The A1c value that is criteria for a diagnosis of Diabetes
≥6.5%
(The test should be performed in a laboratory using a method that is NGSP certified and standardized to the DCCT assay.)
Prevention and lifestyle changes for adults with overweight or obesity at high risk of type 2 diabetes. Name one
- weight reduction goal of at least -7% (achieve and maintain)
- ≥150 min/week of moderate-intensity physical activity.
- A variety of eating patterns, such as Mediterranean style, intermittent fasting, and low carbohydrate, have shown benefit.
- Reducing daily calorie needs by 500-1000 (Diabetes Prevention Program Trial)
These medications have Very high and High efficacy for weight loss
BONUS: list the two specific medications in the category "Very high" and "High"
GLP-1s (listed below)
Very High: Semaglutide, tirzepatide
High: Dulaglutide, Liraglutide
At this A1c you can consider early initiation of insulin
≥10%
This is the goal A1c for most patients
<7%
2 hours post oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) this blood glucose is criteria for a diabetes diagnosis
≥200 mg/dL
This medication ... should be considered in adults at high risk of type 2 diabetes, as typified by the DPP, especially those aged 25–59 years with BMI ≥35 kg/m2, higher fasting plasma glucose (e.g., ≥110 mg/dL [≥6 mmol/L]), and higher A1C (e.g., ≥6.0% [≥42 mmol/mol]), and in individuals with prior gestational diabetes mellitus.
Metformin
This is the goal A1c during pregnancy.
<6% if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia,
but the goal may be relaxed to <7% if necessary to prevent hypoglycemia
List one rapid acting and one long acting
rapid: lispro, aspart, glulisine
long acting: glargine, detemir
A side effect of long term use (≥5 years) of Metformin.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
A1c criteria for pre-diabetes
5.7-6.4%
These medications should be initiated in patients with Diabetes and ASCVD risk
GLP-1 or SGLT2i with proven CVD benefit
GLP-1s w proven CVD benefit: dulaglutide, liraglutide, semaglutide (SUBQ)
SGLT2i w proven CVD benefit: empaglifolzin (Jardiance), canagliflozin
treatment for diabetes or gestational diabetes during pregnancy
What should and what should not be used
Should: Insulin
Should Not: Metformin and glyburide, individually or in combination, should not be used as first-line agents for management of diabetes in pregnancy, as both cross the placenta to the fetus and may not be sufficient to achieve glycemic goals. Other oral and noninsulin injectable glucose-lowering medications lack long-term safety data and are not recommended.
