Large opening at the base of the skull where the brain and spinal cord meet.
What is the foramen magnum
Non-permeable dressing applied to sucking chest wound
What is occlusive dressing?
Two or more adjacent ribs broken in two or more places
What is a flail chest/ segment?
The dose of tetracaine
2 drops in affected eye (q5 for bonus 100pts)
Tiny mark...Major Damage.
This wound is difficult to determine the extent of internal damage.
What is a stab wound?
The most common type of soft tissue closed wounds.
What is a contusion?
The Blue Line indicates this type of fracture
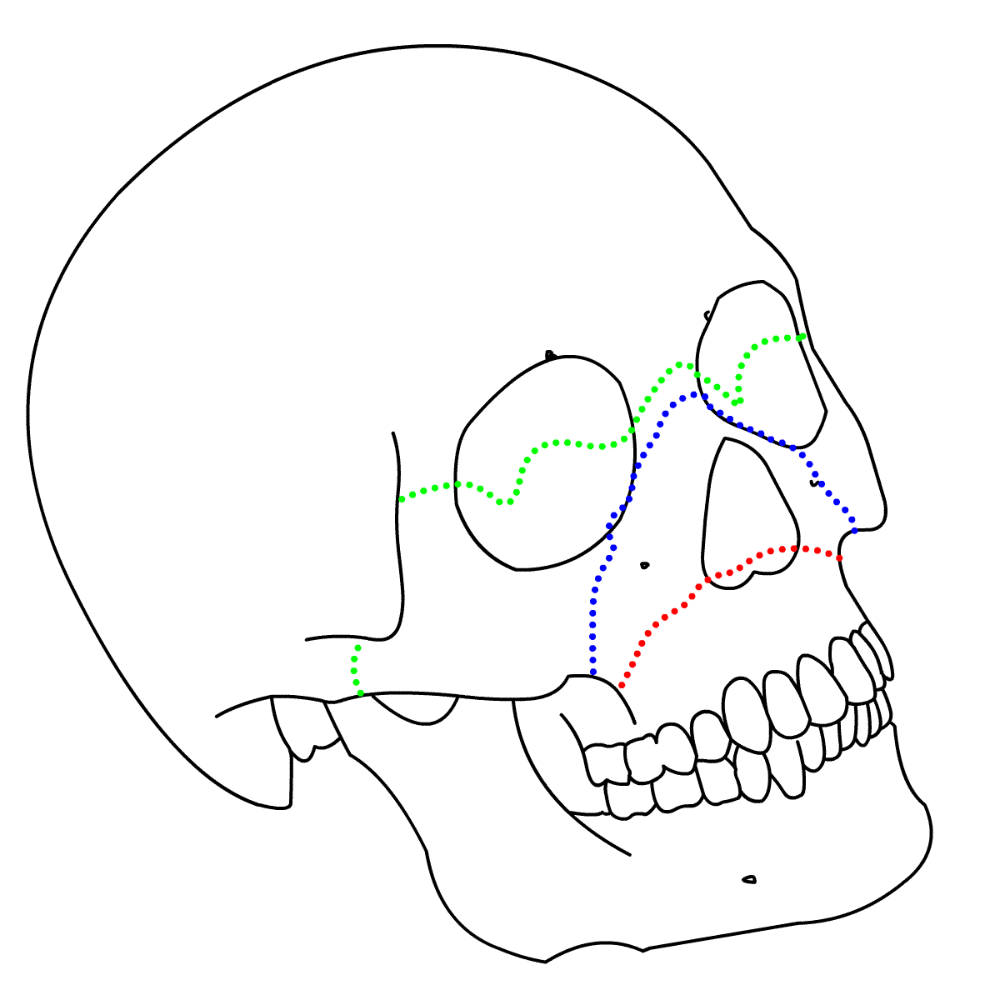
What is La Forte II
Rice Krispie feeling on palpation of neck and shoulders is most indicative of this type of injury
What is a pneumothorax?
Two signs that indicate a basilar skull fracture
What are racoon eyes/ battle sign?
The classification of Toradol
What is an NSAID?
The ______ ________ connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain
What is the corpus callosum?
This is "B" in DCAPBTLS
What is burns?
Bradycardia/Widening pulse pressures/Irregular breathing
What is Cushing's Triad?
Shallow breathing, decreased breath sounds on the injured side, and hemoptysis are signs of this.
What is a hemothorax?
The four types of skull fracture
What are linear, depressed, open and basilar?
Indications for entanox
What are moderate to severe pain, anxiety, apprehension?
Needle decompression is used to treat this type of injury
What is a tension pneumothorax?
Your patient has extensive facial soft tissue injuries. This is your primary concern
What is Airway?
Your patient reports vision loss similar to a curtain obstructing their view after being hit in the face with a softball. You suspect this is most likely the cause
What is a Detached Retina?
The heart, esophagus, and great vessels are encompassed in this anatomic region.
What is the mediastinum?
Temporary dysfunction of the spinal cord that usually lasts 24-48 hours
What is spinal cord concussion?
Contraindications of entanox
Impaired level of consciousness, head injury, inability to comply with instructions
Decompression sickness
Undiagnosed abdominal pain or marked distention, bowel obstruction
Hypotension, shock
COPD (carbon dioxide retention)
Cyanosis
Chest trauma with pneumothorax
CPP=____________
What is MAP-ICP?
The spinal cord ends at this vertebrae
What is L2?
Your patient is now unresponsive with irregular respirations and bounding radial pulse. Witnesses tell you that he was unconscious immediately after the wreck, he woke up and was trying to get out of the vehicle before falling back asleep. This most likely indicates this type of head injury.
What is an Epidural Bleed?
Your patient presents unresponsive with JVD, clear lung sounds, narrowing pulse pressures, and tachycardia after being stabbed in the Left anterior chest. This most likely indicates what injury
What is Pericardial Tamponade?
Hyperventilating an unresponsive/ head injured patient should only be done if you suspect this condition
What is cerebral herniation?
Contraindications of Toradol
Hypersensitivity to ASA or NSAIDs
Hypovolemia
Patients on anticoagulants
CVA or Head Trauma in last 24 hours
Peptic ulcer disease or history of GI bleeding
Pregnancy (Third Trimester)
Known renal insufficiency
These 3 things help determine injury potential from a fall.
What are:
1. Height of the fall
2. Type of surface struck
3. Part of the body that is struck
Pts in neurogenic shock present with warm, dry, red skin because....
What is vasodilation, blood pooling, relative hypovolemia?