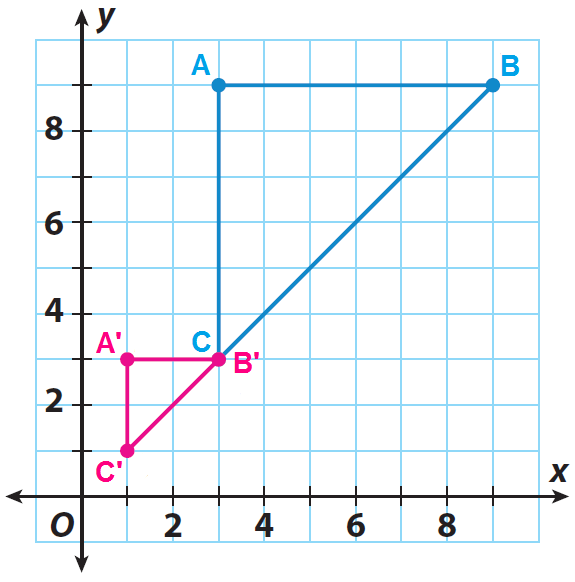
Define Same-Side interior angles.....
Same-side interior angles are in the interior of two lines on the same side of a transversal
Example:
Angles (3 and 6) and Angles (4 and 5) are same-side interior angles
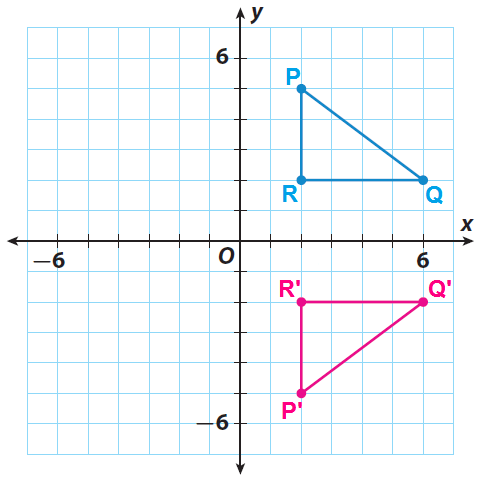
Define Translation.....
Also considered a slide, a translation is a transformation that is a rigid motion that moves every point of a figure the same distance and in the same direction
Example: Triangle ABC was translated 6 units right, and 3 units down 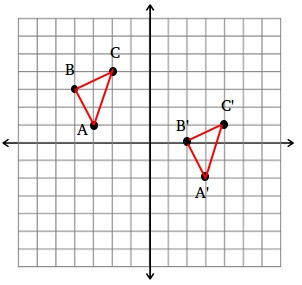
Define Rotation.....
A Rotation is a rigid motion that turns a figure around a fixed point, also known as the Center of Rotation
Example: Triangle XYZ was rotated 180 degrees and rotated around (0,0)

Define Similar.....
A two-dimensional figure is similar to another two-dimensional figure if you can map one figure to the other by a sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations
Example: P'Q'R'S'T' can be mapped onto P''Q''R''S''T'' with a dilation with a scale factor of 2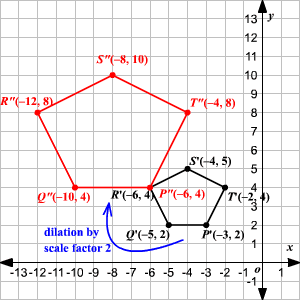
Define Remote Interior Angles.....
The two nonadjacent interior angles corresponding to each exterior angle of a triangle
Example: Angles 1 and 2 are remote interior angles of angle 4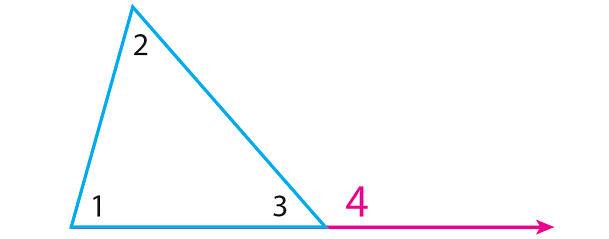
Define Dilation.....
A Dilation is a transformation that moves each point along the ray through the point, starting from a fixed center, and multiplies distances from the center by a common scale factor. If a vertex of a figure is the center of dilation, then the vertex and its image after the dilation are the same point.
Example: The Scale Factor is 2 and is being dilated around the origin, (0,0)