site of mandibular fracture.
Condyle
Max amount of 0.25% marcaine can a 40kg child receive.
40mL
We know 0.25% marcaine has a max dose of 2.5mg/kg
(40kg*2.5mg/kg)*(1mL/2.5mg)=40mL
65M fisher from FL with 1.8mm thick lesion. Name the surgical margin and staging procedure.
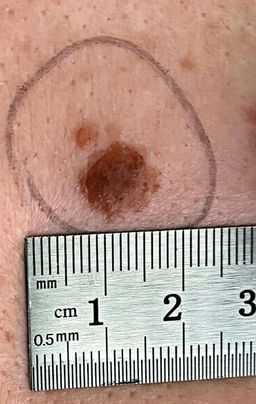
2 cm margin + sentinel lymph node biopsy
Describe the treatment.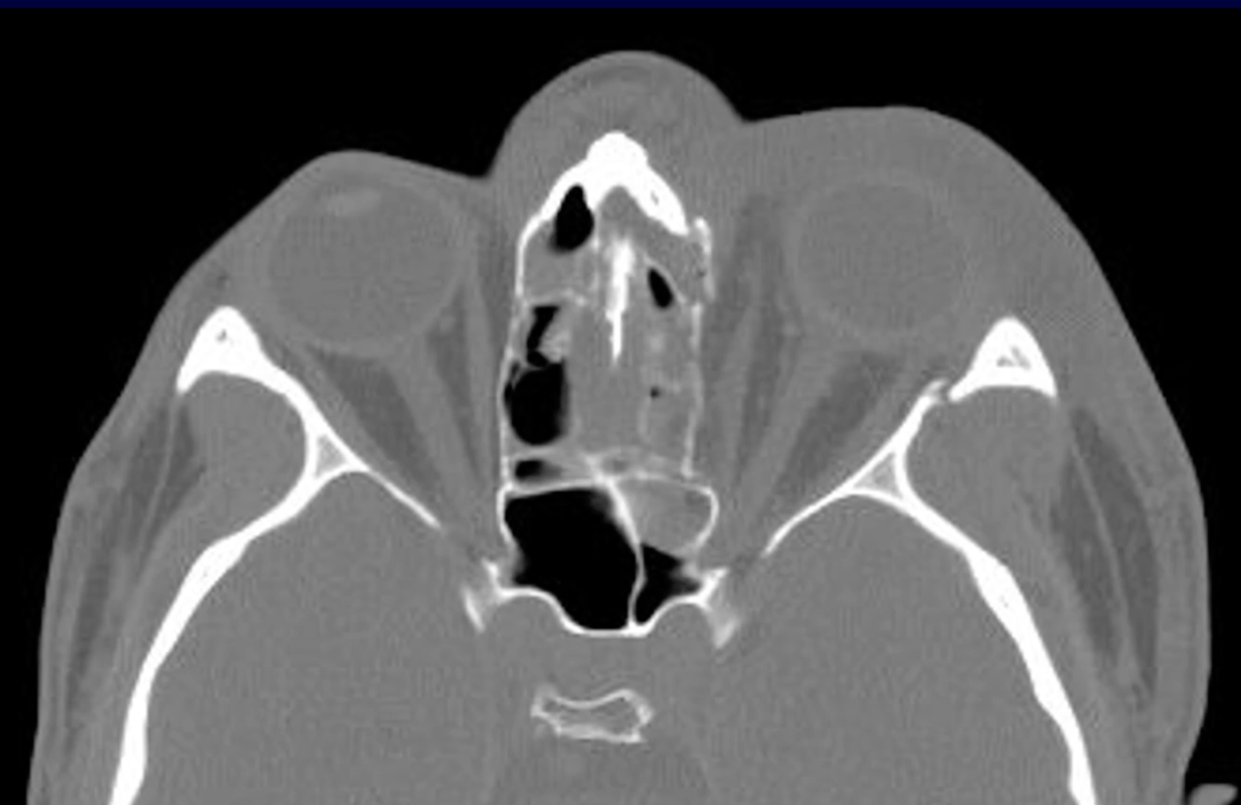
MCT is the pivotal soft tissue in NOE area, which supports the canthus, enables proper apposition between the eyelid and the globe, and performs as the lacrimal pump
As a general rule, the intercanthal distance should be overcorrected, i.e., narrowed beyond the normal intercanthal distance to compensate for the lateralization that inevitably occurs postoperatively.