Add these drugs if injectable therapy is needed to lower A1c before starting insulin
Consider GLP-1 or Dual GIP/GLP-1 in most individuals prior to insulin
Dual GIP/GLP-1 (Tirzepatide)
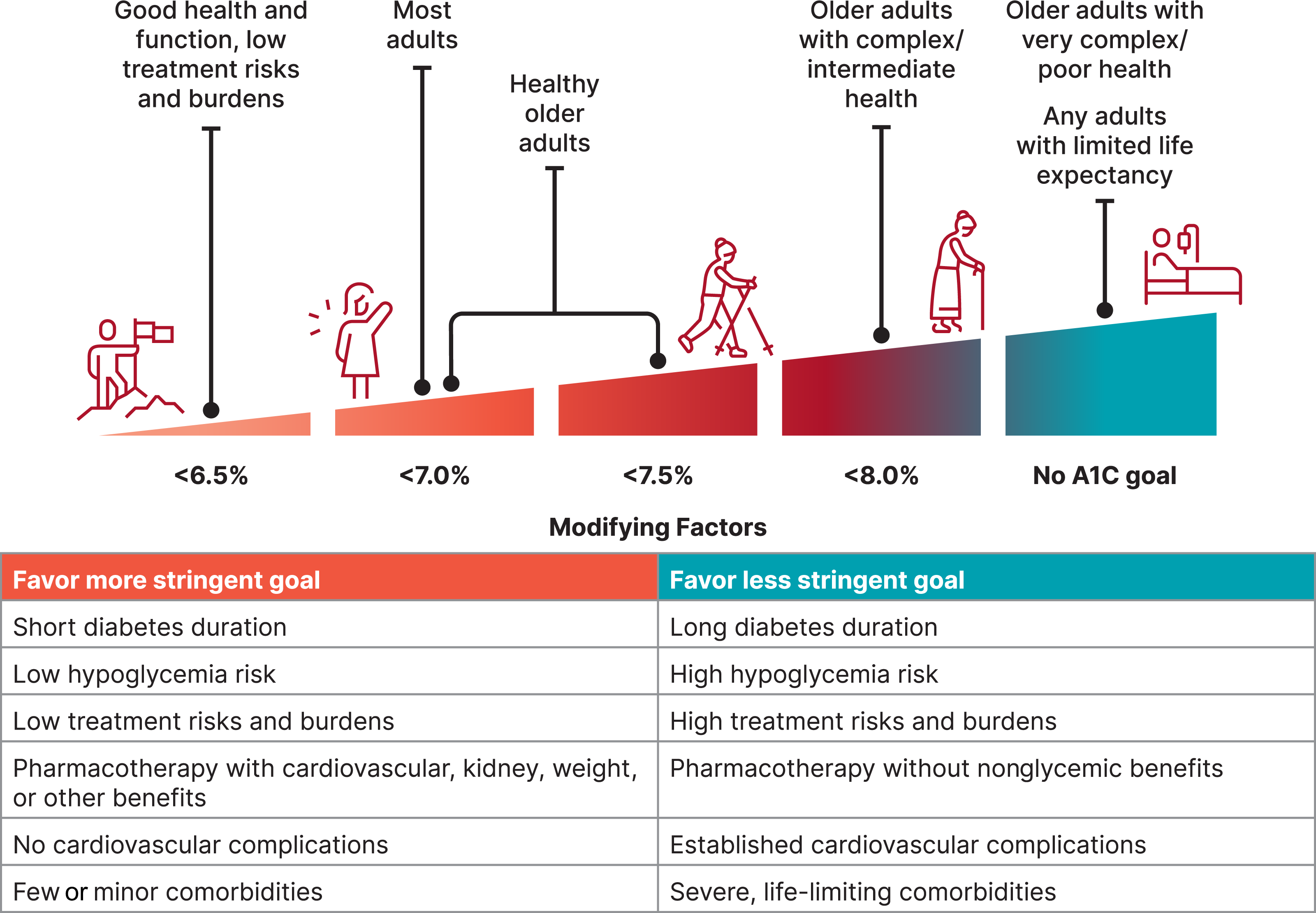
In these situations / patients, a less stringent A1c goal is recommended
individuals with limited life expectancy or where the harms of treatment are greater than the benefits
The FPG (fasting plasma glucose) that is criteria for a diagnosis of diabetes.
≥126 mg/dL
These medications should be initiated in patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure
SGLT2i w proven HF benefit
-dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
-empagliflozin (Jardiance)
Goal for percent of time in range for patients with CGM
>70%
The total daily dosing for starting basal insulin (weight based or total)
10 units per day OR 0.1-0.2 units/kg per day
Preprandial glucose goal
Postprandial glucose goal
preprandial 80-130 mg/dL
Postprandial <180 mg/dL (measured 1-2 hours after meal)
If a person is experiencing classic hyperglycemic symptoms AND has a random blood glucose of ____ this is a criteria of diagnosing diabetes.
BONUS: what are some symptoms of hyperglycemia
≥200
Symptoms of hyperglycemia:
- Urinating large amounts
- Excessive thirst
- Feeling tired
- Frequent hunger
- Dry mouth
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Recurrent infections (e.g., urinary infections, skin infections)
- Wounds (cuts, scrapes) that heal slowly
These medications should be initiated in patients with diabetes and CKD (on maximally tolerated ACEi or ARB)
SGLT2i w proven CKD benefit or GLP1 w proven CKD benefit
SGLT2i: canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin
GLP-1: dulagluti, liraglutide, semaglutide (SUBQ)
Give the generic for these brand medications(partial credit allowed):
Tradjenta
Januvia
Victoza
Rybelsus
Synjardy
Farxiga
Tradjenta (Linagliptin)
Januvia (Sitagliptin)
Victoza (liraglutide)
Rybelsus (semaglutide)
Synjardy (empagliflozin-metformin)
Farxiga (dapagliflozin)
This insulin has the longest duration of action
Insulin degludec (Tresiba)... ≥42 hours
For every 1% of A1c = _______ (amount of) estimated average glucose
(if you get within +/- 5-10 I'll give you credit)
28.7 mg/dL ~ approx 30