define renewable vs non-renewable energy
Renewable = energy sources that can be recycled and reused
Non-renewable = energy sources that are consumed
The uninterrupted availability of energy sources at an affordable price = ?
Energy Security
Difference between weather and climate.
Weather = the daily outcome of temperatures, pressure, and precipitation in the atmosphere (what actually occurs)
Climate = the average weather patterns over many years for a location (what you would expect to occur)
Define Mitigation vs Adaptation
Mitigation = reduction and/ or stabilization of greenhouse gas emissions and their removal from the atmosphere.
Adaptation = reduces the adverse effects of climate change and maximize any positive effects
name two renewable and two non-renewable energy resources
Renewable: coal, gas, nuclear, oil
Non-Renewable: wind, solar, geothermal, wave/ tidal, hydroelectric, etc
What is energy diversification?
Energy diversification = the ability of a country to gain its energy from multiple sources, so as to not be reliant on a single source.
What is a tipping point and how is it related to the climate change debate?
A tipping point = a change disrupting the equilibrium of a system allowing the system to be unable to return to normal.
Concern around the debate, is if humans are causing a tipping point. If we are on course to create a tipping point, then we need to stop it immediately.
The following is an example of mitigation or adaptation?
Improved efficiency of energy production
Mitigation
Suggest two reasons for the increase in global energy demand worldwide.
1. Population growth - more people = more demand for energy
2. More people entering the middle class and demand for a middle class life style increases.
3. Increased urbanization = increased demand specifically in large cities.
4. Increase in vehicle consumption = increase in oil demand
What is an energy crisis?