The bright green bone.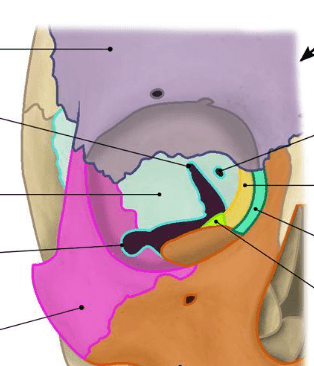
palatine bone
closed tendon injury in the hand among athletes.
Mallet finger
In burn pts, the acute cause of death vs long term cause of death.
1. inhalation injury
2. sepsis
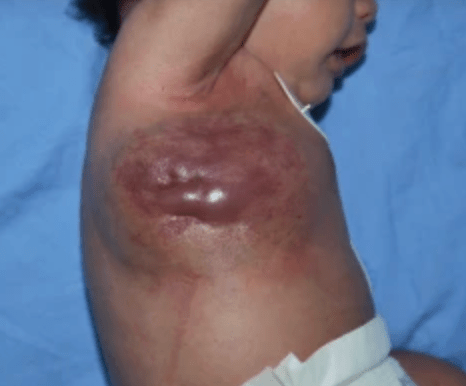 A 2-month-old boy was found to have a chest wall mass after birth. The mass became progressively indurated and purpuric. The boy developed profound thrombocytopenia and consumptive coagulopathy. MRI shows the lesion infiltrating the R lateral chest wall. Histology show spindle cell nodules.
A 2-month-old boy was found to have a chest wall mass after birth. The mass became progressively indurated and purpuric. The boy developed profound thrombocytopenia and consumptive coagulopathy. MRI shows the lesion infiltrating the R lateral chest wall. Histology show spindle cell nodules.
