This ventilator mode provides a set tidal volume for every breath and triggers mandatory breaths at a set rate.
Assist-Control (AC) ventilation
A 32-year-old woman with fatigue and weight gain has a TSH of 8.2 with a normal free T4. She is 10 weeks pregnant. According to ATA guidelines, this is the recommended treatment.
Initiate levothyroxine therapy, subclincal should be treated in pregnancy.
A homeless man found outdoors in freezing weather has a core temperature of 31°C (87.8°F). He is confused, bradycardic, and shivering stops soon after arrival. This clinical finding marks the transition to moderate hypothermia.
Cessation of shivering
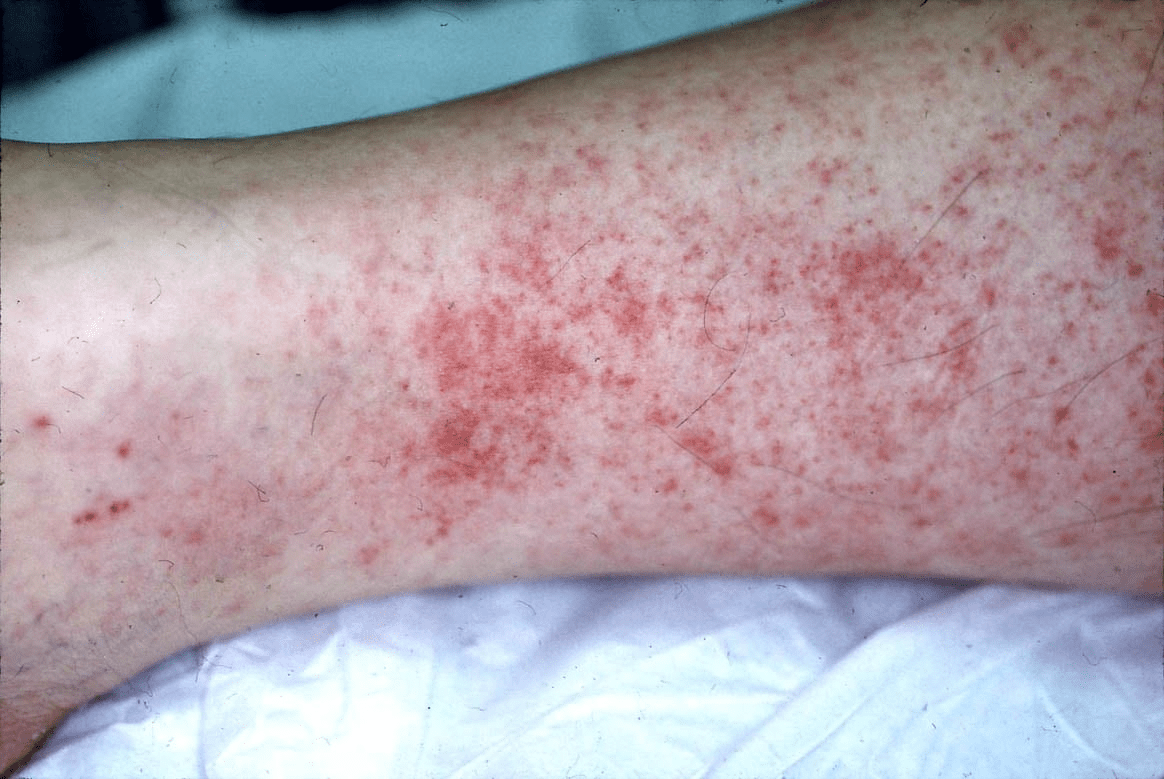
A 29-year-old woman presents with episodic abdominal pain and a red, raised ‘rash’ on her legs that is tender to touch and does not blanch. She also has arthralgias. Labs show elevated ESR and creatinine. UA reveals RBC casts. These purpuric lesions suggest this small-vessel vasculitis.
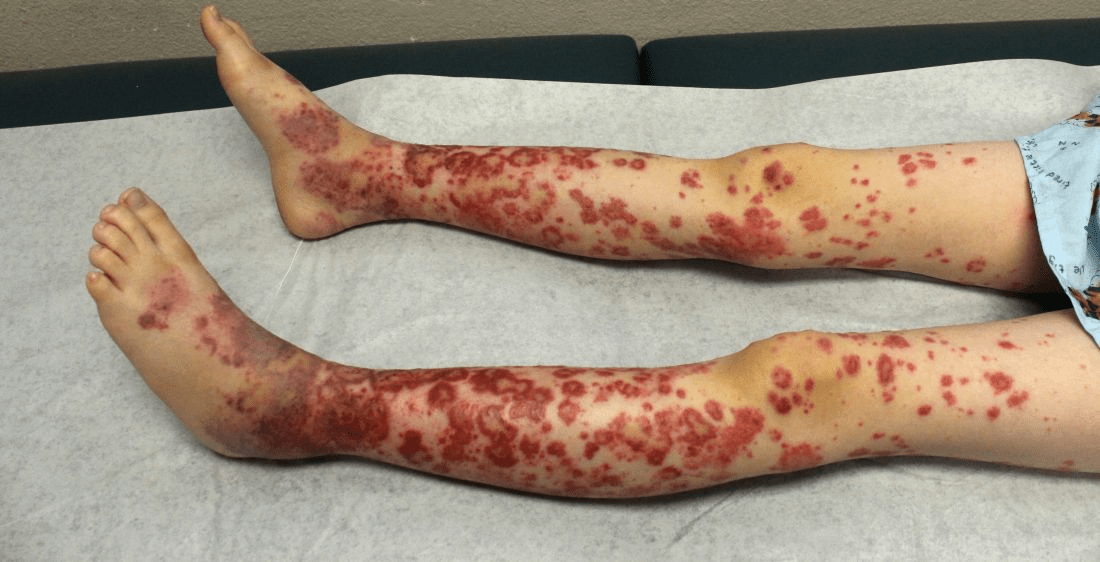
IgA vasculitis (Henoch–Schönlein purpura)
A 68-year-old with sudden dyspnea has a highly elevated D-dimer, but labs also show new-onset thrombocytopenia, low fibrinogen, and prolonged PT/PTT. These labs together move the patient to this diagnosis.
DIC
In response to communication failures being a leading cause of preventable harm, many hospitals adopted the I-PASS handoff mnemonic. The “A” represent these key component of a safe and structured patient sign-out.
Action list, (I-PASS = Illness severity, Patient summary, Action list, Situation awareness/contingency planning, Synthesis by receiver.)
A 58-year-old woman with decompensated cirrhosis presents with rapidly rising creatinine, FeNa <1%, bland urine sediment, and no response to 48 hours of albumin. She is in the ICU with continuous vital monitoring. According to current evidence, this IV vasoconstrictor is the preferred first-line treatment in the ICU:
Terlipressin or Norepinephrine
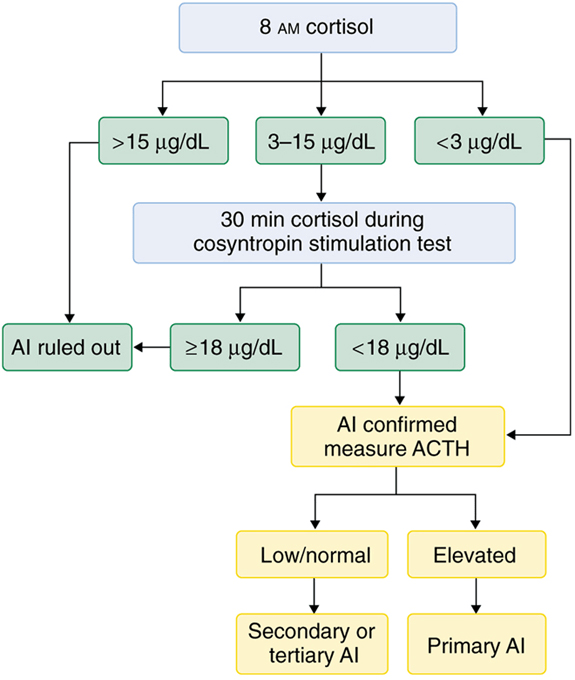
A patient recently tapered off long-term prednisone presents with hypotension, hyponatremia, and low 8 am cortisol (<1). ACTH level is low. This test is used to confirm secondary adrenal insufficiency.
No need for further testing. (If gray zone cortisol 5-15, cosyntropin (ACTH stimulation) test)
A climber with deep frostbite to the fingers arrives after 6 hours of exposure. The affected areas are hard, pale, and anesthetic. According to guidelines, the first-line in-hospital treatment is rapid rewarming using this method:
Immersion in warm water at 37–39°C (98.6–102.2°F)
A 35-year-old woman presents with constitutional symptoms, arm claudication, and unequal blood pressures between her arms. Angiogram is performed showing these findings. What is the Dx?
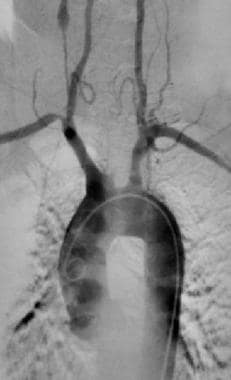
Takayasu arteritis
A 56-year-old man with bulky diffuse large B-cell lymphoma starts R-CHOP. Twelve hours later, labs show: K⁺ 6.1, phosphate 7.0, uric acid 11, calcium 6.8, and creatinine rising from 1.1 to 2.0. These labs together place him firmly on this list and indicate this life-threatening emergency.
TLS
Updated national patient-safety goals stress avoiding medication reconciliation errors during transitions of care. This phase of hospitalization has the highest rate of preventable adverse drug events.
Discharge
A mechanically ventilated patient has pH 7.52, PaCO₂ 25, HCO₃ 22 and is currently managed for multifocal pneumonia. Ventilator settings are: AC/VC with a tidal volume of 450 mL, respiratory rate 24, FiO₂ 40%, and PEEP 5. The most appropriate ventilator adjustment is to do this morning is:
Decrease the respiratory rate (or tidal volume) to reduce over-ventilation
A 44-year-old patient with hypercalcemia (Ca 12.1), low phosphorus, elevated PTH, and kidney stones. A sestamibi scan shows a focal area of increased uptake. According to guidelines, this is the recommended management. (From grand rounds)
Parathyroidectomy (Criteria: Ca >1 mg/dL above ULN, kidney stones, osteoporosis, eGFR <60, age <50.)
A 42-year-old man who drinks 12–15 beers daily presents with confusion and gait instability. Labs show Na 112, serum osmolality 255, urine osmolality 70, and urine sodium <20. He has poor dietary solute intake. This is the most likely diagnosis:
Beer protomania
A patient has episodic severe abdominal pain, neuropathy, and reddish urine that darkens when exposed to sunlight. Symptoms worsen with fasting or new medications. This rare heme synthesis disorder is the likely cause.
Acute intermittent porphyria
A 40-year-old woman presents with fatigue and jaundice. Labs show anemia, elevated LDH, indirect hyperbilirubinemia, low haptoglobin, and spherocytes on smear. The direct Coombs test is positive for IgG. This diagnosis should be suspected.
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (warm AIHA)
During designated educational blocks, residents are required to complete a minimum number of MKSAP questions. According to program policy, each structured session requires completing at least this many questions.
60 questions per session
Rapid is called for a 62-year-old man in shock. He is hypotensive on vasopressors, hypoxic despite 100% FiO₂, and CTA chest is shown below. He was admitted under Neuro ICU initially for intracranial surgery for glioma removal. This is the recommended definitive therapy for this patient:
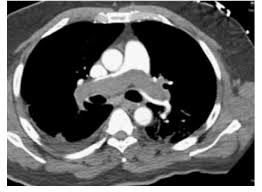
Catheter-directed thrombectomy (mechanical or aspiration thrombectomy)
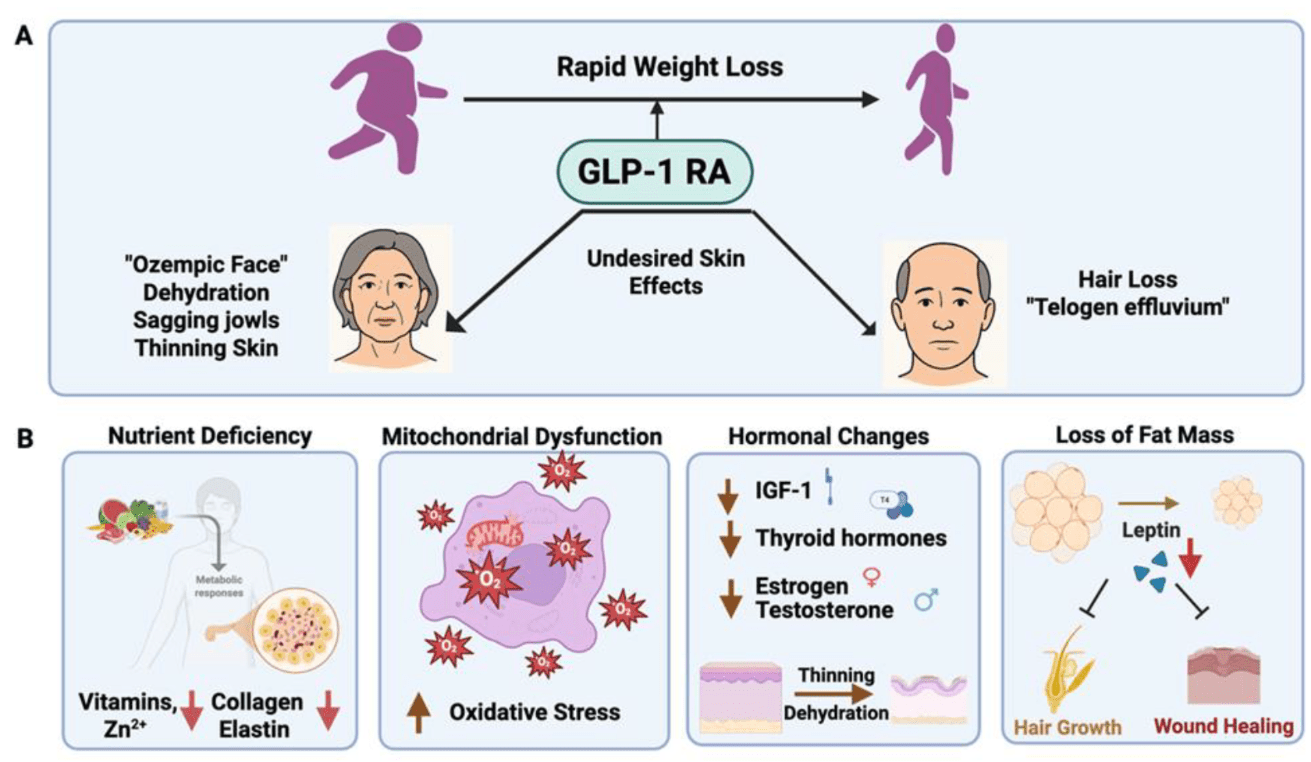
A 45-year-old woman started semaglutide 3 months ago for obesity. She reports increased hair shedding when brushing and showering. Labs show normal TSH, ferritin, B12, and zinc. Her weight loss has been rapid (15% of total body weight). This type of hair loss—commonly reported with GLP-1 therapy—is most consistent with this diagnosis.
Telogen effluvium
A 68-year-old woman admitted for vomiting has persistent hypokalemia (K⁺ 2.8) despite multiple IV potassium replacements. Her EKG shows frequent PVCs. Labs reveal Mg²⁺ 1.1 mg/dL. What is the next step in the management of her hypokalemia?
Correct hypomagnesemia first.
Magnesium is required to block ROMK channels in the distal nephron. When magnesium is low, these channels stay open → the kidneys dump potassium.
A 45-year-old hiker from North Carolina develops fever, severe headache, photophobia, myalgias, and a maculopapular rash that begins on wrists and ankles and spreads centrally. Platelets are low. This disease and vector should be suspected.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever transmitted by American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis)
A 67-year-old man presents with massive splenomegaly, early satiety, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss. Peripheral smear shown below. What is the most likely Dx?
