The Most Common Cause of Preventable Death in a Trauma Patient.
What is Hemorrhagic Shock?
Direct Force Transmitted along the Length of the Vertebral Column.
What is Axial Loading?
Tear-Shaped Pupil, Loss of Vision, Scleral and Corneal Damage.
What May Be Seen With a Ruptured Globe?
Rib Fractures with Paradoxical Chest Wall Movement.
What is Flail Chest?
Intervention for a Hypotensive and Supine Pregnant Patient.
What is Turn the Patient to Her Left Side?
Presence of Rectal Tone and Perianal Sensation in Spinal Cord Injury.
What is Sacral Sparing?
Hypothermia, Coagulopathy, and Metabolic Acidosis.
What is The Trauma Triad of Death?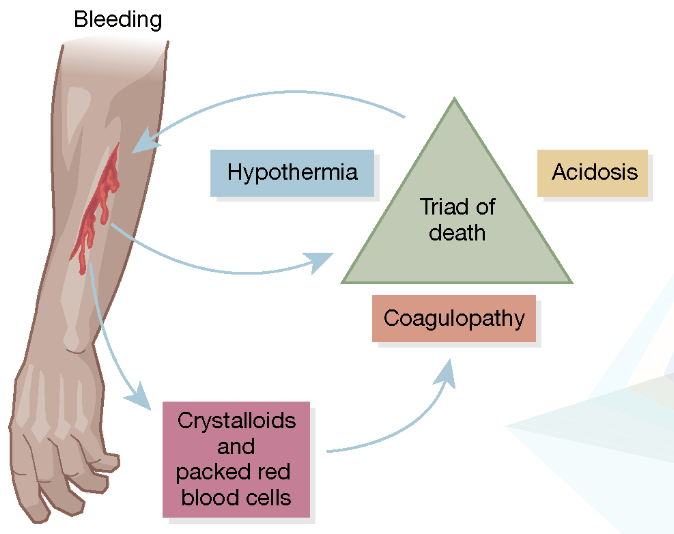
In this Type of Blast Injury, Pulmonary Barotrauma and Tympanic Membrane Rupture can occur.
What is Primary Blast Injury?
This Triad Consists of Bradycardia, Widening Pulse Pressure, and Diminished Respiratory Effort.
What is Cushing's Triad?
A Symptom often Associated with Splenic Injruy.
What is Left Shoulder Pain (KEHR'S SIGN)?
Cervical Arthritis, Cerebral Atrophy, Gait Instability, Decreased Muscle Mass.
What are Anatomic or Physiologic Changes in the Older Adult?
No Midline Tenderness, No Focal Neuro Deficit, Normal Alertness, No Intoxication, No Painful/Distracting Injury.
What are Clinical C-Spine Clearance Criteria?
In This Stage, There is Hypotension and Tissue Damage.
What is Decompensated or Hypotensive Shock?
This Type of Energy Increases FOUR Times when Velocity is Doubled.
What is Kinetic Energy? KE = 1/2 mv2
This Type of Facial Fracture has the Highest Risk of Airway Compromise.
What is a Lefort III Fracture?
Muffled Heart Sounds, Hypotension, and Distended Jugular Veins.
What are Signs of Pericardial Tamponade (BECK'S TRIAD)?
In this Process, Victims Disrobe, Wash with Soap and Water, and Dry with a Towel.
What is Decontamination?
The Presence of Spinal Cord Injury Despite Negative Imaging.
What is Spinal Cord Injury without Radiograph Abnormality (SCIWORA)?
This Management Strategy Allows a Lower Blood Pressure to Avoid "Popping the Clot."
What is Hypotensive Resuscitation (PERMISSIVE HYPOTENSION?)
The Trajectory of a Driver Thrown Through the Windshield.
What is the "UP AND OVER" Pathway?
Drowsiness, Nausea, Vomiting, and Headache.
What are Early Assessment Findings of Increased ICP?
Bowel Sounds Heard in the Chest after Blunt or Penetrating Trauma.
What is a Sign of a Ruptured Diaphragm?
Attach CO2 Detector and Assess for CO2, Observe Chest Rise and Fall, Listen to Epigastrium, then Lungs.
What is Confirmation of ETT Placement?
An Injury at or Above this Level of the Spine will Likely Result in a Paralyzed Diaphragm and the Inability to Breathe.
What is the 5th Cervical Vertebrae?
This Stage is Manifested by an Anxious Patient with Tachypnea, Normal Systolic BP, and a Rising Diastolic BP.
What is Compensated Shock?
In this Impact, the Internal Organs Collide within the Body Cavity.
What is Third Impact?
Widespread Microscopic Hemorrhagic Lesions and Cerebral Edema.
What is Diffuse Axonal Injury?
Is Dependent on the Operator Performing or Interpreting the Exam, and 150-200 mL of Fluid is Necessary.
What are the Limitations of the FAST exam?
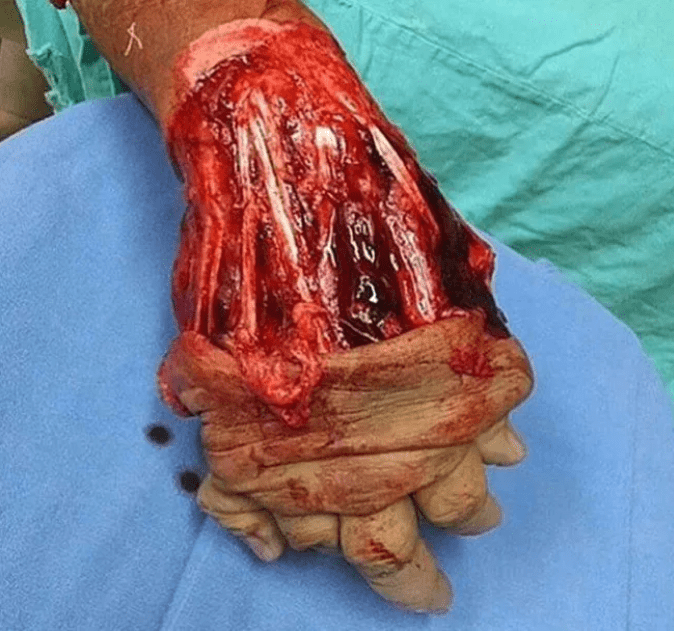
What is Degloving Injury?
The Type of Shock Demonstrated by the Loss of Vascular Tone.
What is Neurogenic (Distributive) Shock?