What does the pt have and what is the treatment?
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma with Kasabach-Merritt phenomenon
Tx: vincristine is 1st line; steroids help normalize plt count
* do not give plt transfusion unless bleeding because the vascular lesion will just eat it up
The treatment and proper sequence of fracture repair.
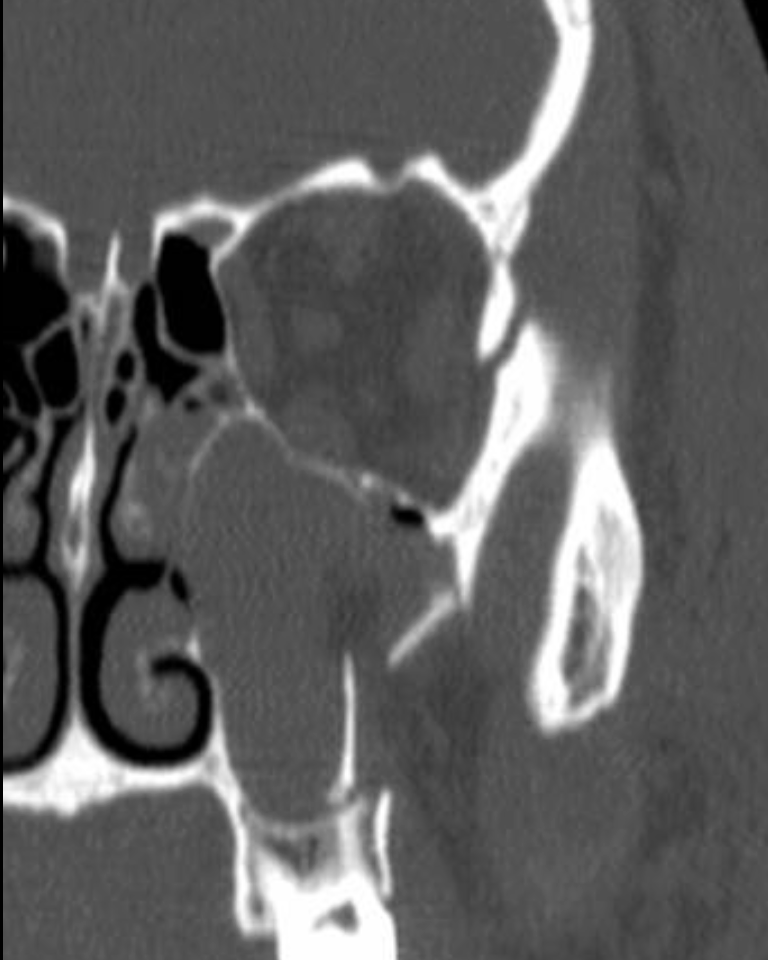
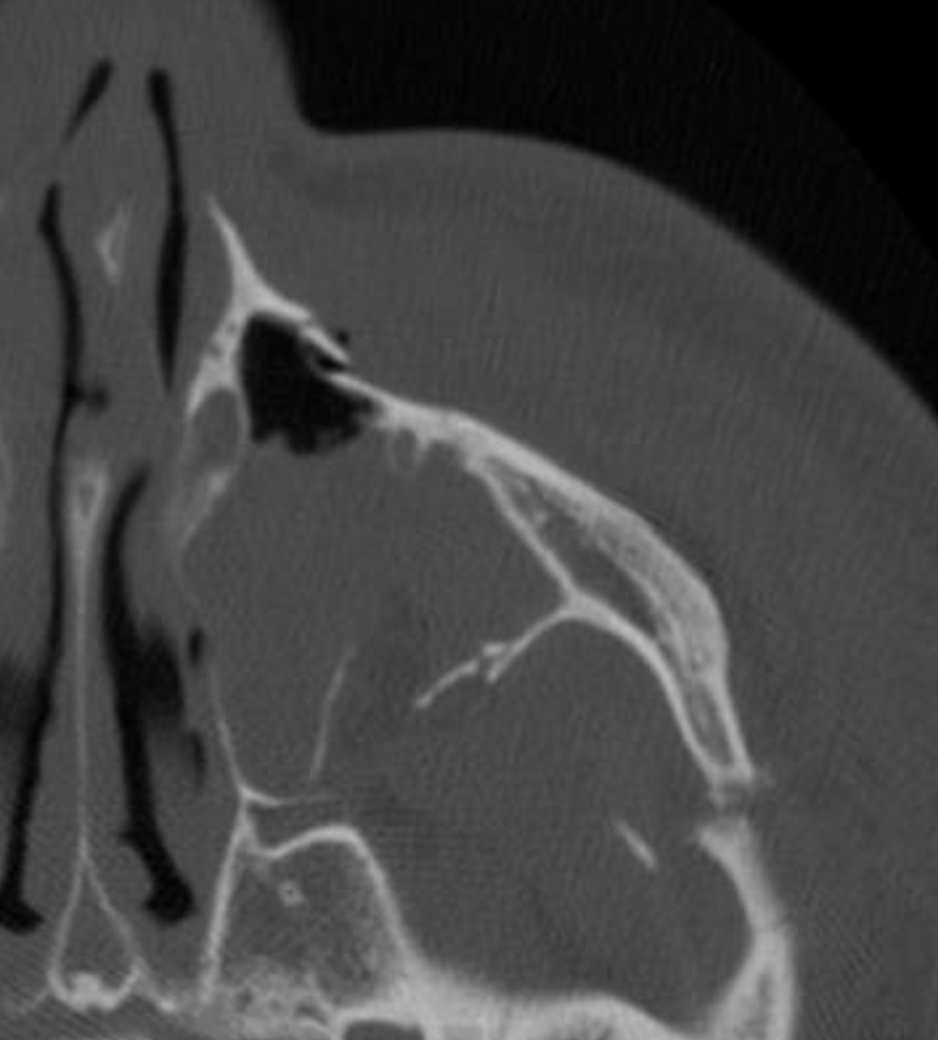
ZMC fracture - treat with 3 point fixation
ORIF sequence: ZF > assess alignment via SZ > ZM > IOR
Lastly, arch may be popped out or fixated depending on fx
Point to the plane for TAP block. Which nerves are targeted?
