What is a rigid transformation?
A transformation that preserves size & shape.
A square with side length 2 units is translated 5 units up. What happens to its area?
The given graph depicts a rigid transformation.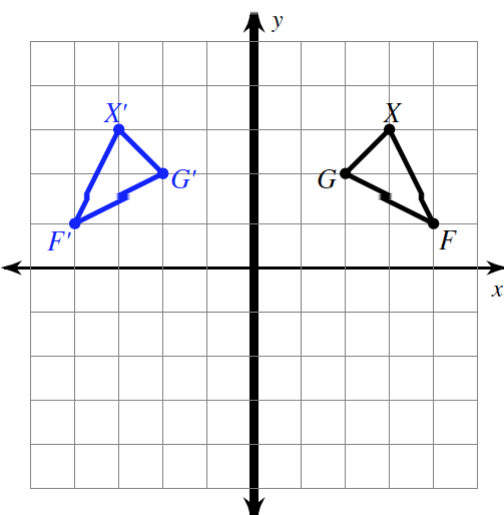
What is a reflection in the y-axis?
The given graph depicts a rigid transformation.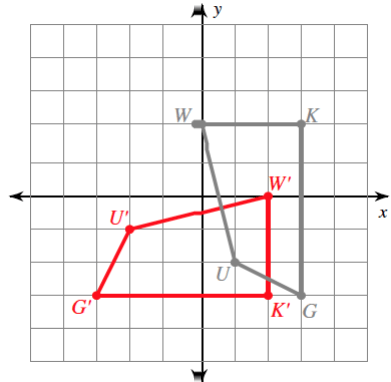
What is a 90-degree clockwise rotation?
What does it mean for two figures to be congruent?
Same shape and size.
Name the three types of rigid transformations.
Translation, reflection, rotation.
Translate point A(–2, 4) by the rule (x, y) →
(x + 3, y – 2). What is A′?
(1, 2)
The figure has been reflected over this line.
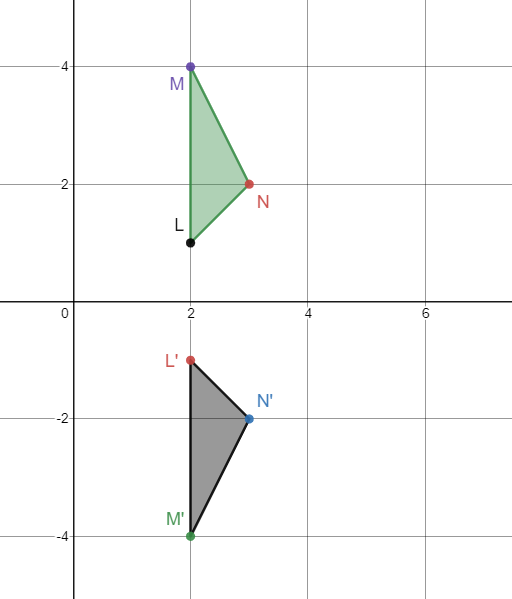
What is the x-axis?
A square is rotated 90° counterclockwise, then translated up 3 units. How is its size affected?
Size unchanged.
True or False: If two figures can be mapped onto each other using rigid transformations, they are congruent.
True.
Define congruent figures
Figures with same shape & size.
Write a Sequence of transformations that moves point P(–5, 0) to P′(2, 7).
(x + 7, y + 7)
Reflect point (4, –2) across the y-axis. What is the new point?
(–4, –2)
The given graph depicts rigid transformations of the pre-image *. This triangle represents a Rotations of * 90-degrees counterclockwise about the origin. 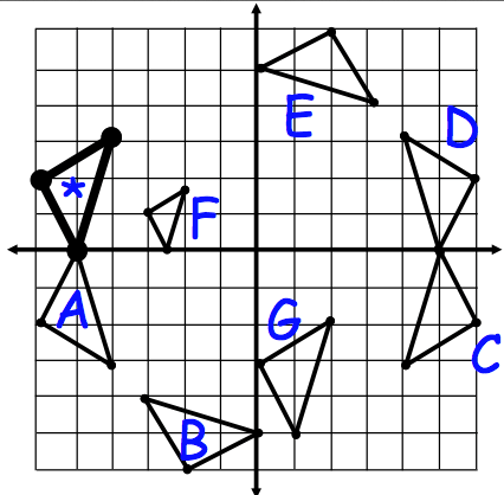
What is figure B?
A triangle has vertices at (0,0), (2,0), (1,3). Another triangle has vertices (–2,0), (0,0), (–1,3). Describe the transformation(s) that prove the triangles are congruent.
Reflection across y-axis.
True or False: Dilations are rigid transformations.
False, surprise that is your next unit;)
Translate triangle with vertices (1,1), (2,3), (3,1) 4 units right. List new coordinates.
(5,1), (6,3), (7,1)
A triangle at (1,2), (2,4), (3,2) is reflected over the y-axis and then translated 1 unit down. Write its new coordinates.
(–1,1), (–2,3), (–3,1)
Rotate point (0, 5) 180° about the origin. What is the new point?
(0, –5)
Two triangles are congruent. One has sides 3, 4, 5. What are the side lengths of the other triangle?
3, 4, 5.
Explain the difference between a rigid transformation and a non-rigid transformation.
Rigid = preserves size; non-rigid (dilation) = changes size.
A figure is translated left 2 and up 3. Describe this movement using a coordinate rule.
(x – 2, y + 3)
Reflect triangle with vertices (1,1), (2,2), (3,1) across the x-axis. List new coordinates.
(1, –1), (2, –2), (3, –1)
Rotate point (–3, 2) 90° clockwise about the origin.
(2, 3)
Explain why all rigid transformations preserve congruence. Give an example using coordinates.
They preserve distance and angle measures