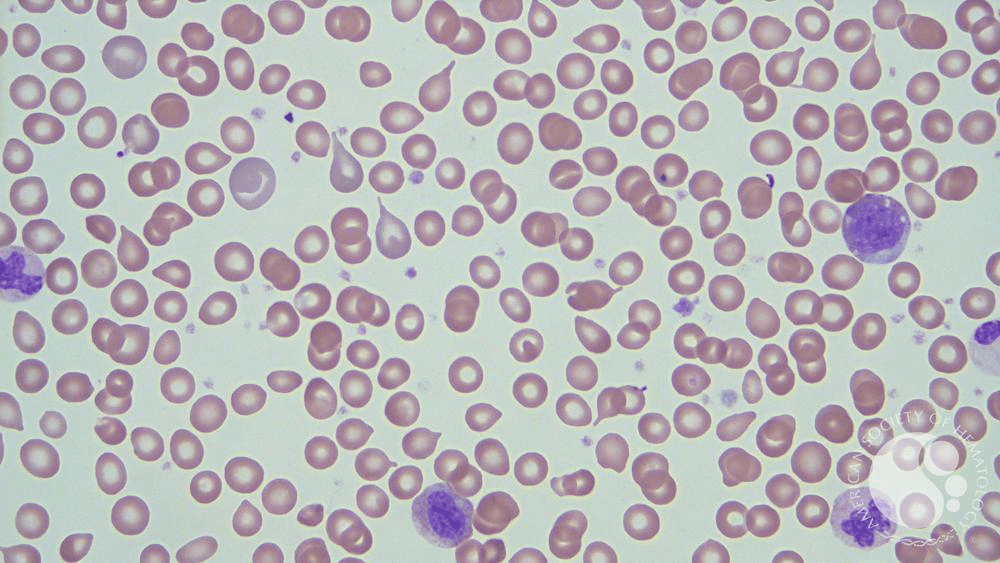
Primary myelofibrosis
According to program expectations, senior residents in MICU rotations must update their ___________ every day after the end of their shift. This is is required to track clinical workload and ensure exposure to high-acuity patients. Failure to do so is considered a deficiency in this professionalism domain.
MICU Census Log
In ARDS, this ventilator strategy is proven to reduce mortality: low tidal volume ventilation targeting ___ mL/kg of predicted body weight.
4–6 mL/kg
A 58-year-old man with type 2 diabetes reports numbness in his feet and worsening fatigue. Labs show macrocytosis (MCV 104) and low vitamin B12. His TSH is normal. This medication effect used in the long term explains his clinical picture.
Metformin-associated vitamin B12 malabsorption, check vitamin B12 every 2–3 years.
