The skin is the first part of the _____ most pathogens will encounter.
What is the innate immune system?
Cells in this layer of skin are highly proliferative, migrate superficially, and die in order to act as one of the first layers of the innate immune system.
What is the Epidermis?
These are the primary cells of the adaptive immune system.
What are lymphocytes - B cell and T cells?
What chemical mediator of inflammation is activated by the exposure of negatively charge collagen?
What is Hageman Factor (Factor VIII)?
A small wound with apposed edges is classified as____.
What is primary intention?
These are the primary cells of the epidermis helping to maintain the skin barrier function and produce cytokines for dermal dendritic cells.
What are keratinocytes?
The dermis is split into these two layers.
What is the papillary and reticular dermal layers?
Positive selection of T- cells occurs here.
Cortex of the thymus
These are the 5 cardinal signs of inflammation:
What is redness, swelling, pain, heat, and loss of function?
The following is an image of ______. An important step in the wound-healing process which keeps the wound sterile.

What is granulation tissue?
These specific tissue-residing antigen-presenting cells are found in the epidermis and are activators of the innate and adaptive immune responses. 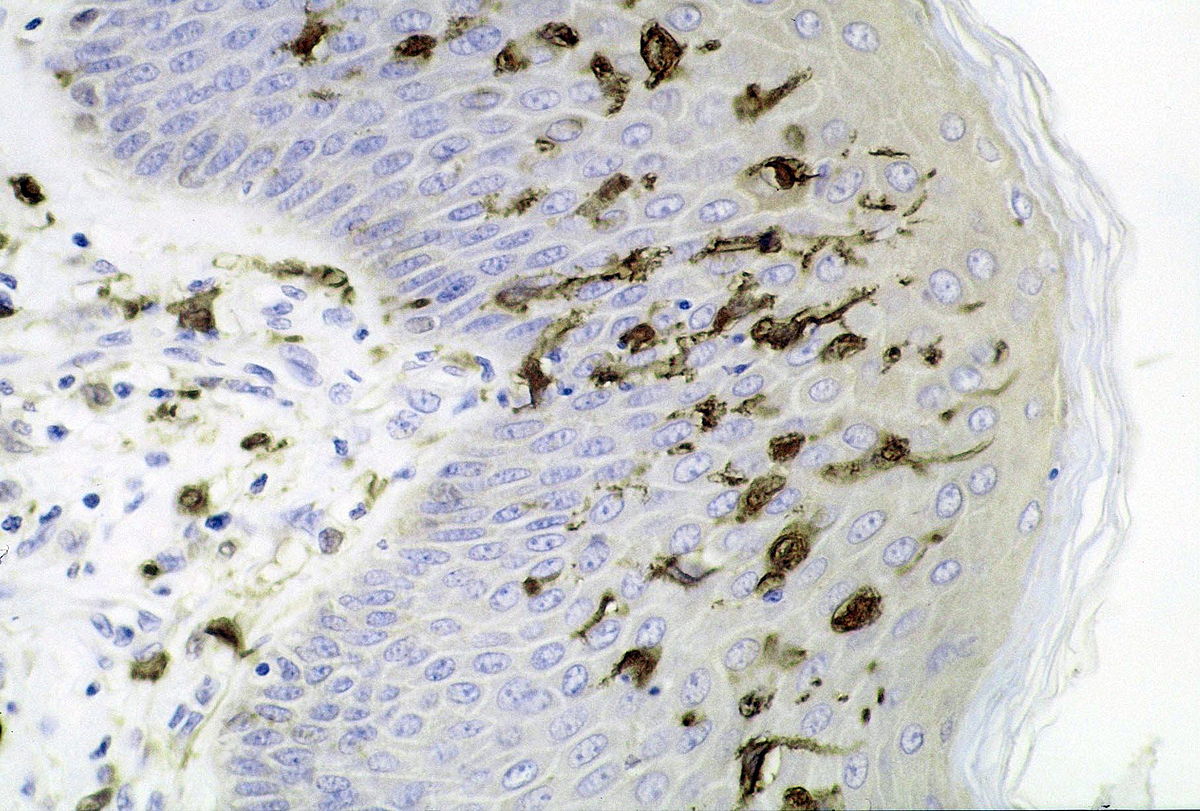
Langerhans cells (Epidermal dendritic cells)
Layer only found in "thick" skin.
Stratum lucidum
T-cell independent activation of B-cells is only able to produce this immunoglobulin.
What is IgM?
Leukocyte margination is mediated by the _____ glycoprotein, while emigration/diapedesis is mediated by _____.
What are selectins and integrins?
Gram-negative bacteria is an example of ______, which helps lead to the systemic manifestation of inflammation/fever?
What is an exogenous pyrogen?
Keratinocytes and Langerhans cells present ______ that help to identify the presence of PAMPs.
What are toll-like receptors (pattern recognition receptors)?
This skin feature is only found in "thin skin"

_____ is found on all cells while _____ is only found on antigen-presenting cells (B, plasma, and dendritic).
What is MHC I then MHC II?
Along with its roles in the intrinsic coagulation pathway, this enzyme aids in vasodilation and vascular permeability.
(kininogen...kinin...bradykinin)
What is kallikrein?
_______, is Emma's favorite Philly restaurant so far.
What is Miss Saigon specifically because I think about the Porkbelly Bao at least once a day?
This substance secretes fatty acids which work to make the skin inhospitable for alkaline pathogens and stimulate anti-microbial peptide production.
What is sebum?
This cell-matrix junction helps connect the epidermis to dermis through anchoring keratin intermediate filaments to the basement membrane.
What are hemidesmosomes?
This determines the isotype of an antibody.
What is the heavy chain?
This cytokine provides the gradient that neutrophils follow to injured tissue.
These two classes of bacteria are commonly found in normal human microflora.
What are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus?