What are the 3 states of matter in order from the LEAST to MOST amount of energy of the particles?
SOLID, LIQUID, GAS
The term for when a liquid turns into a gas?
vaporization
What happens when heat is added to matter?
Adding heat makes the particles move faster.
How do the molecules of ice MOVE and how are they ARRANGED?
They vibrate.
They are close together
Name the following states of matter in order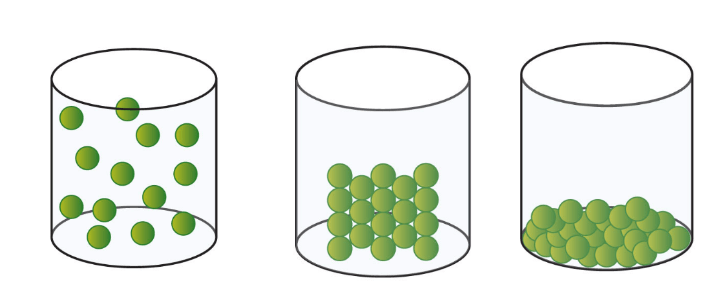
Gas, Solid, Liquid
Liquids have a fixed shape, but not a fixed volume. True or False?
False. Liquids have no fixed shape, but have a fixed volume.
What is the term called for when a gas turns into a liquid?
Condensation.
What happens to the spaces between the particles when a solid is heated and why?
The spaces between the particles in the sold increases because they are vibrating faster and so need more room to move.
How do water molecules behave ?
They move past each other.
All matter is made up of
Atoms
Name two properties of a solid.
Example: has a fixed shape, they have a fixed volume , cannot be compressed.
What is the opposite of vaporization?
Condensation.
Give 2 examples of what happens to the particles in a liquid during contraction (when heat is taken away).
The lose KE, particles move closer together
How do water vapour molecules behave?
They move around radomnly.
Matter can exist in different states, depending on its
Temperature and pressure
Which states of matter take the shape of their container?
Liquids and gas.
What do you call when a liquid becomes a solid?
solidification
When a liquid is heated what happens to the volume of the liquid?
The volume increases
What happens to water molecules if we add energy to them?
They move faster
Can matter be created or destroyed?
NO!
Which states of matter cannot be compressed?
Solids and Liquids.
Name the changes of state from 1-6 in the diagram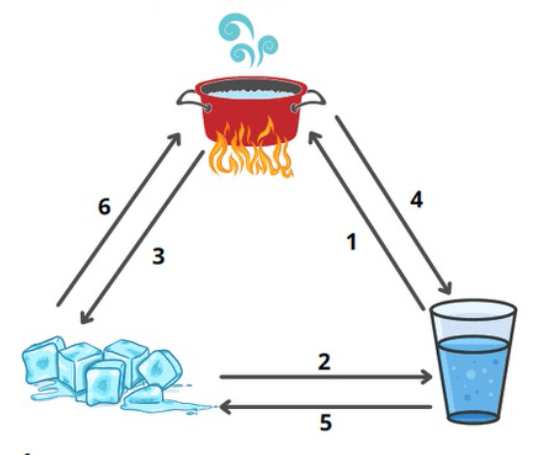
1. vaporization
2. melting
3. Deposition
4. condensation
5. solidification
6. sublimation
When we add heat, what are we adding to the molecules?
Energy.
What happens to water vapour molecules when we remove energy?
They move slower. The water vapour becomes water.
What is NOT matter
forms of energy
Which state/s of matter do not have a fixed VOLUME?
Gases
What is happened in the graph when the temperature plateau's (stops rising) between points B and C and points D and E?
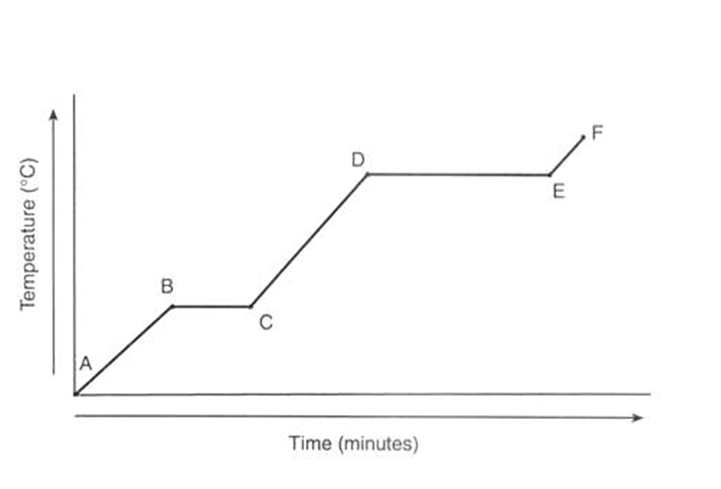
The plateau's represent the changes in state
In this heating curve of ice, what state/s is the water in during:
stage B and C and stage D and E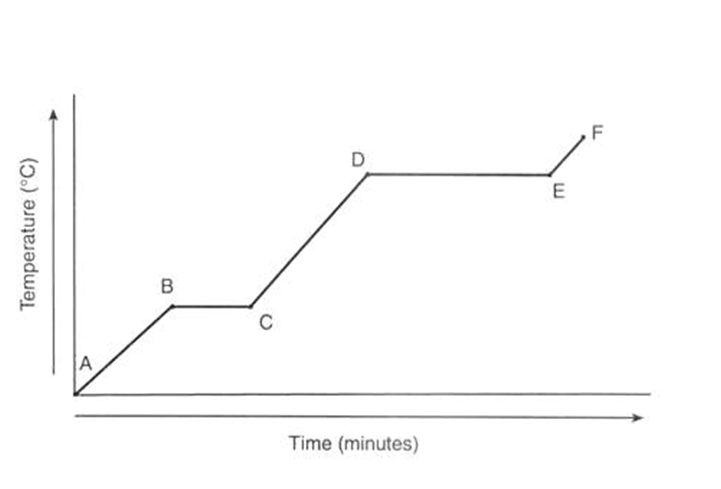
B and C -a mixture of solid ice and water
D and E - water and steam (gas)
In which state of matter are the particles moving
All of them
what is the definition of matter
Anything that has MASS and takes up SPACE