A 47-year-old man presents with dark urine, edema, and new hypertension. UA reveals 3+ protein, and microscopy below. Creatinine is rising. These findings are most specific for this category of kidney injury.
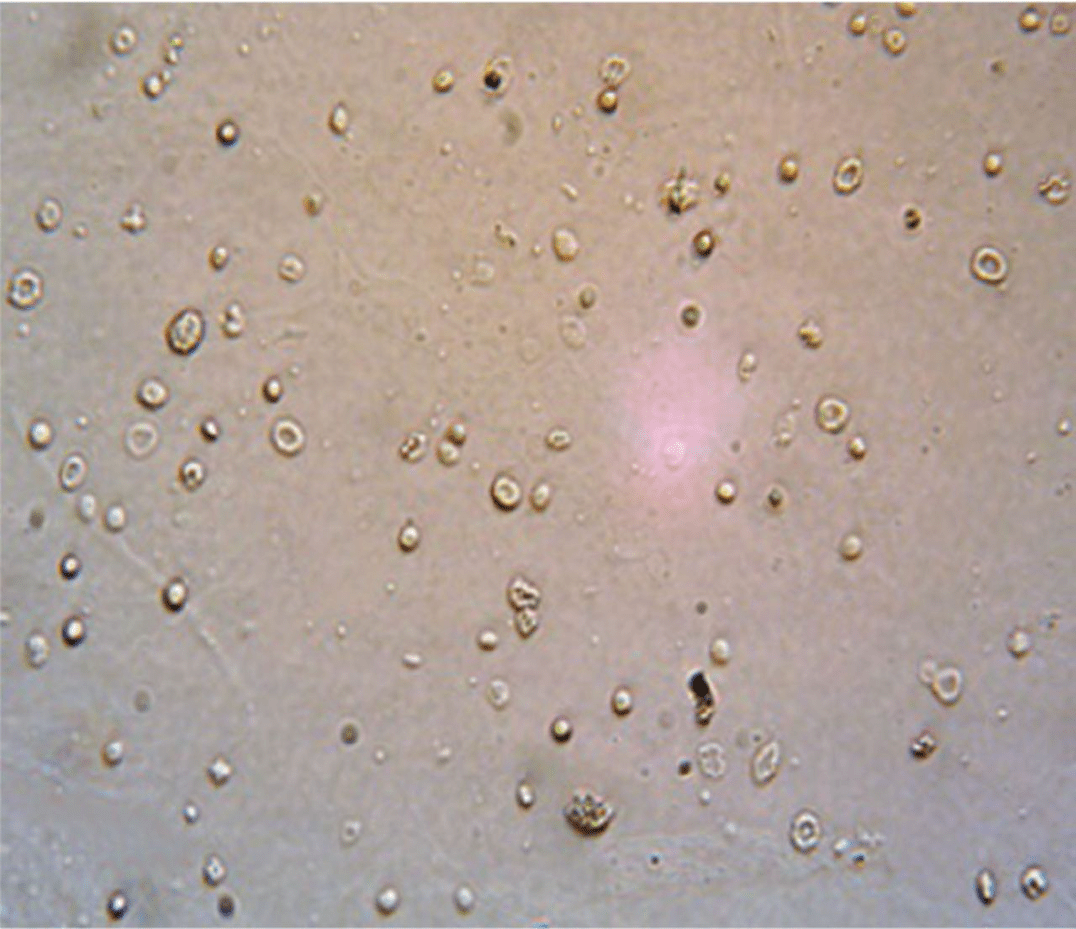
Glomerulonephritis (RBC casts—pathognomonic for glomerular bleeding)
A patient from rural Central America develops megacolon, cardiomyopathy with EF <30%. EKG is remarkable for the following findings below. This parasite is the cause of this clinical entity:
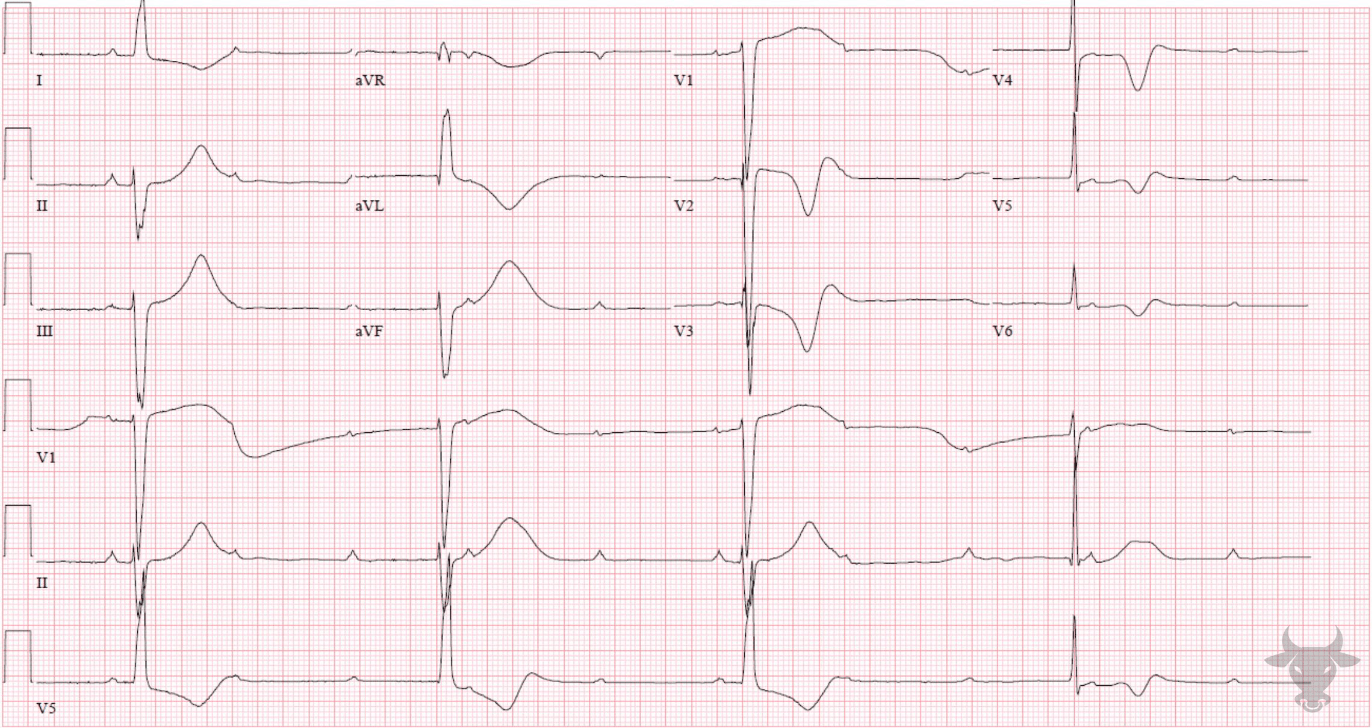
Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas disease)
A 39-year-old woman comes to the ED with fever, confusion, petechiae, and acute kidney injury. Labs show platelets of 9,000, hemoglobin 9.1 smear shown below, LDH 1,500, undetectable haptoglobin, and creatinine 2.8. Coagulation studies (PT/aPTT) are normal. Based on this life-threatening constellation of labs, this is the most appropriate immediate treatment.