Any significant bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy
Name four impacts of the climate changing.
Why does mitigation tend to be more global in scale?
Mitigation involves dealing with the source of the problem, which if only dealt with on a local level will often not solve the problem of greenhouse gases, which are global in scope. As a result, the source of the problem must be dealt with on a global scale.
Describe the pros (3) and cons (3) of EITHER Wind, hydropower, or nuclear
Answers will vary, here are some.
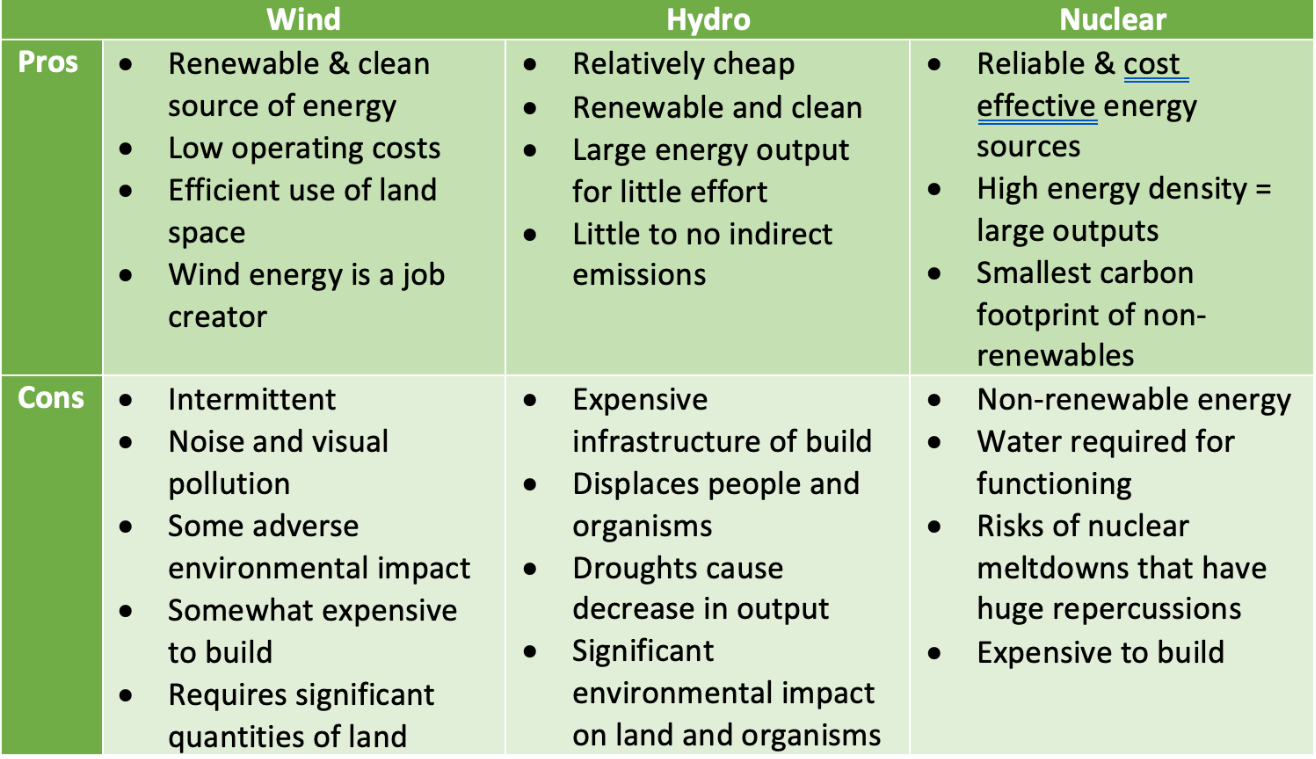
Name three specific reasons for a countries energy choices.
Geography of a country may determine the accessibility of some renewables like wind or hydro.
Economic reasons such as cost of set up vs energy produced. Resources available and what can be harvested/ used/ already accessed.
Public sentiment on a certain type: example nuclear
International aggrements that limit or monitor the type of energy.
Etc.
Using a specific example, how do both positive and negative feedback loops affect the climate?
Answers will vary. But should talk about the ways in which a negative feedback loop returns a system to normal while the positive one speeds up the process.
Give three examples of adaptations that could be used to combat climate change.
Examples may include: Changing land use policies - such as not being allowed to build on flood plains; building or resisting flooding through water catchments or minimizing run-off, building houses on stilts or with garages underneath which can be flooded; changing agricultural production through irrigation techniques, rainwater storage for water reuse, GMOs for more drought tolerant crops, growing different crops; managing weather through seeing clouds for rainfall, planting trees to encourage more rainfall. etc.
Accept any reasonable adaptation that can be justified as a LOCAL change.