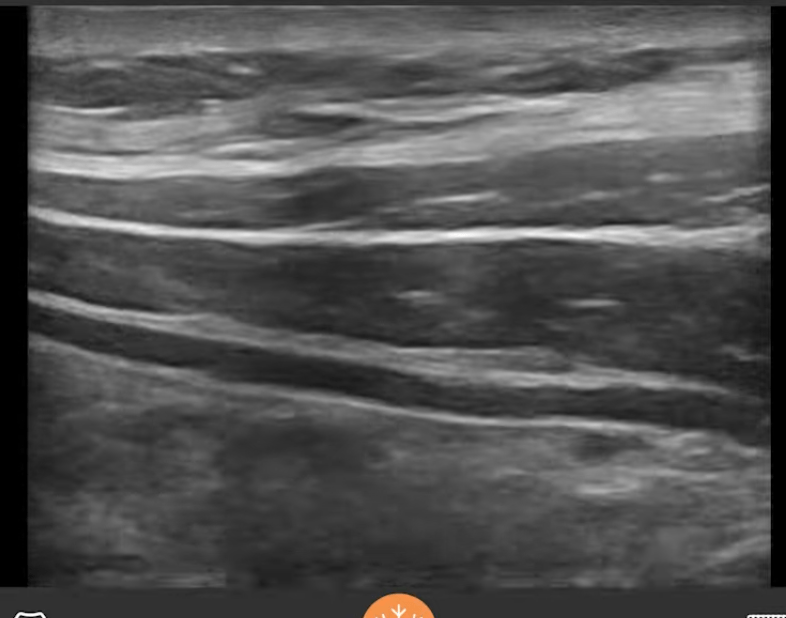
Spinal nerves T6-L1
complication after breast augmentation.
capsular contracture
!!!BONUS 100: what is the MC proposed cause? how could you ppx?
2 hours for muscle, 6 hours for skin
S/p BBL in DR with pain & drainage from buttock. Name the growth medium used to culture the most likely bug?
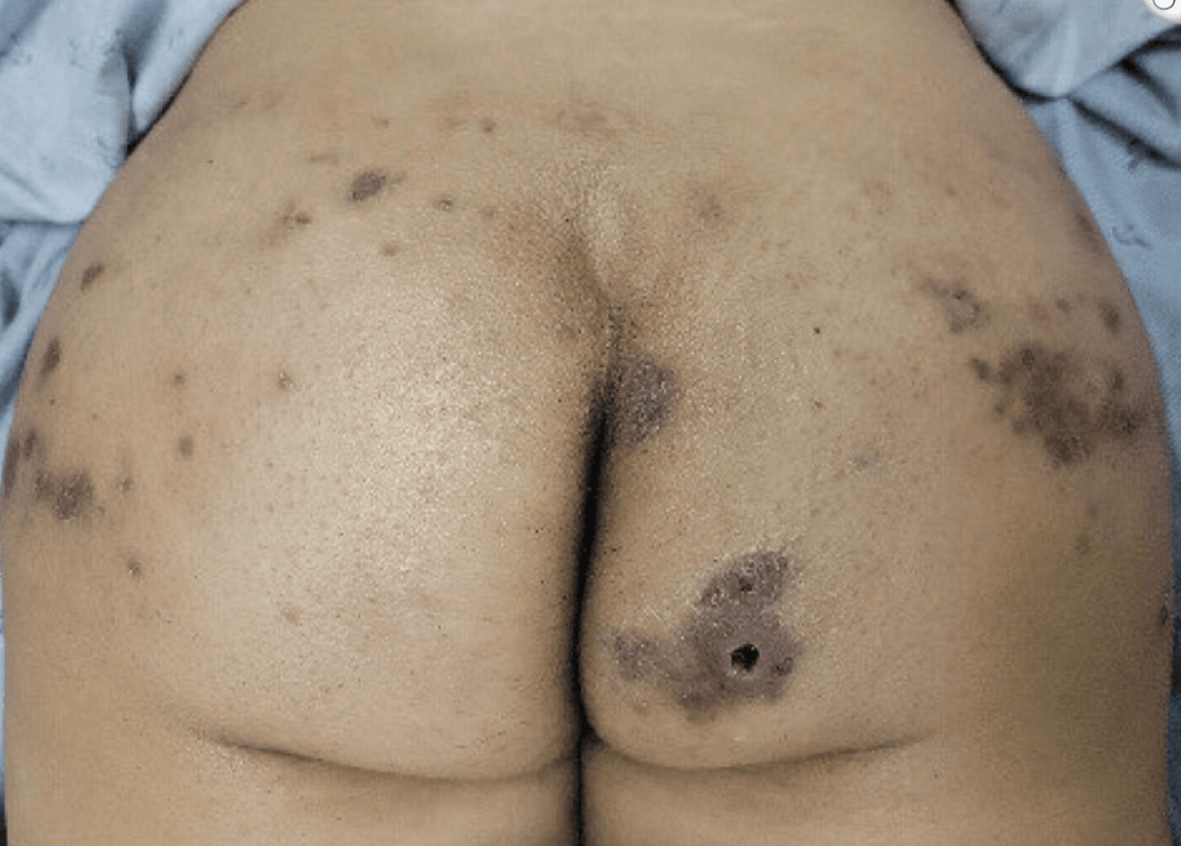
Lowenstein-Jensen(LJ), agar-based media
Exam with +Watson's Test. Describe treatment plan.
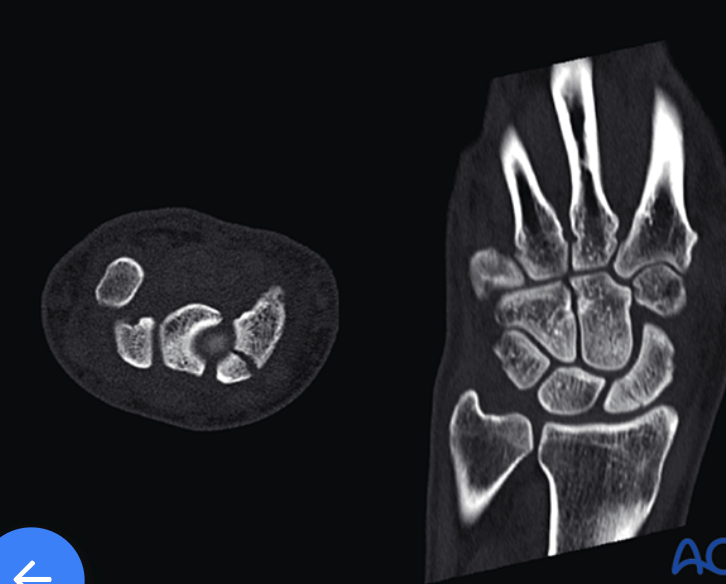
