The leafy part of a tree is called the ___________.
crown/canopy
What are the two main types of trees?
angiosperms (deciduous) and gymnosperms (evergreens)
Is this leaf simple or compound?

Compound
These keep the tree anchored in the ground.
roots
What makes a tree a tree?
having bark, tall trunk for support, over 13 feet, lives for multiple seasons
How would you describe the edges of this leaf?
toothed
Identify the needle arrangement. 
Single needles
What does the cambium do?
It makes new cells for the tree to grow.
What does angiosperm translate to? (Latin to English)
"covered seed"
How would you describe the edges of this leaf?

lobed and smooth
Identify the venation (veins) on the following leaf.

Palmate
In what season to trees grow and bloom?
Spring
What does gymnosperm translate to? (Latin to English)
"Naked seed"
How would you describe this leaf?
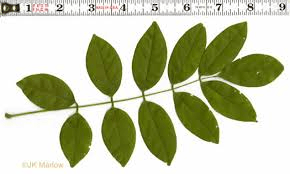
Pinnately compound
Identify the needle arrangement

Bundle of 2
What is the role of phloem/inner bark?
Moves food made in the leaves to the roots
What is this leaf arrangement?

Alternate
Identify the needle arrangement

Clusters
What is the heartwood?
Nonliving inner core of the trunk