Compare (1) and contrast (2) the renewable energy consumption of China vs the USA.
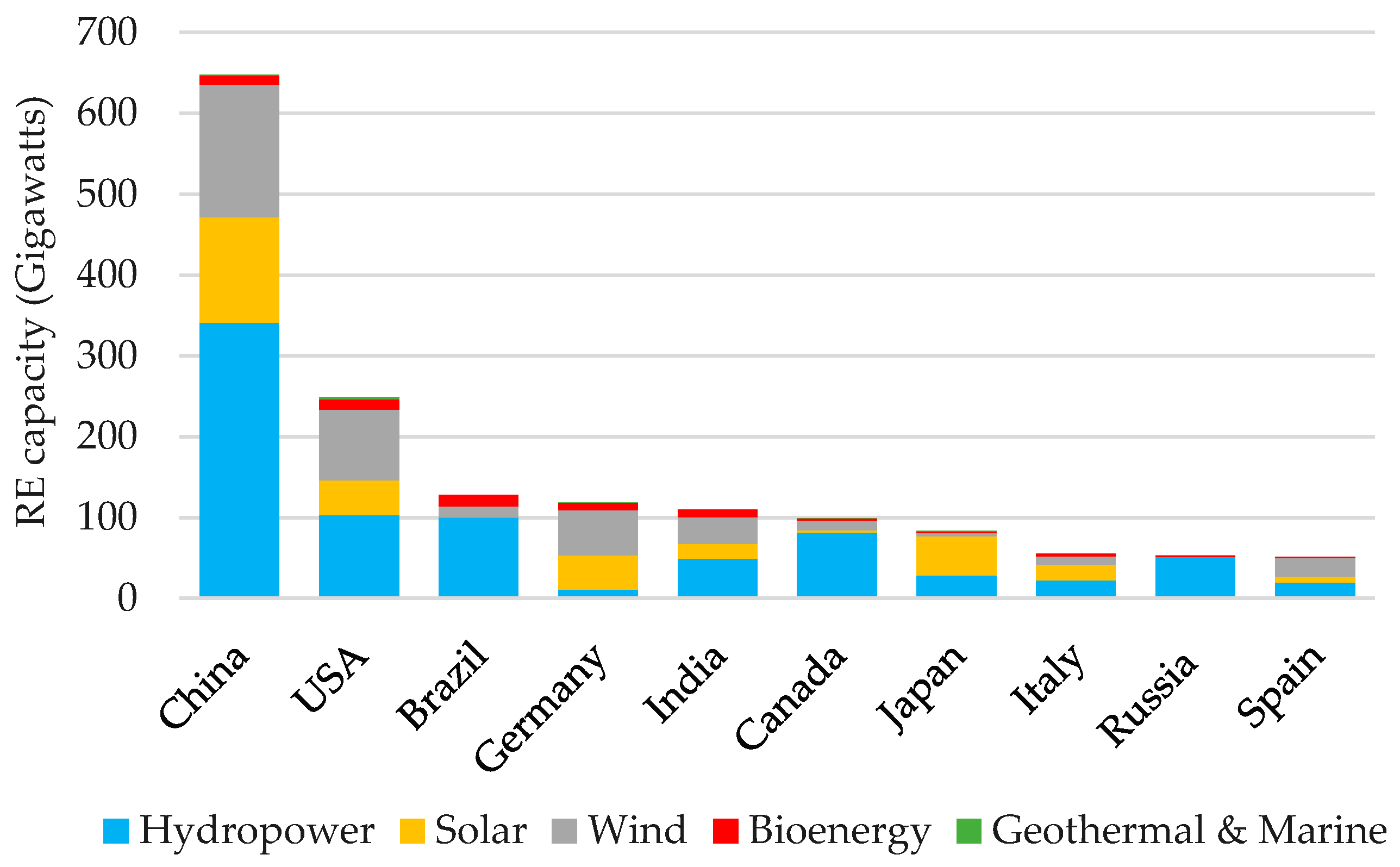
Answers will vary.
Compare: Both use hydro, solar, wind, and bioenergy.
Contrast: China uses more of all of them in general; US uses some geothermal; US uses less solar as a percentage of the total than China.
Suggest two reasons for Germany's current energy crisis.
1. Gas is a fairly large percentage- and it comes from Russia.
2. Shut down of nuclear power plants - could increase issues with demand.
others?
Discuss two reasons as evidence for human caused climate change and two reasons against it.
For: rising CO2 levels, we know that our practices put more CO2/ GHGs into atmosphere than previously thought; current impacts seen of rising temperatures;
Against: Possibility that temperature causes rising CO2, the other way around; earth occurs in natural cycles anyway; other things that could be causing temperatures rising have not been researched;
Accept reasonable answers.
Name an international agreement around climate change, and discuss its success or failure in addressing climate change.
Answers will vary.
Example 1: Kyoto Protocol (1997/2005) - signed by many nations (160) called for the first legally binding commitments to reduce CO2 emissions. But still considered ineffective as at least 55 countries have not fully adopted it in order to reach reduction goals. (USA did not sign)
Example 2: Paris Agreement (2015) - Countries agreed to specific reductions in of their own making to reducing carbon emissions (not binding under international law). On paper it is a good idea, at those who made commitments make up 70% of emissions, however, the non-binding nature of the agreement, means it only works if the nations do their part, which has yet to be seen. (USA pulled out under Trump administration & rejoined under Biden administration)