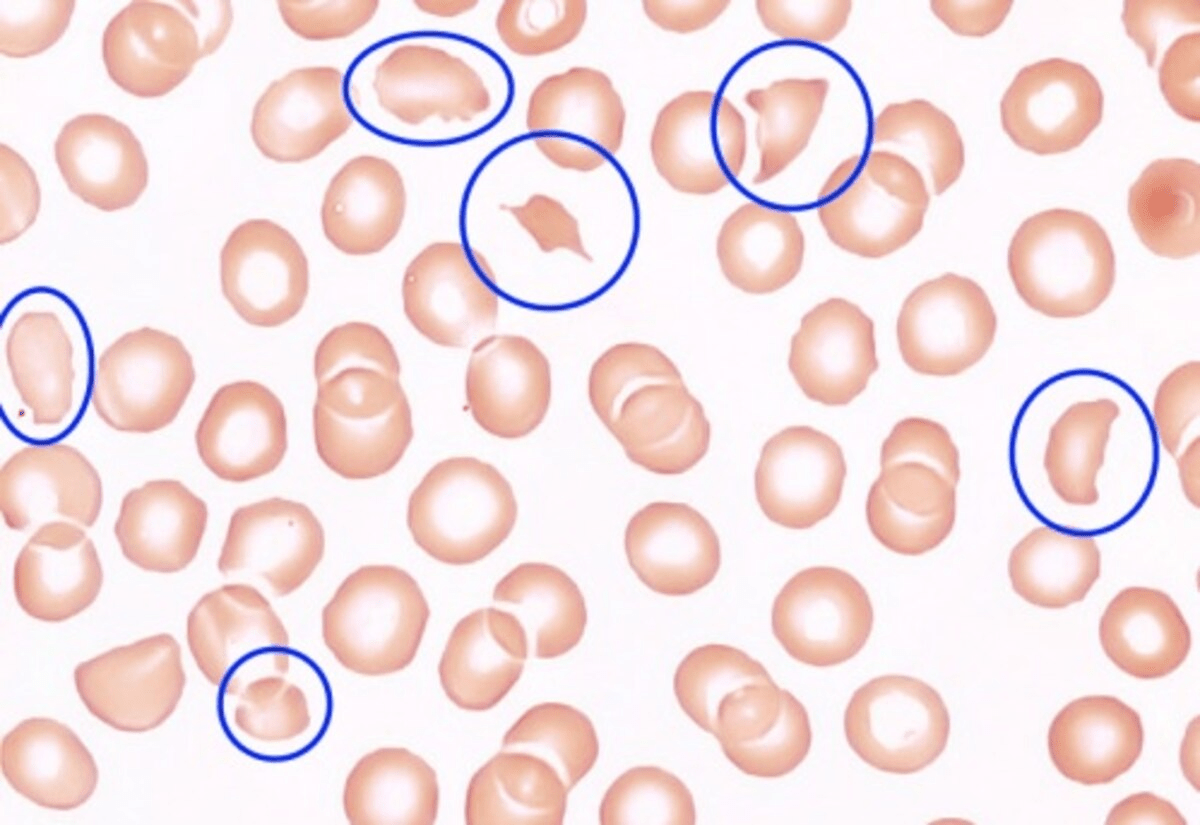
Urgent plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) for the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
Hospital policy requires that discharge summaries for all inpatient admissions be completed within this time frame after the patient leaves the hospital.
within 72 hours, but its better to submit in the same day