scaphoid with proximal pole fx: cannulated, headless, self-compressing screw (2.4 or 3.0 mm) fro large defects (5mm), anterograde via dorsal approach
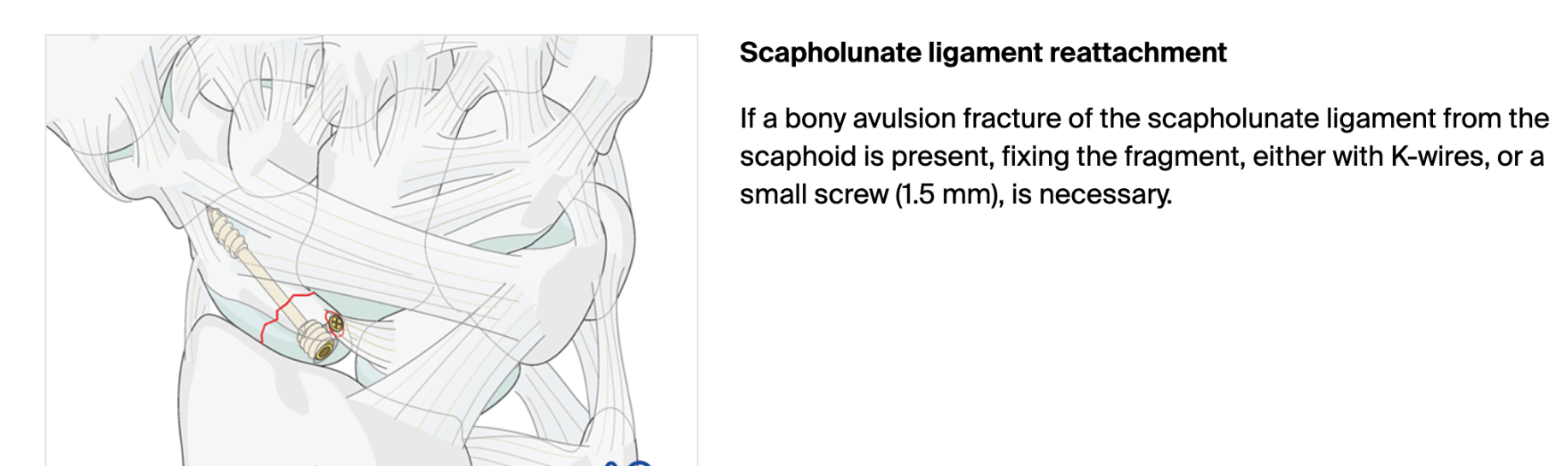
+Watson's Test = pressure is applied to the scaphoid tubercle while the wrist is moved from ulnar to radial deviation; a positive result is a painful click, thud, or subluxation of the scaphoid as the pressure is released, indicating a tear in the scapholunate ligamen
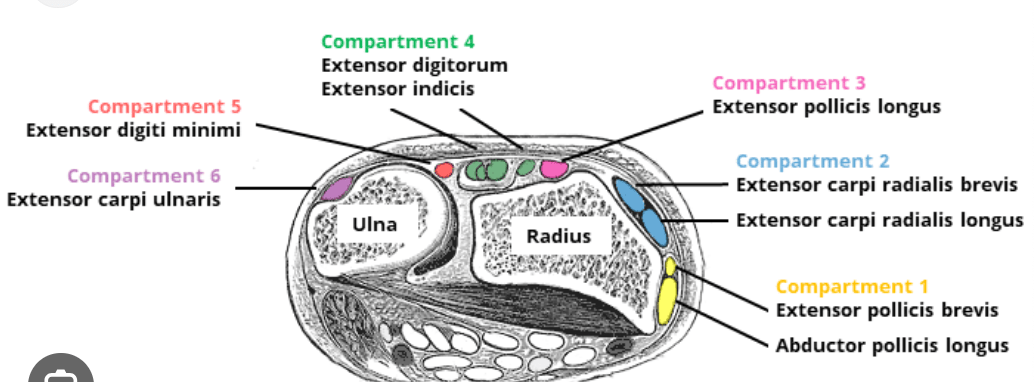
Name the compartments.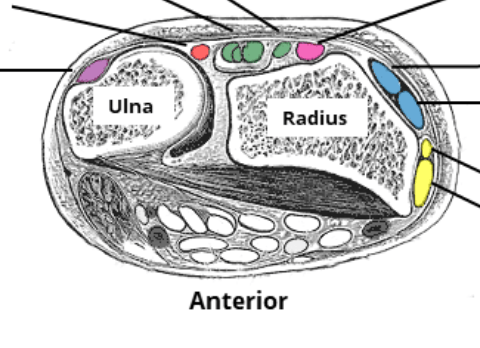
cause of free flap failure.
Venous congestion
What is the free flap failure rate?
3-5%
22F with stab would to R hand. Please describe exam and the 2 injured structures seen in the exam? What is the treatment?
SF FDS injury & low ulnar nerve injury
Fall onto his right hand, with pressure on the thumb and index fingers resulting in metacarpophalangeal pain, swelling and functional limitation.
What is the best next step?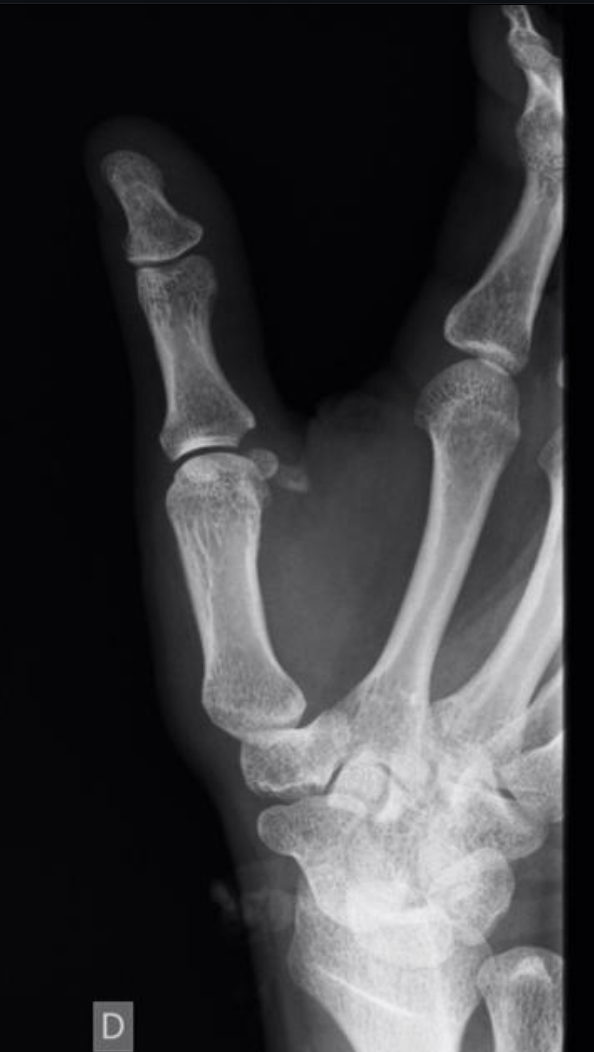
What is MRI to assess for Stener lesion.
BONUS: what is this lesion?
Which numbers represent the muscles of mastication and what are their names.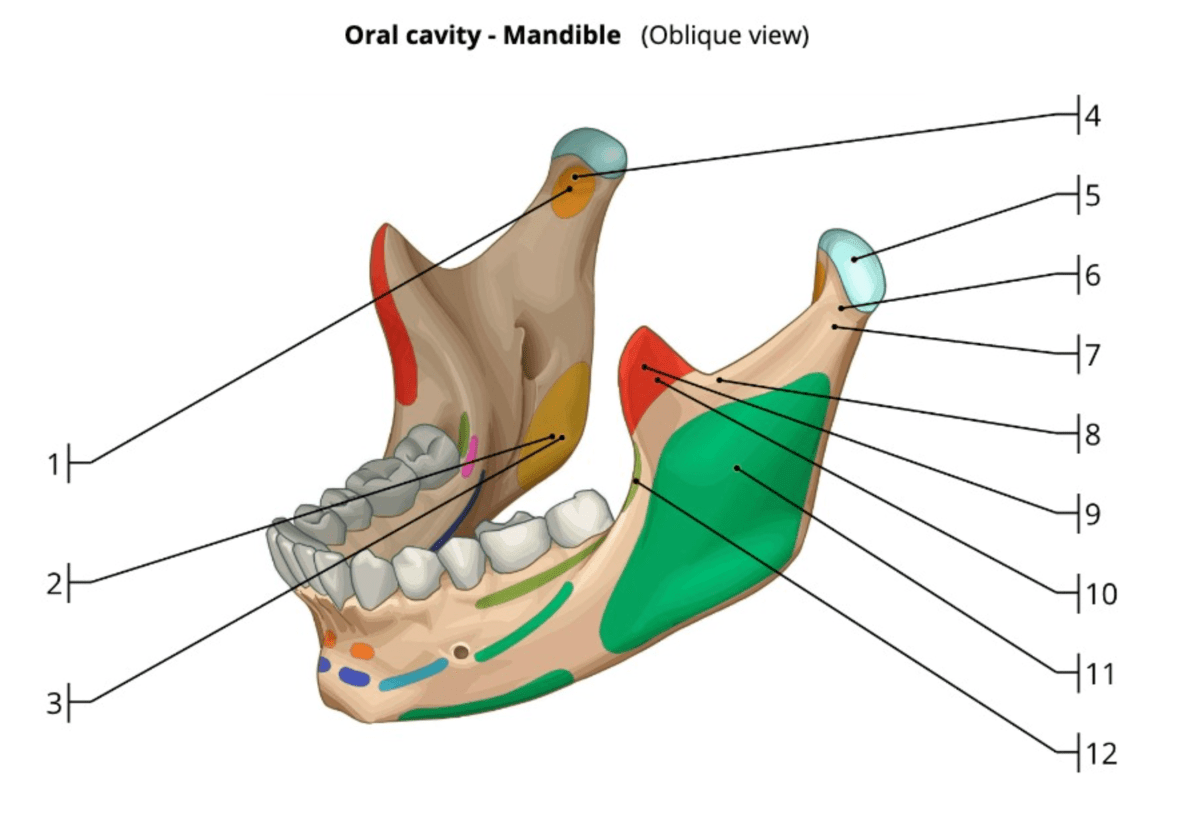
What is
1/4. lateral pterygoid
2/3. medial pterygoid
9/10. temporalis
11. masseter
site of tendon rupture in rheumatoid arthritis.
Extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
Tram flap is to _____ as _____ is to seroma
Tram flap is to fat necrosis as lat flap is to seroma
47M presents with multiple facial injuries following high impact car accident where he slammed the side of his chin/face into steering wheel. Endorses malocclusion. CT max face shows medial displacement of condyle.
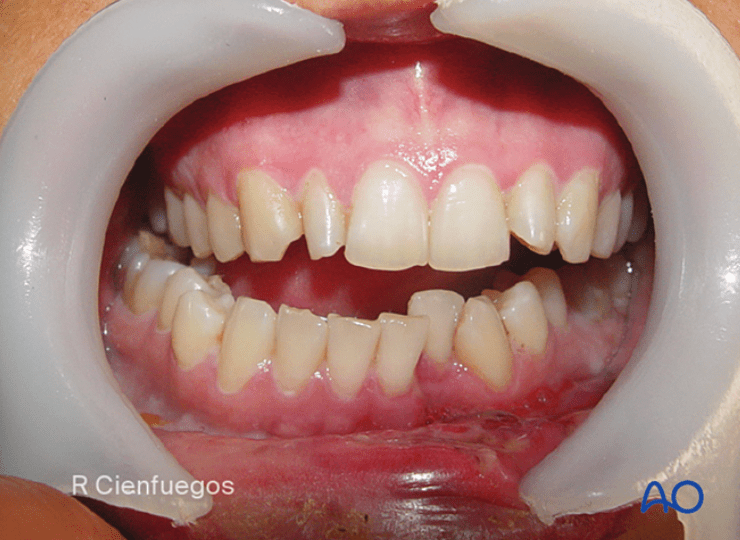
Where does he most likely have fractures? In what order should they be repaired and how?
R condylar neck fx and L mandibular body or parasymphysis fx
First, you place pt in pre-morbid occlusion with arch bars and MMF. Then, you repair fx's within dental arch, moving anterior to posterior to guarantee proper occlusion. At the end, you reduce edentulous fractures (ie. condyle)
Can use 1 monocortical mini plate (2.0mm) per fracture making sure to have 3 holes on each side.
**studies no longer support needing rigid fixation of one of the fractures (with 2 mini plates, locking plate or 2.0 recon plate) - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37772893/
Then you can treat the condylar neck fracture with MMF for 2 weeks or fixate it with 1-2x 2.0mm miniplates depending on height of fx.